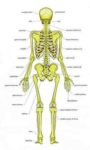
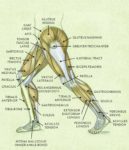
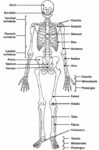
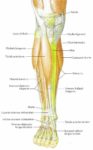
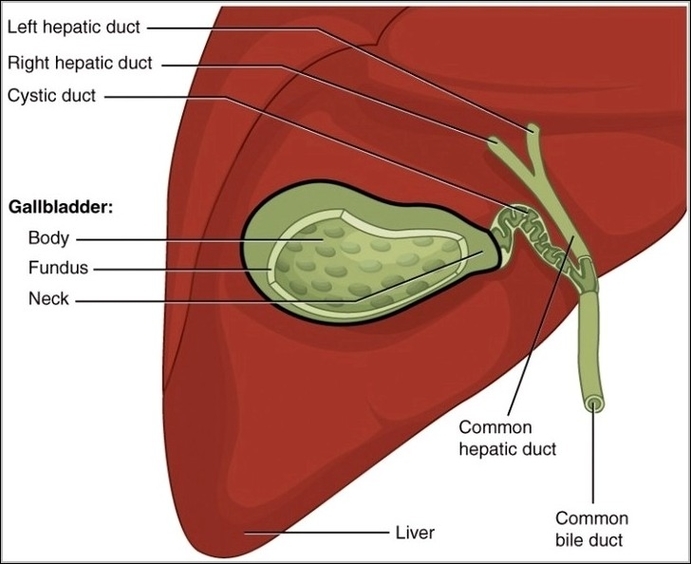
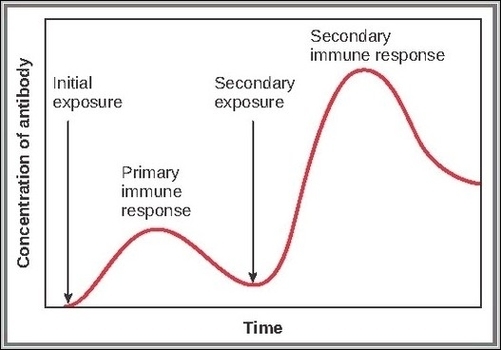
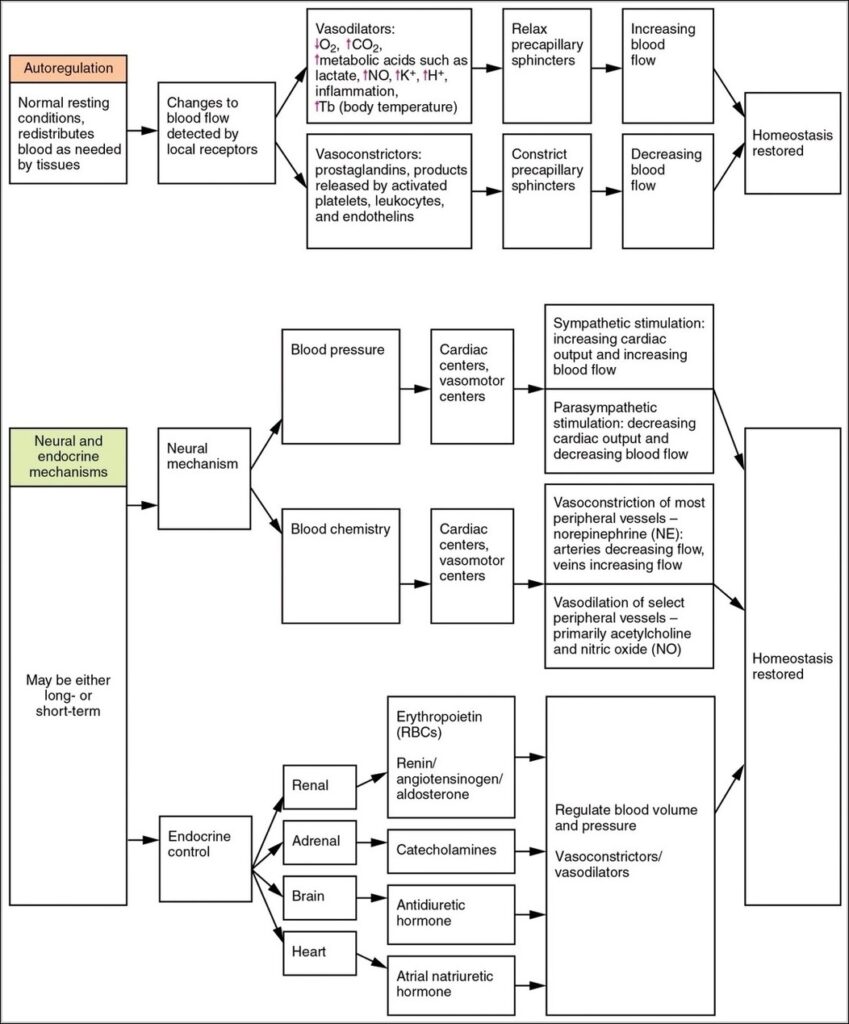
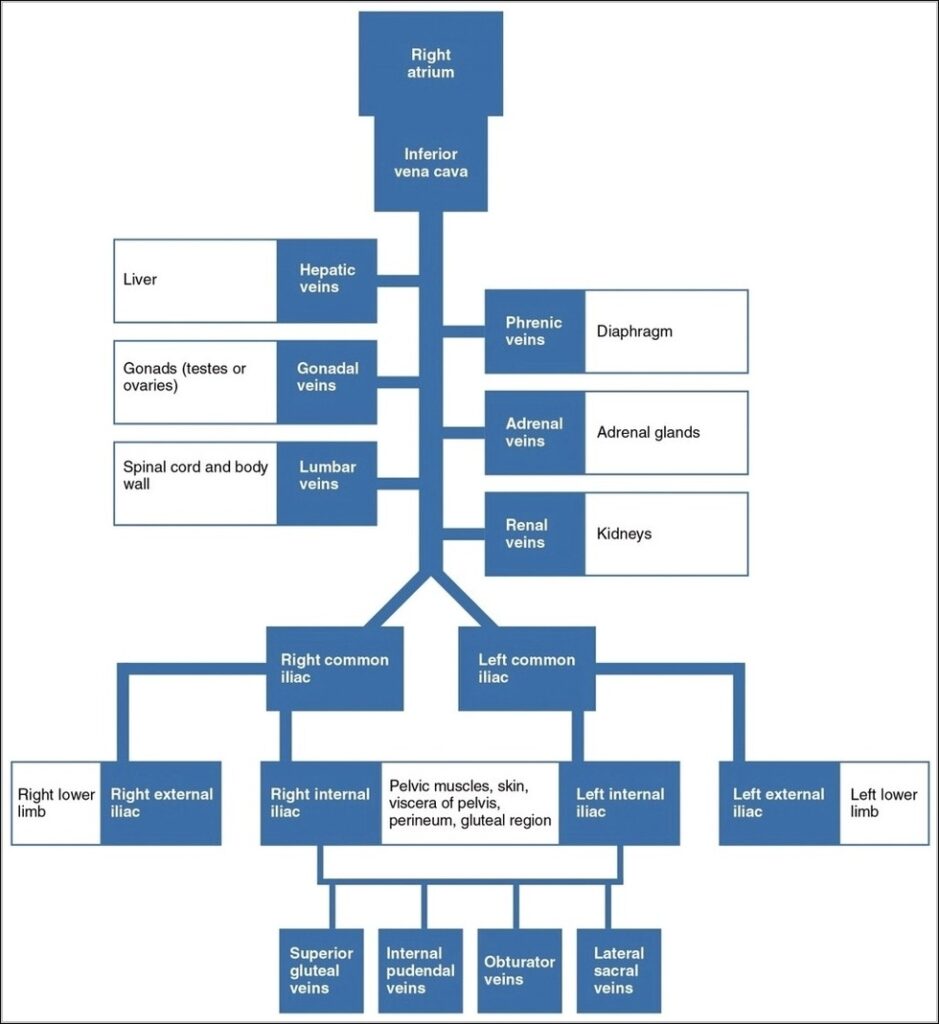
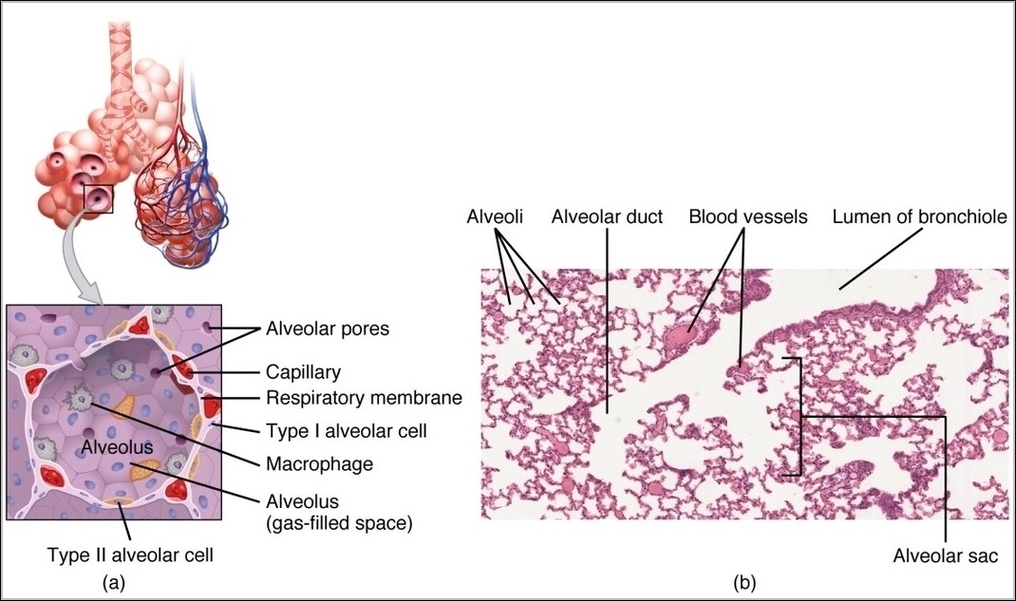
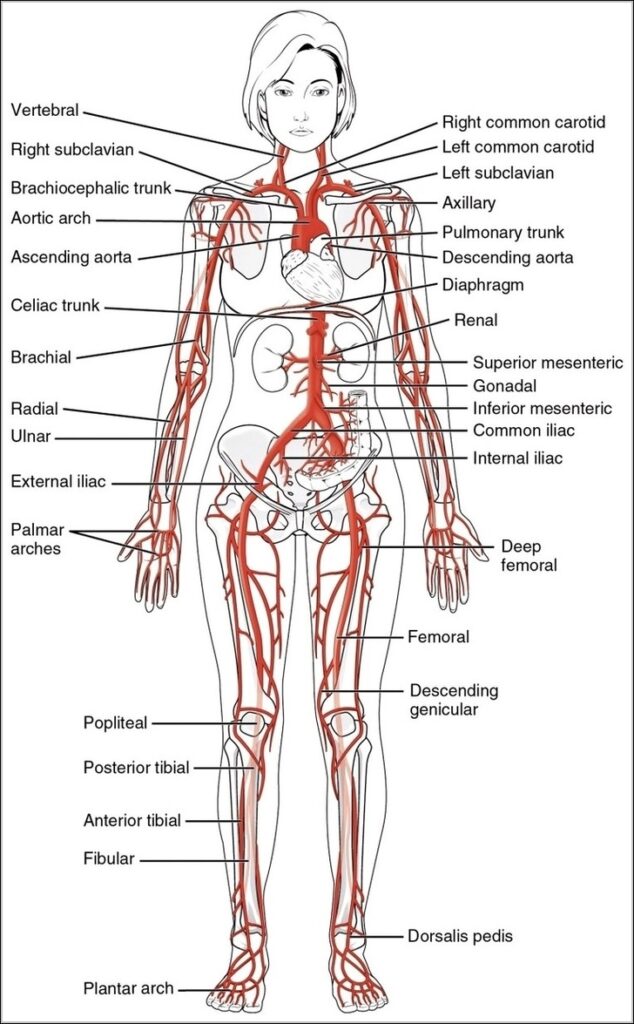
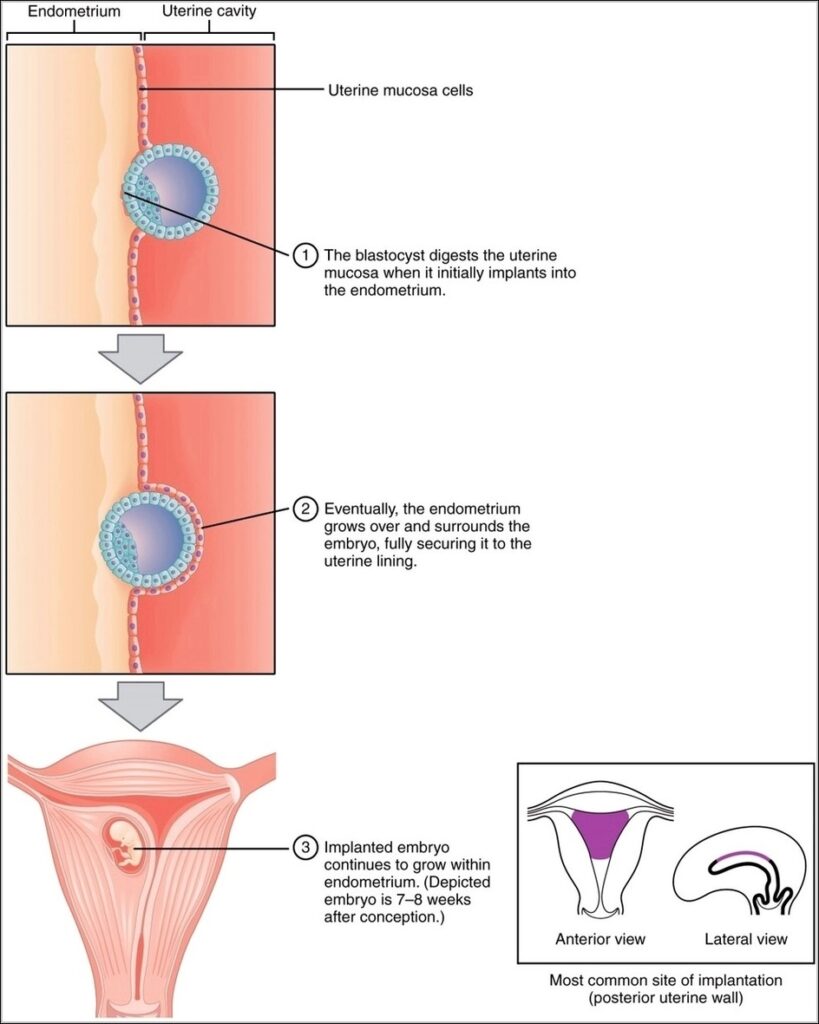
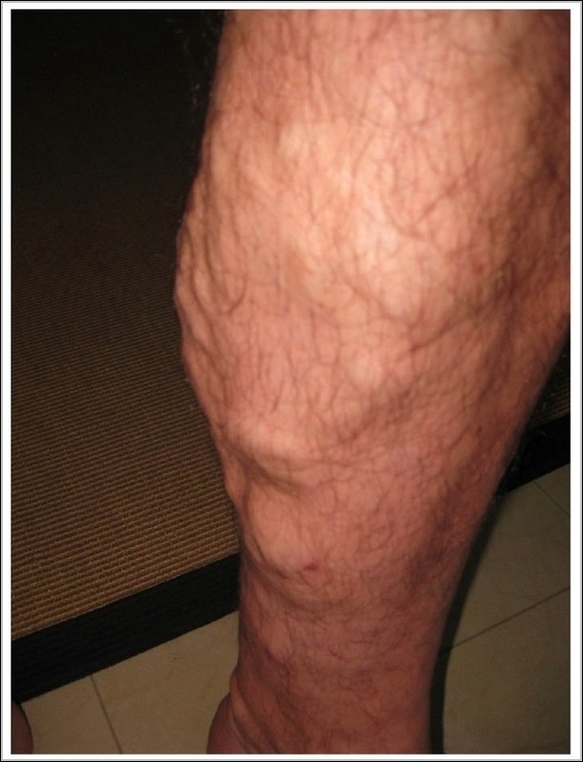
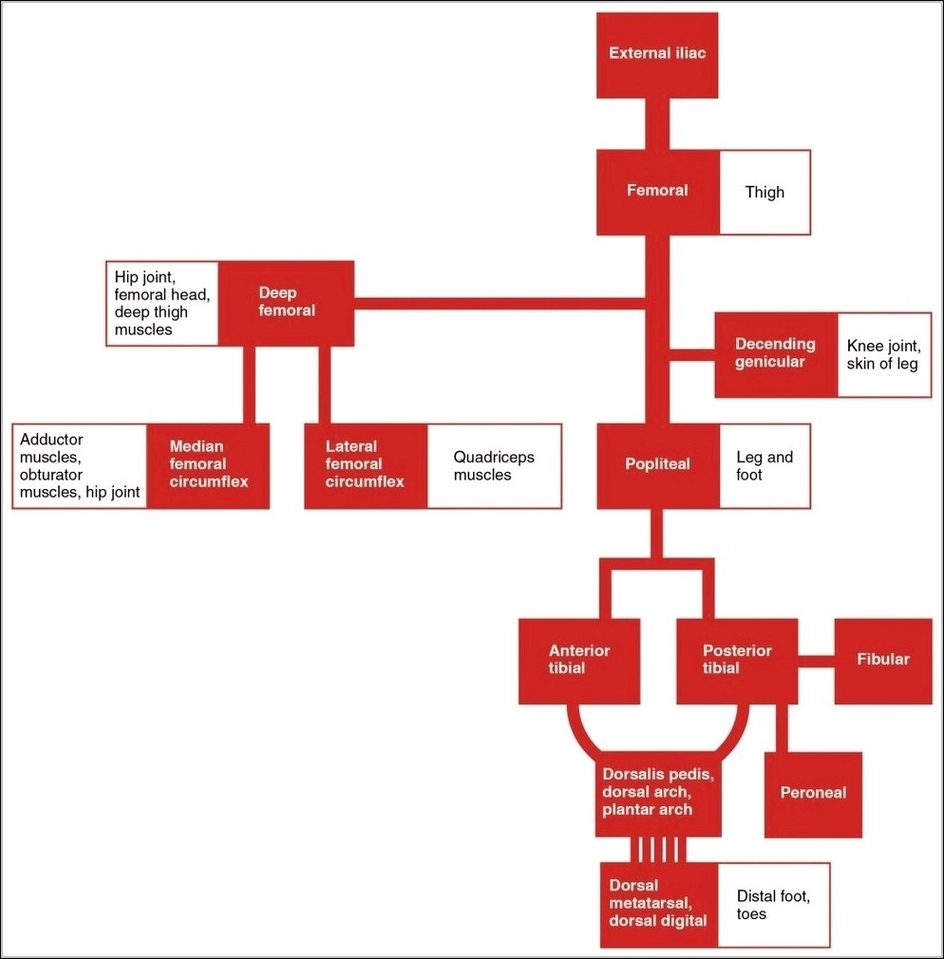
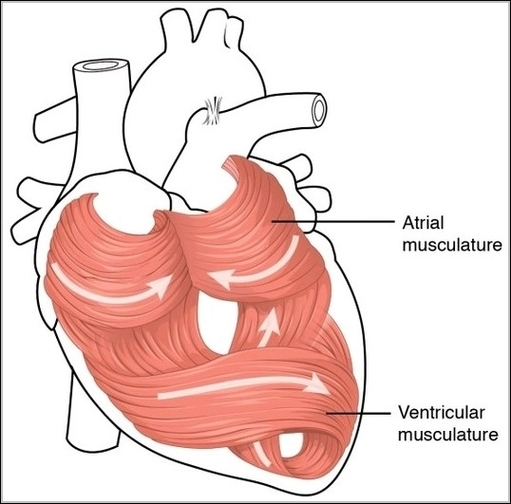
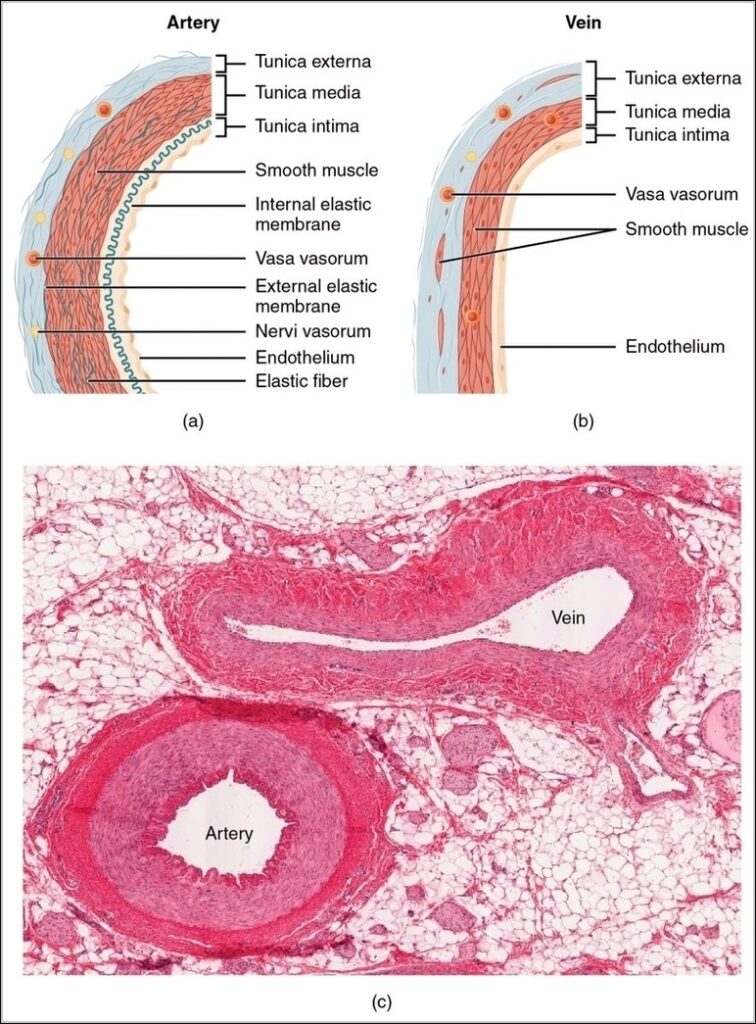
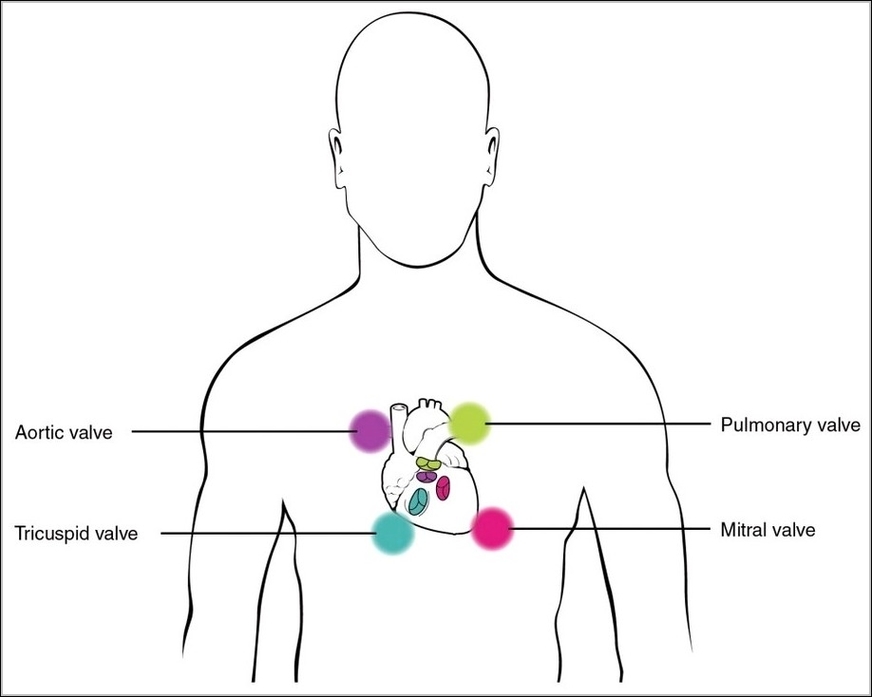
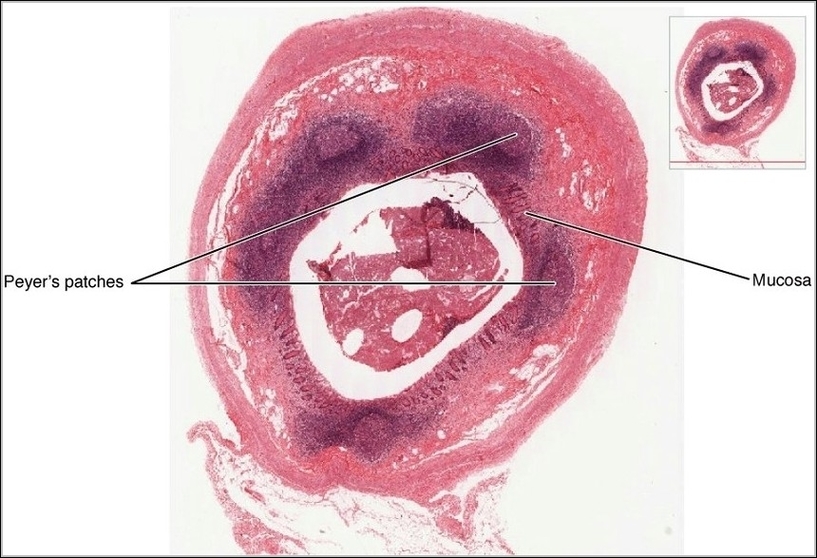
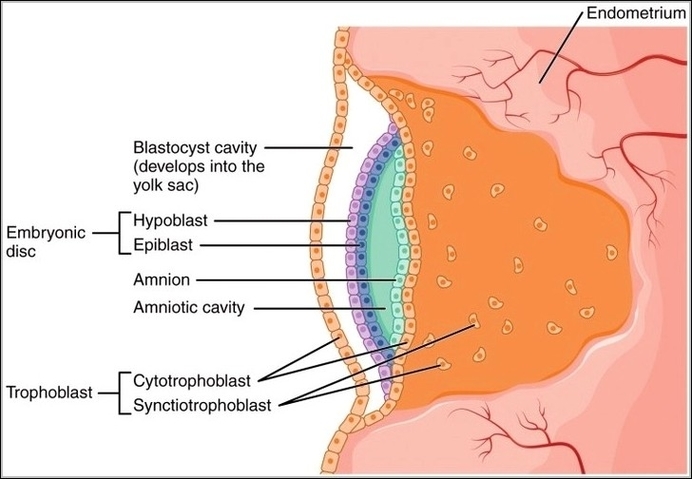
Posted inOrgans
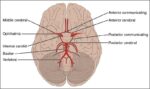
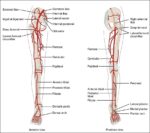
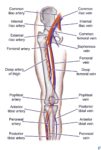
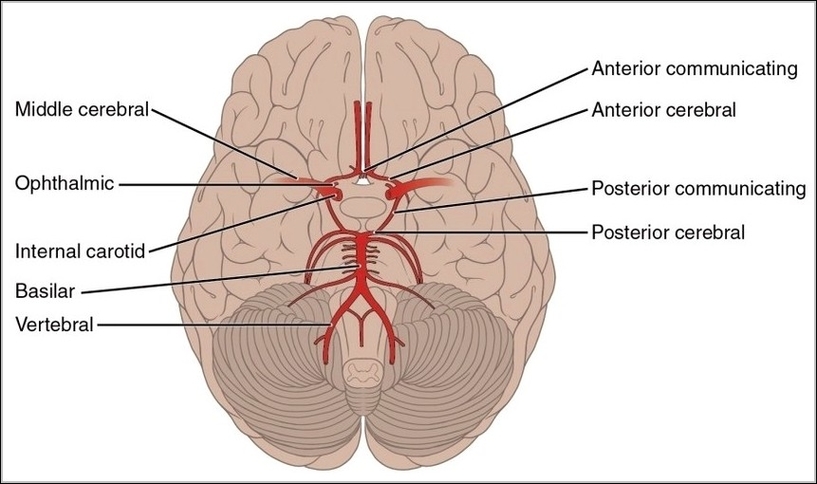
Arteries of the Brain
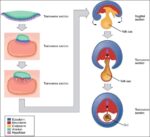
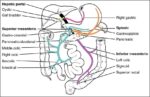
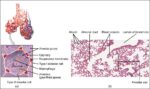
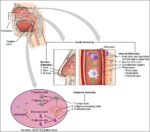
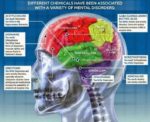
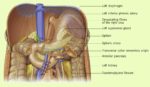
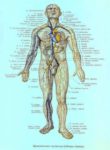
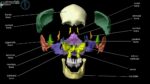
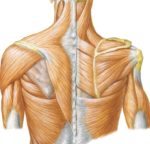
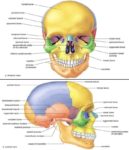
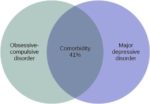
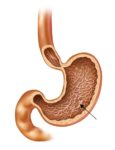
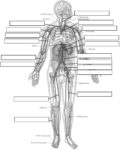
A cerebral circulation map displays arteries supplying the brain, including the carotid arteries and Circle of Willis. The interconnected layout highlights redundancy in blood supply, which helps protect brain tissue…