Functions of Bones
Bones are living, active tissues that the body is constantly remodeling. They serve many vital functions in your body, including:
1. Support: Bones provide a rigid framework as well as support for other parts of your body. For example, the larger bones of the legs offer support to your upper body while you’re standing up. Without our bones, we’d have no defined shape.
2. Movement: Bones also play an important role in the movement of your body, transmitting the force of muscle contractions. Your muscles attach to your bones via tendons. When your muscles contract, your bones act as a lever while your joints form a pivot point. The interaction of bones and muscles contributes to the wide range of movements your body is capable of making.
3. Protection: Your bones also protect many of your internal organs. Good examples of this include the way your rib cage surrounds organs such as your heart and lungs or how the bones of your skull surround your brain.
4. Blood Cell Generation and Maintenance: The many cells of your blood red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are formed within your bones. This process is called hematopoiesis, and it occurs in a part of your bone marrow called the red marrow.
5. Storage: Important minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus, are stored within your bones. When your body needs more of these resources, they can be released back into your bloodstream for use. In addition to red marrow, bones also contain another type of marrow called yellow marrow. This is where some fat tissue is stored. The fats in this tissue can be broken down and used for energy if required.
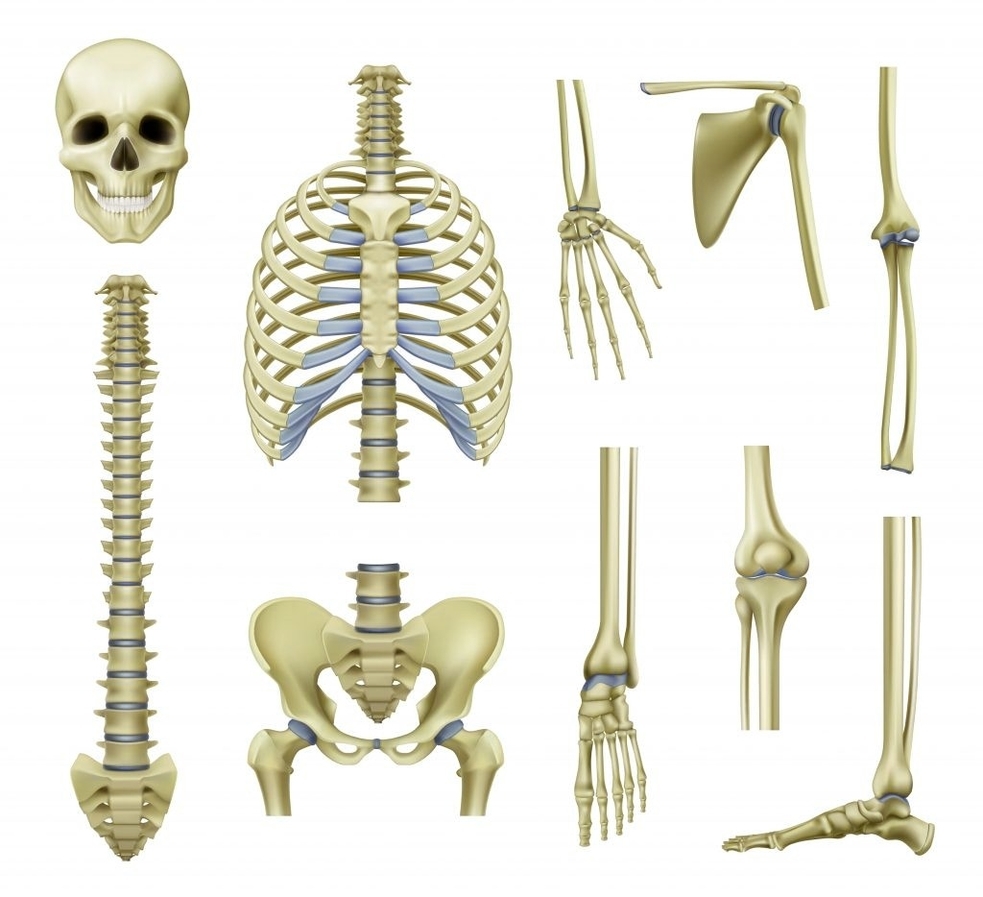
The bones of your body are divided into five different types based on their shape and function: long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones, and sesamoid bones. Each type of bone has a specific role in the body. For instance, long bones, such as the femur (thigh bone) and humerus (upper arm bone), support the weight of your body and facilitate movement. Short bones, found in the wrists and ankles, provide stability and help facilitate some movements. Flat bones, like the cranial bones and scapula (shoulder bone), often serve to protect your internal organs.
In conclusion, bones are an essential part of the human body. They provide structure, facilitate movement, protect internal organs, produce blood cells, and store essential nutrients. Understanding the functions of bones is crucial to understanding the overall function and health of the human body..