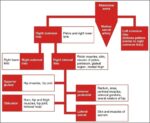
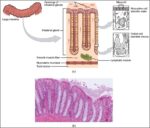
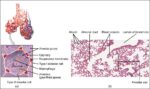
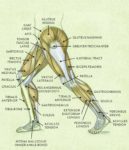
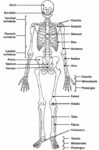
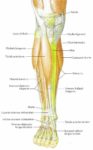
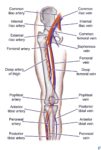
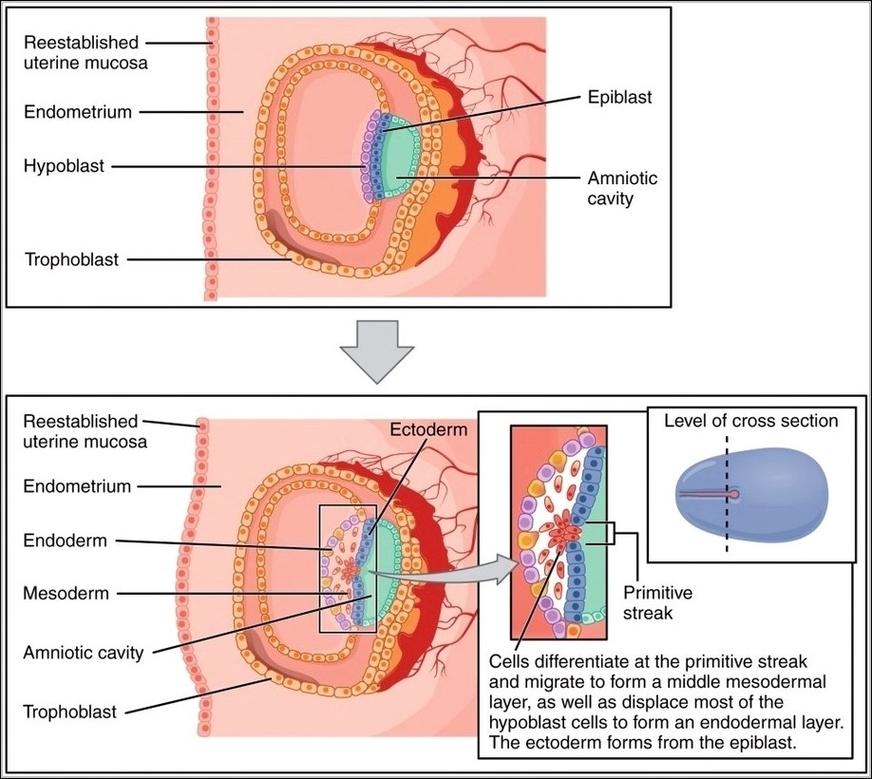
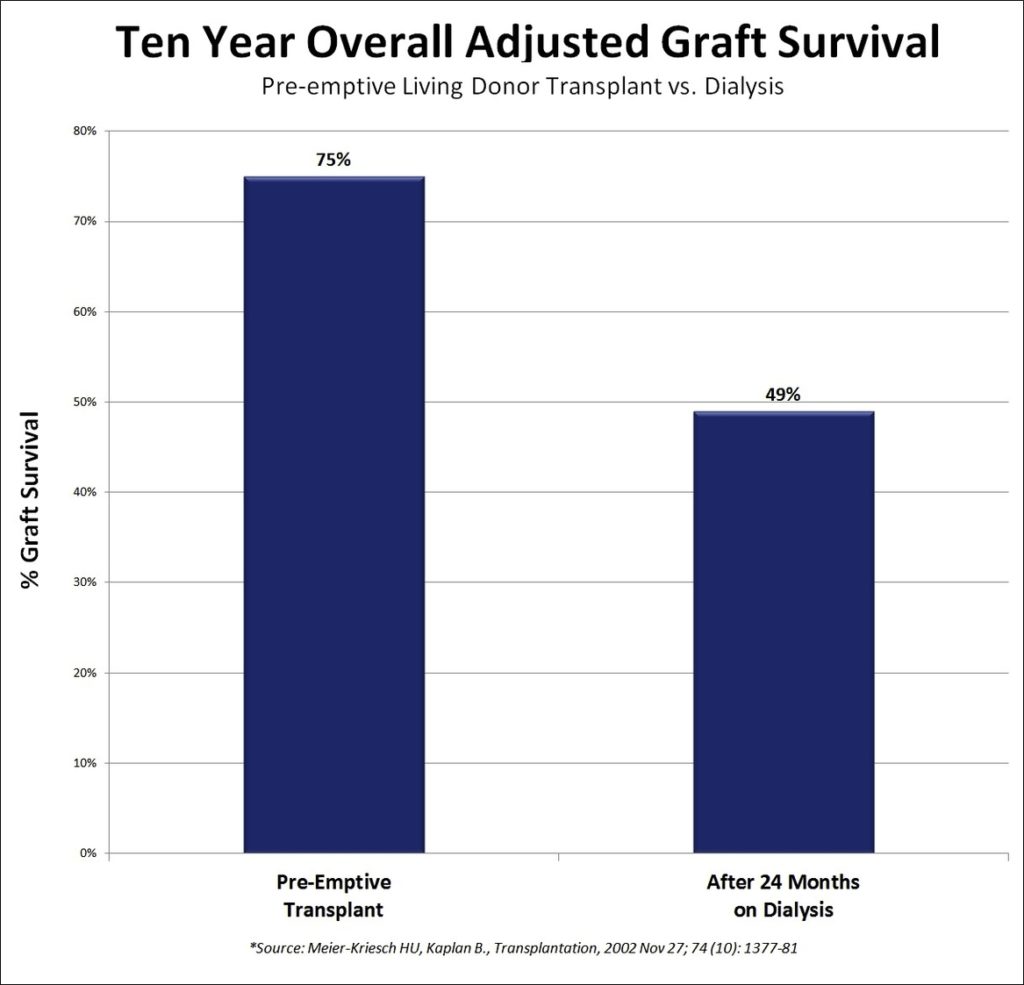
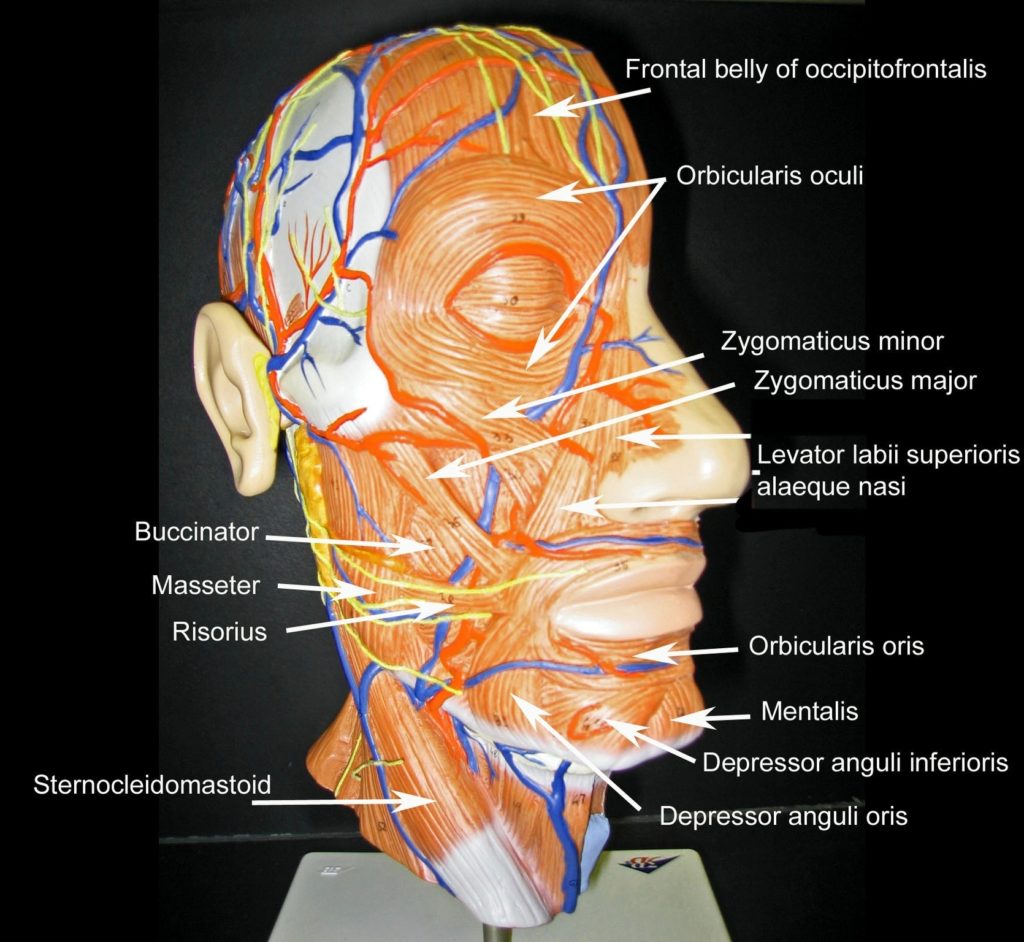
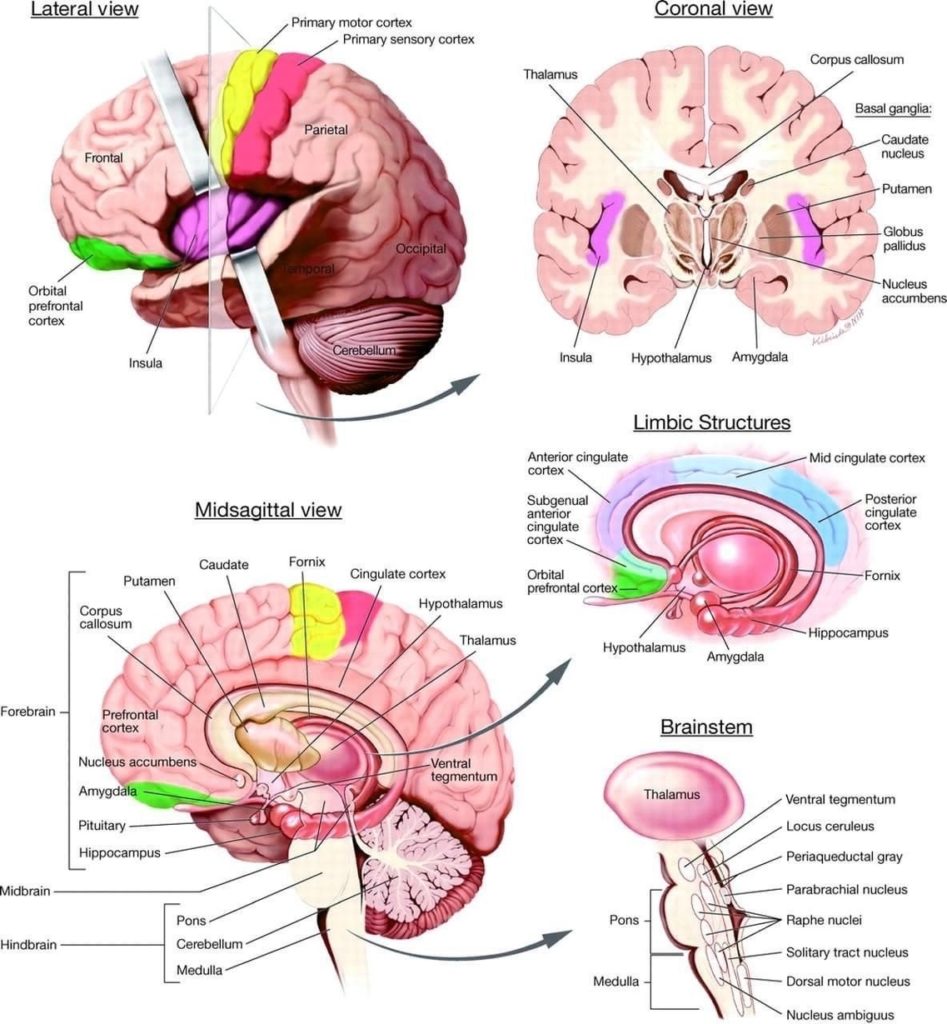
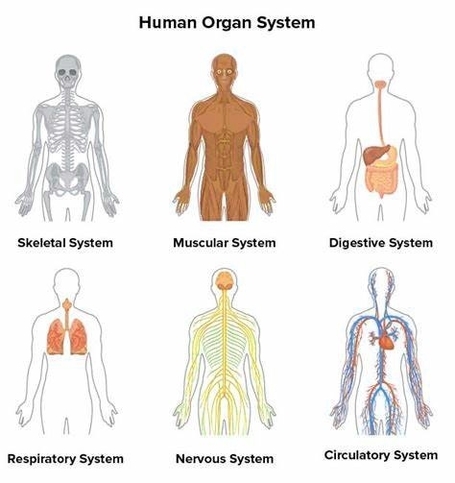
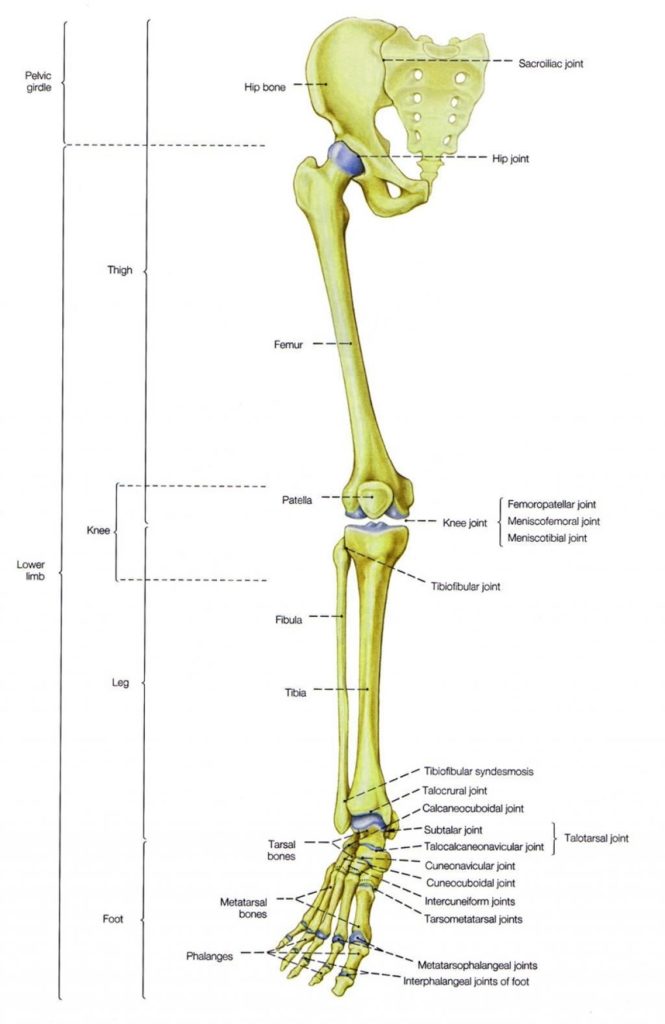
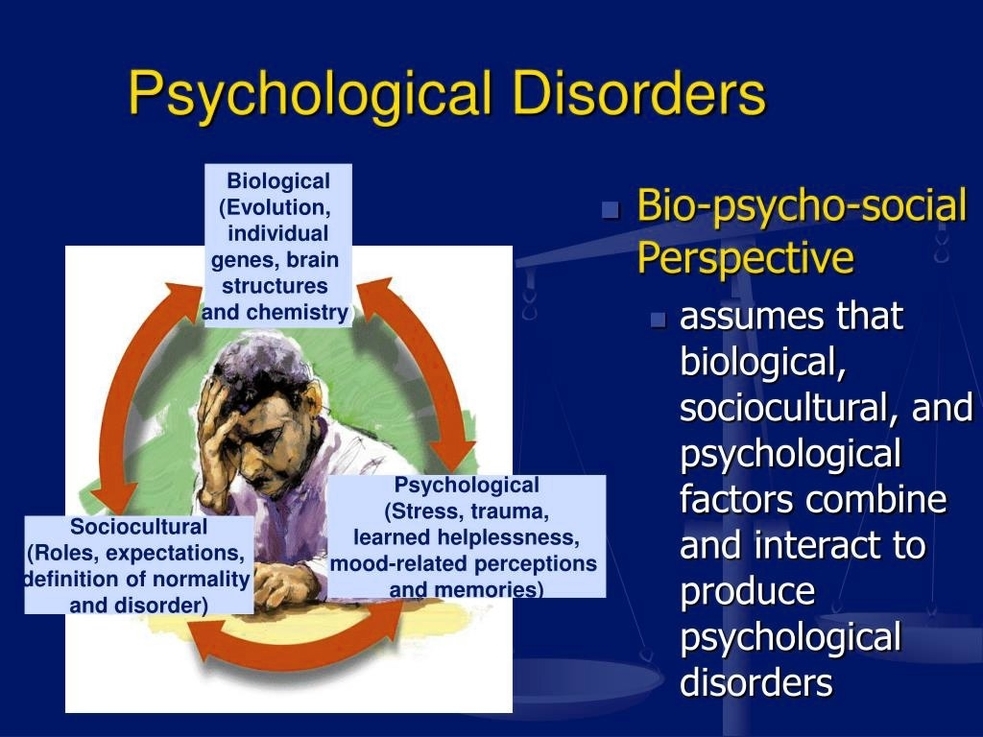
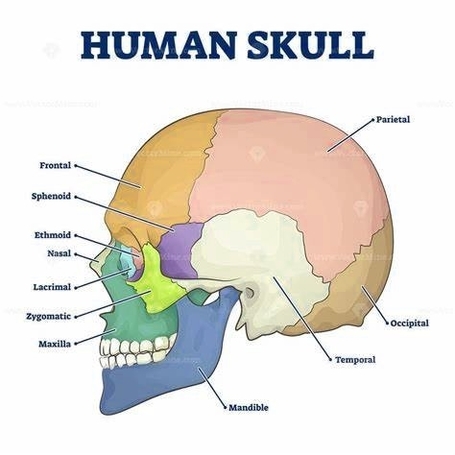
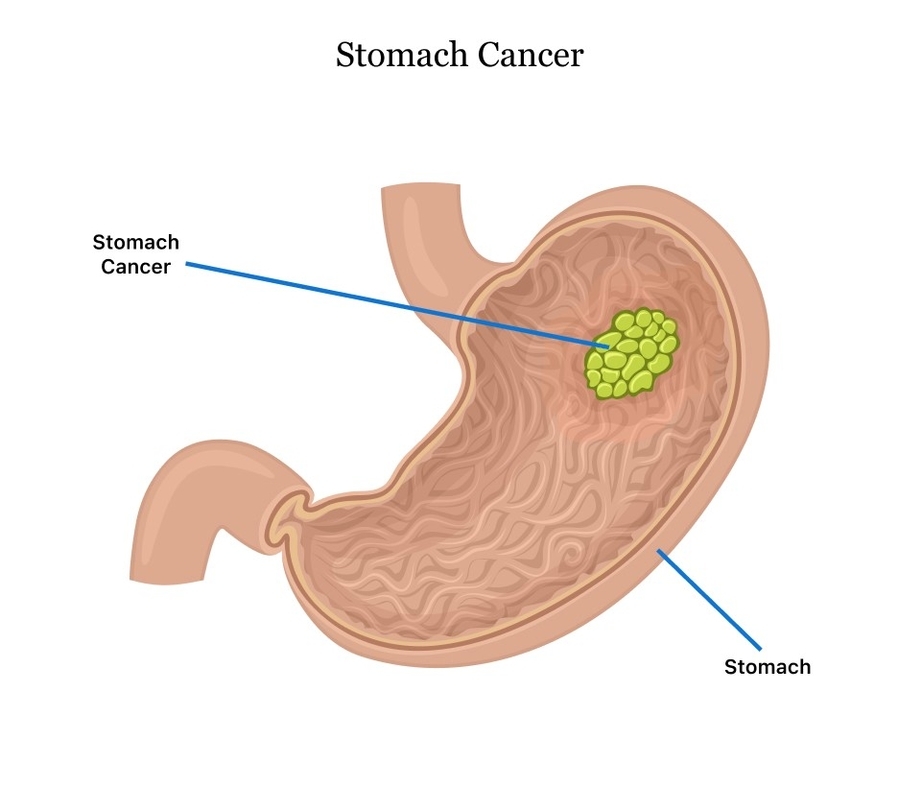
Posted inMedical
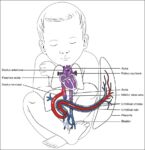
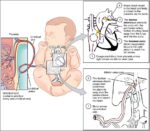
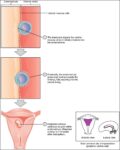
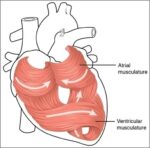
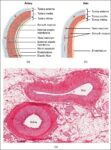
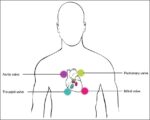
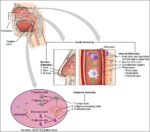
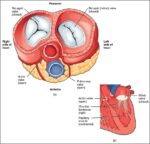
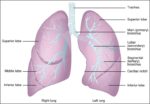
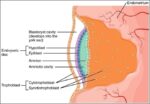
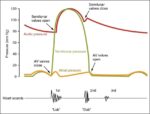
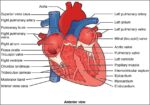
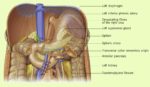
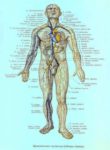
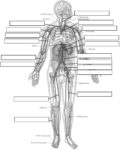
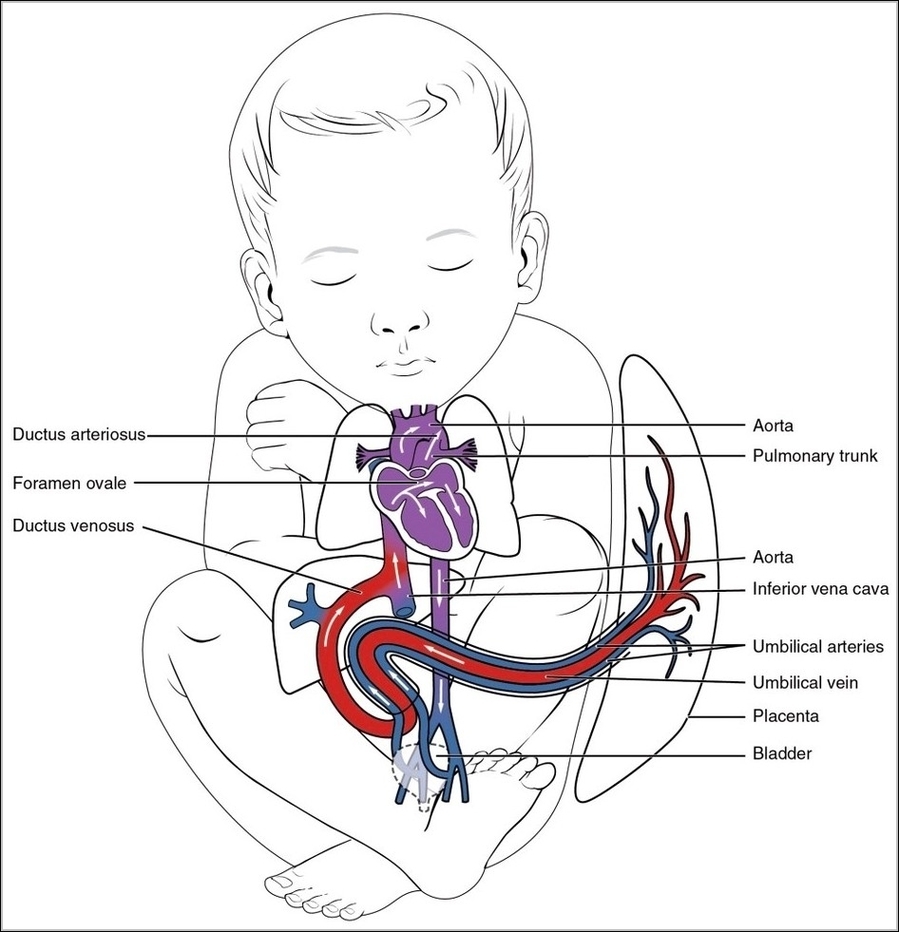
Fetal Circulation
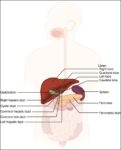
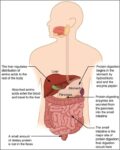
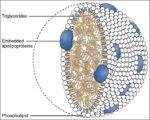
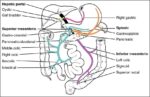
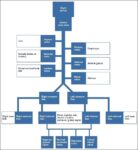
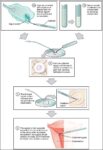
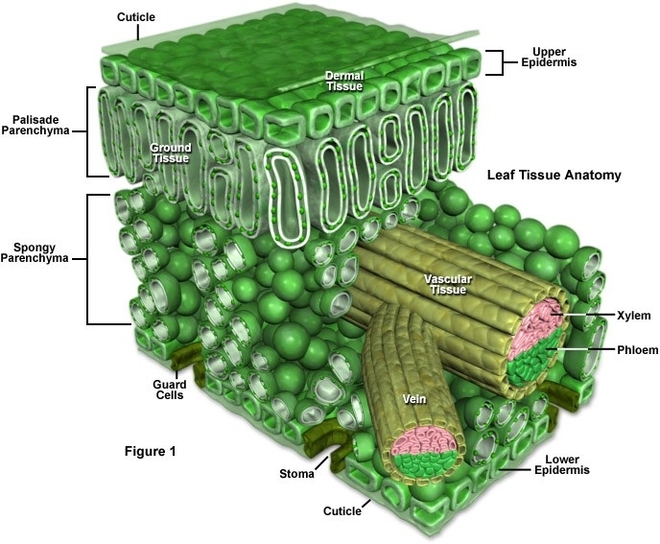
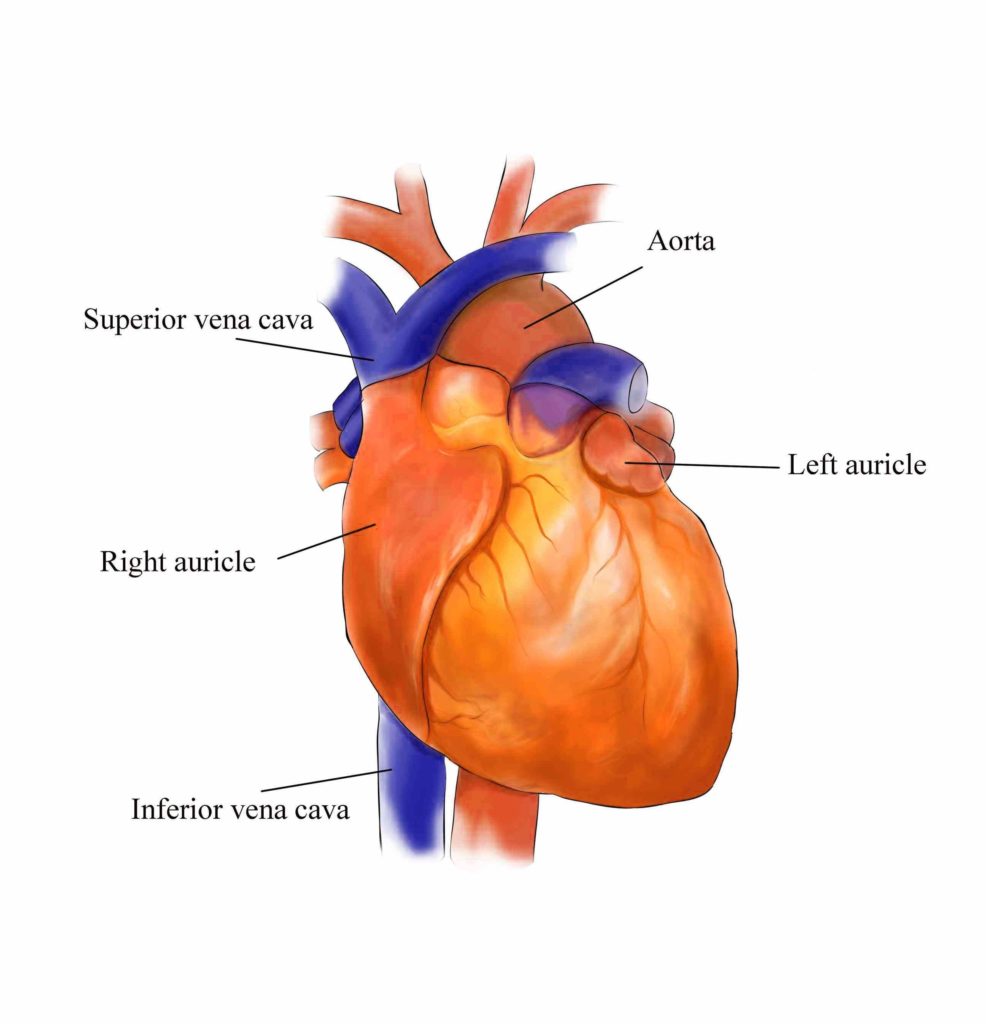
Before birth, the fetus relies on unique circulatory shortcuts because its lungs are non-functional and it gets oxygen and nutrients from the placenta via the umbilical cord. Oxygen-rich blood enters…