Stomach Facts
Stomach Facts
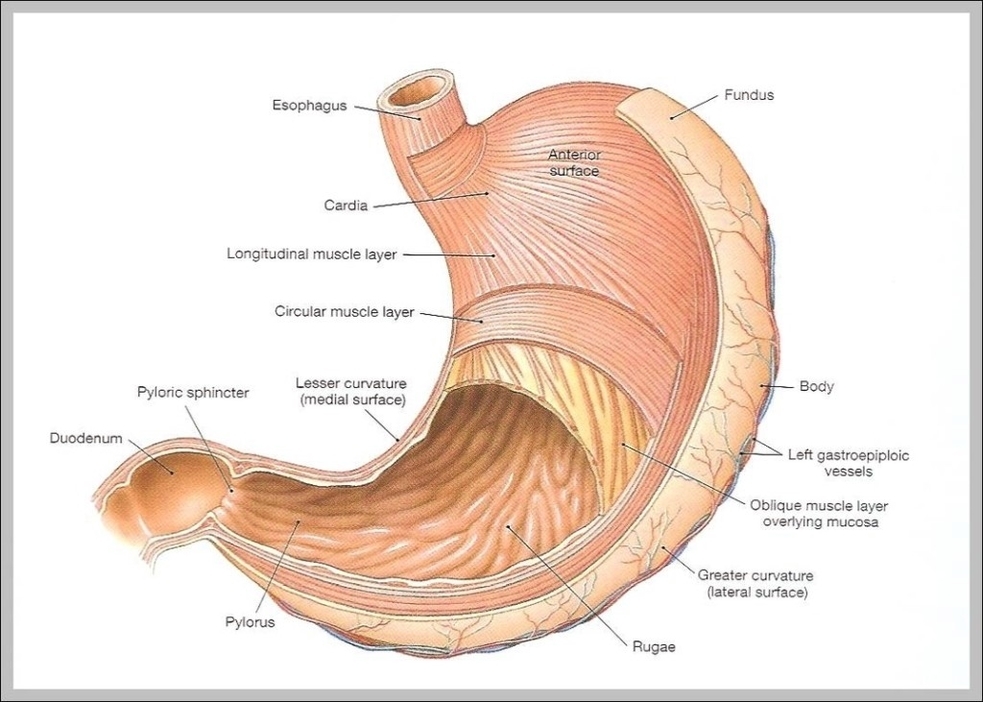
The stomach, a vital organ in the digestive system, is a muscular, J-shaped structure located in the upper left abdominal area. It’s a bean-shaped, sack-like structure situated behind the lower ribs and between the esophagus and small intestine. Here are some interesting facts about the stomach:
1. Size and Capacity: The stomach is about 12 inches long and 6 inches across. On average, it can hold more than a quarter-gallon or half-pound of food.
2. Digestion: The stomach secretes gastric juices, digests, and stores food molecules. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. However, the major part of the digestive process takes place in the small intestine.
3. Nutrient Absorption: The stomach is mainly responsible for absorbing necessary nutrients like vitamin B12 from the food we have eaten.
4. Digestion Time: The maximum time required to digest a normal meal ranges between five to seven hours or longer. Protein-rich and fatty foods take a longer time to digest compared to high-fiber foods.
5. Survival without Stomach: A person can survive even after their stomach is removed by altering the diet and having frequent and smaller meals.
6. Stomach Removal Surgery: Total Gastrectomy is the procedure in which the stomach of a patient is totally removed and the esophagus is attached directly to the small intestine.
7. Stomach in Animals: Some animals, including cows, giraffes, deer, cattle, and other ruminants, have four-chambered stomachs, which help them in digesting plant-based food. Some animals, including carp, lungfishes, seahorses, and platypuses, have no stomach.
8. Hormone Synthesis: Besides digestion, the stomach also synthesizes hormones, which helps in stimulating appetite, secretion of digestive enzymes and gastric acid, and repeating discharging and contraction of the gallbladder.
9. Mucous Layer: Our stomach produces a new layer of mucous every two weeks and protects the stomach and other organs from being digested by the hydrochloric acid.
10. Burping: Burping releases the air molecules which we have consumed along with food from the digestive tract through the mouth.
11. Hydrochloric Acid: The hydrochloric acid or the stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve most metals. It plays an important role in destroying harmful microorganisms entering into the body along with food and drink.
12. Digestion of Different Foods: Foods high in sugars digest very quickly, making us feel more hunger, whereas foods high in fats and protein digest much slower and allows us to stay full for a longer time.
13. Immune Defense: The stomach serves as the first line of defense for our immune system. The acid present in our stomach sterilizes and kills off the bacteria and other toxins present in the food we have eaten.
In conclusion, the stomach is a fascinating organ with a multitude of functions beyond just digestion. It plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being..
