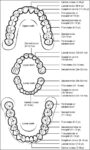
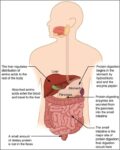
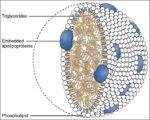
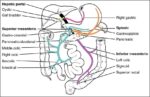
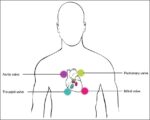
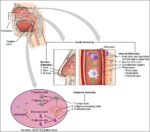
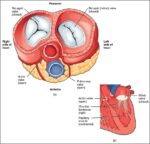
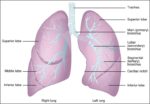
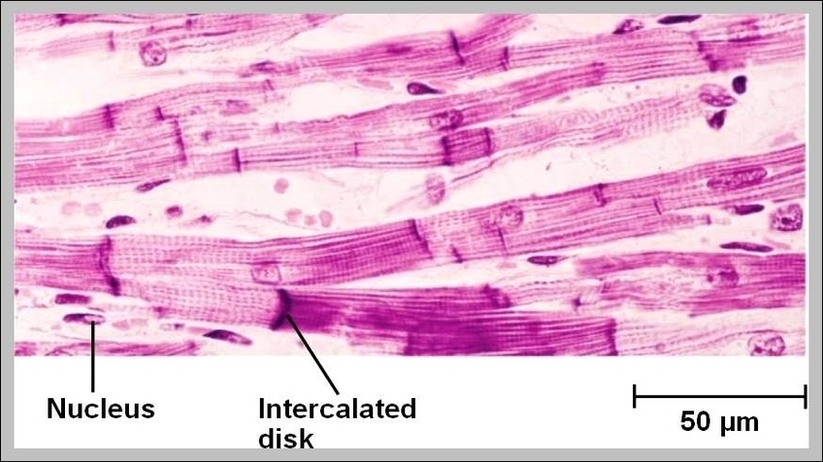
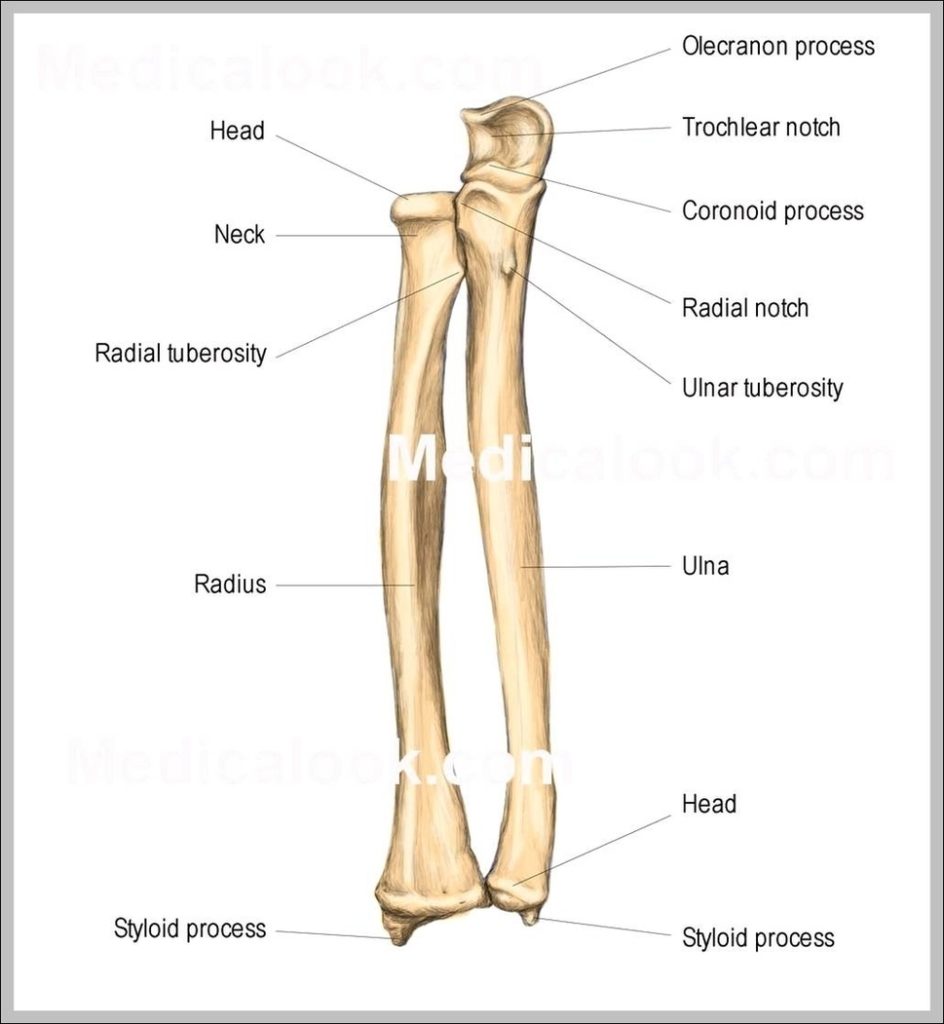
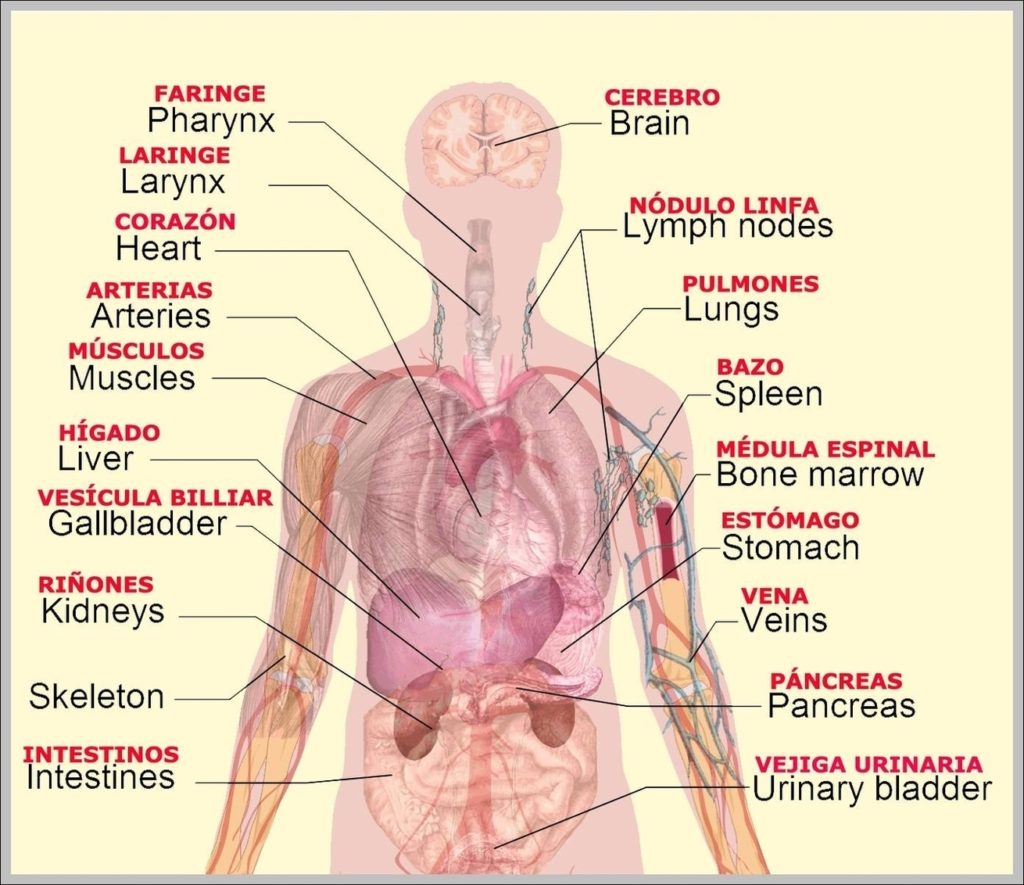
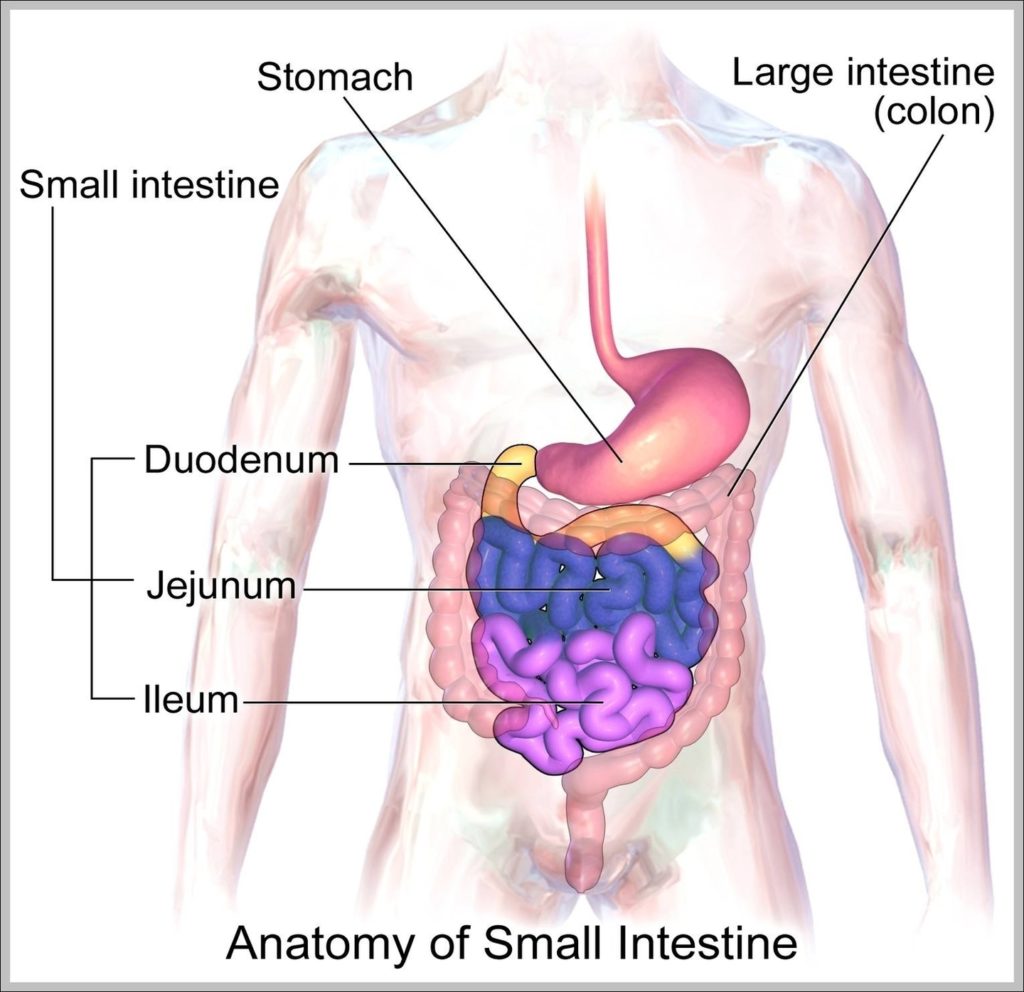
Posted inWomen
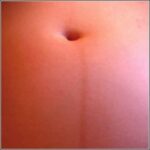
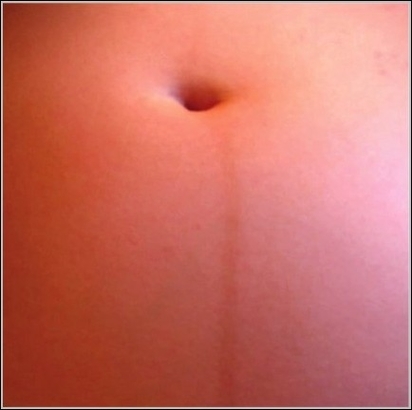
Photo of Linea Nigra
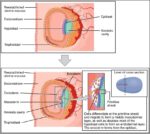
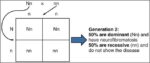
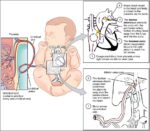
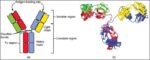
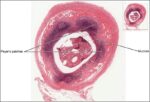
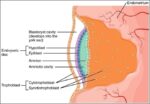
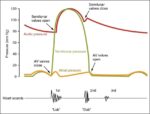
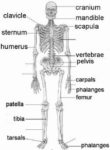
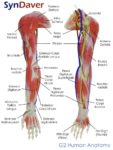
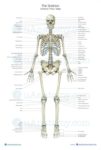
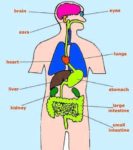
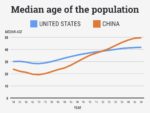
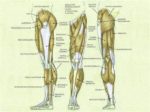
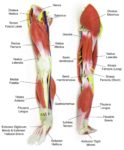
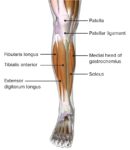
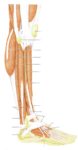
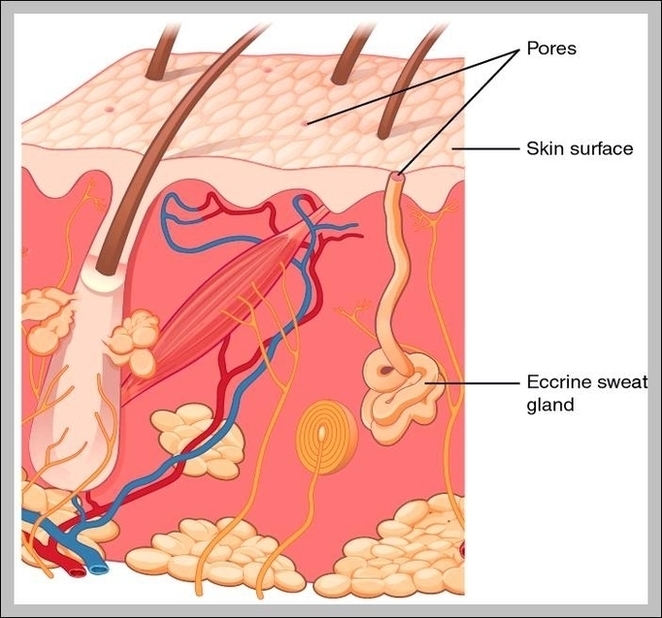
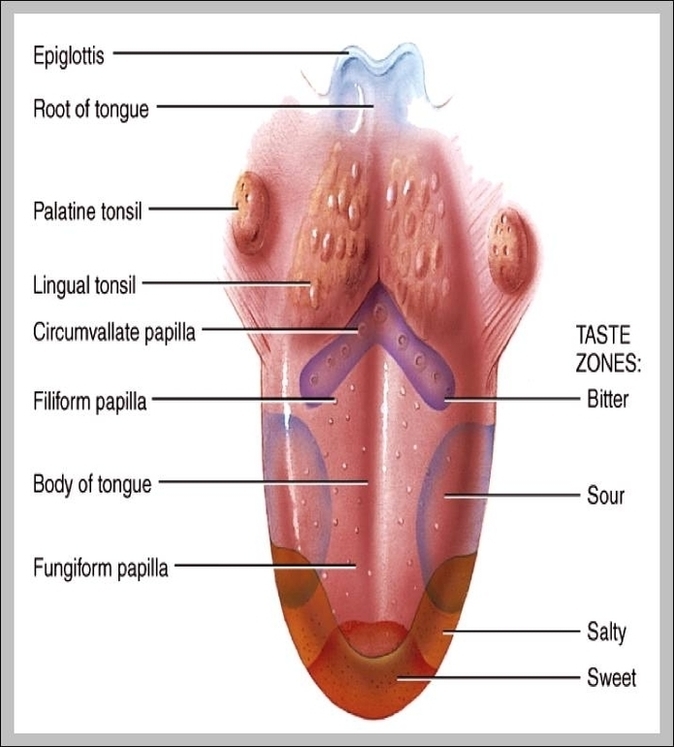
Linea nigra is a dark vertical line running from pubis to sternum or navel on pregnant abdomen, resulting from melanocyte-stimulating hormone increase darkening the normally faint linea alba, more pronounced…