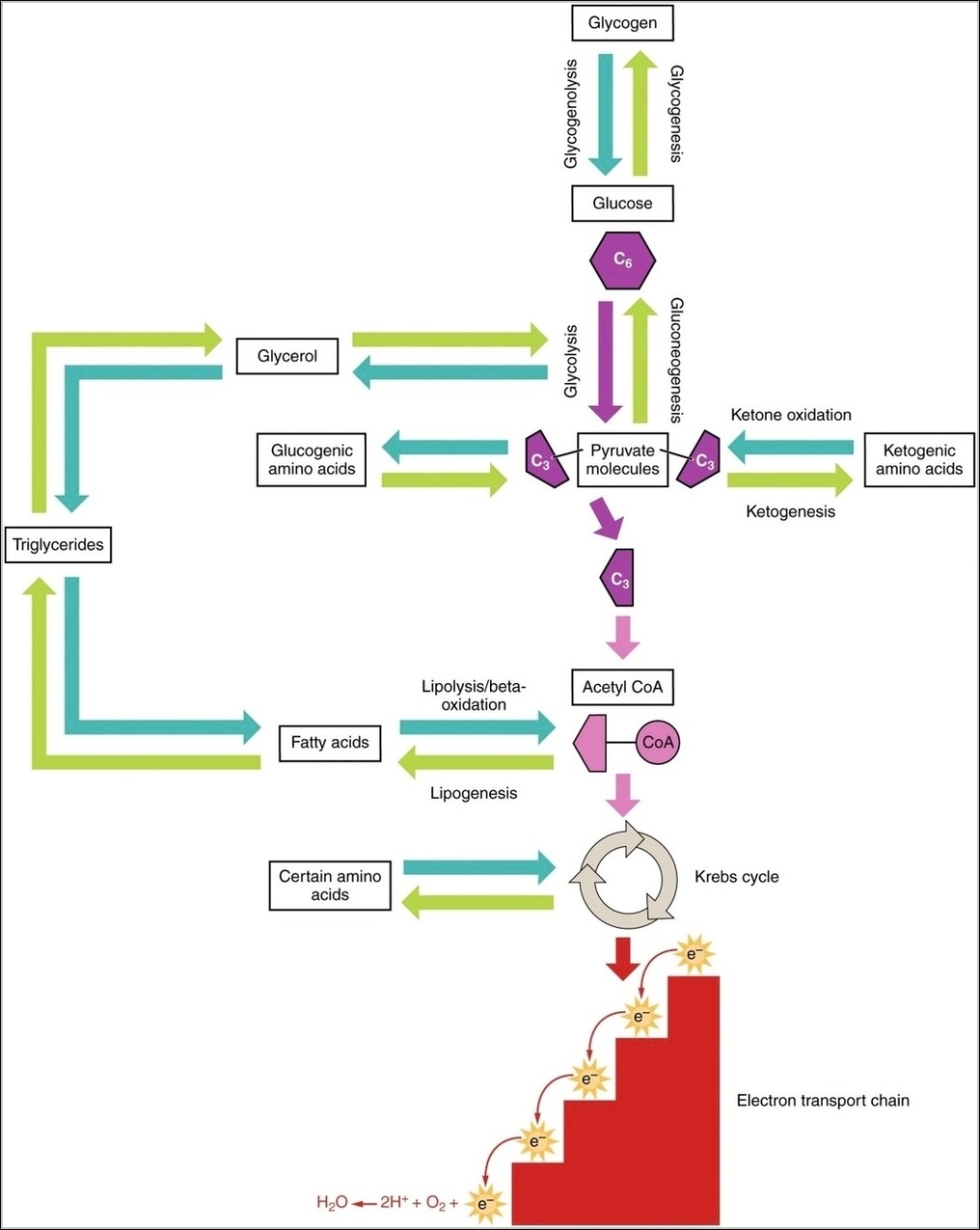
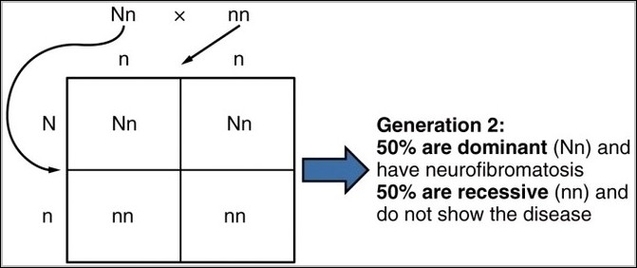
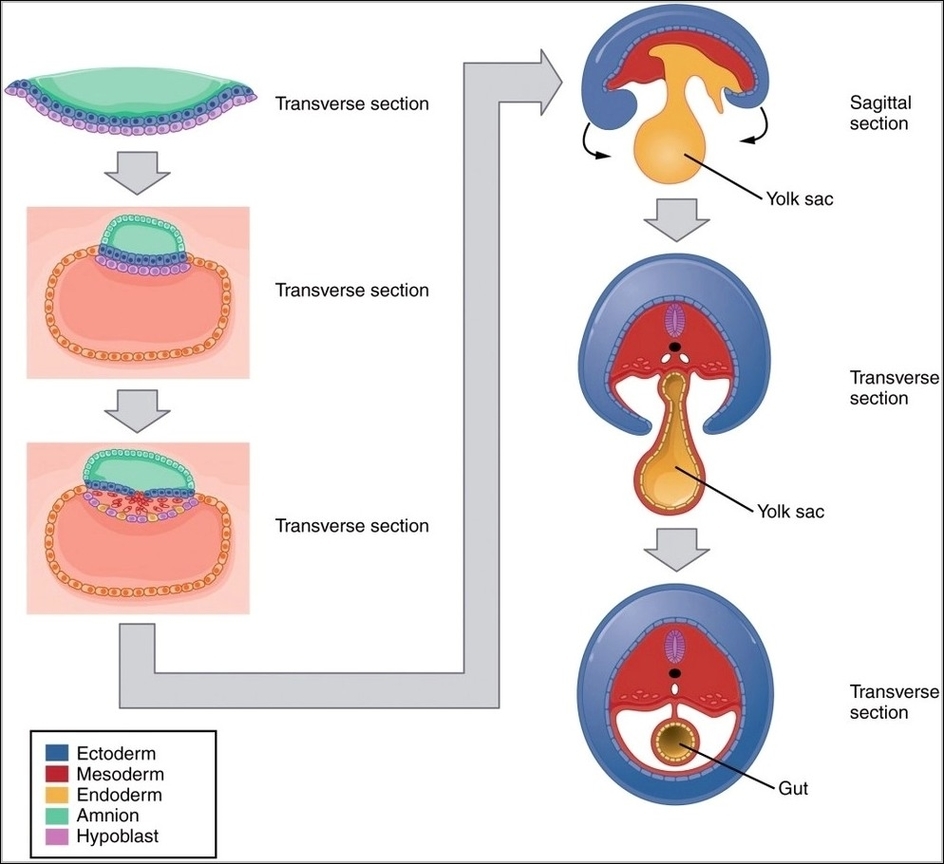
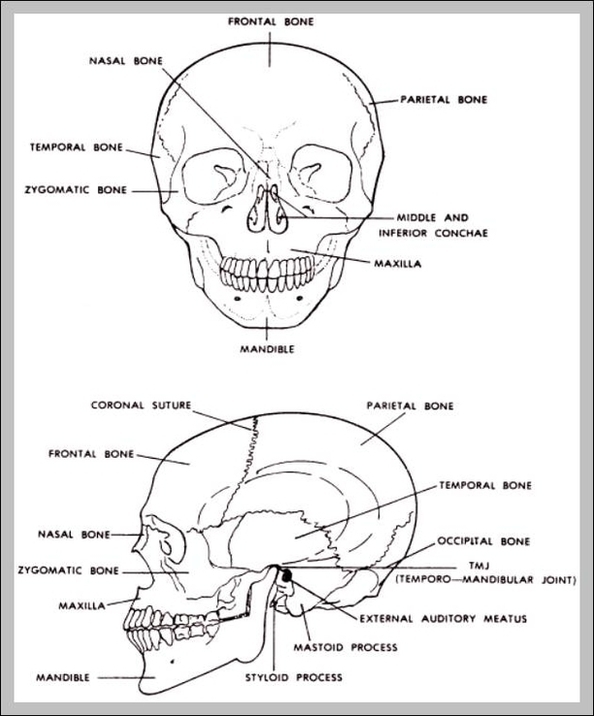
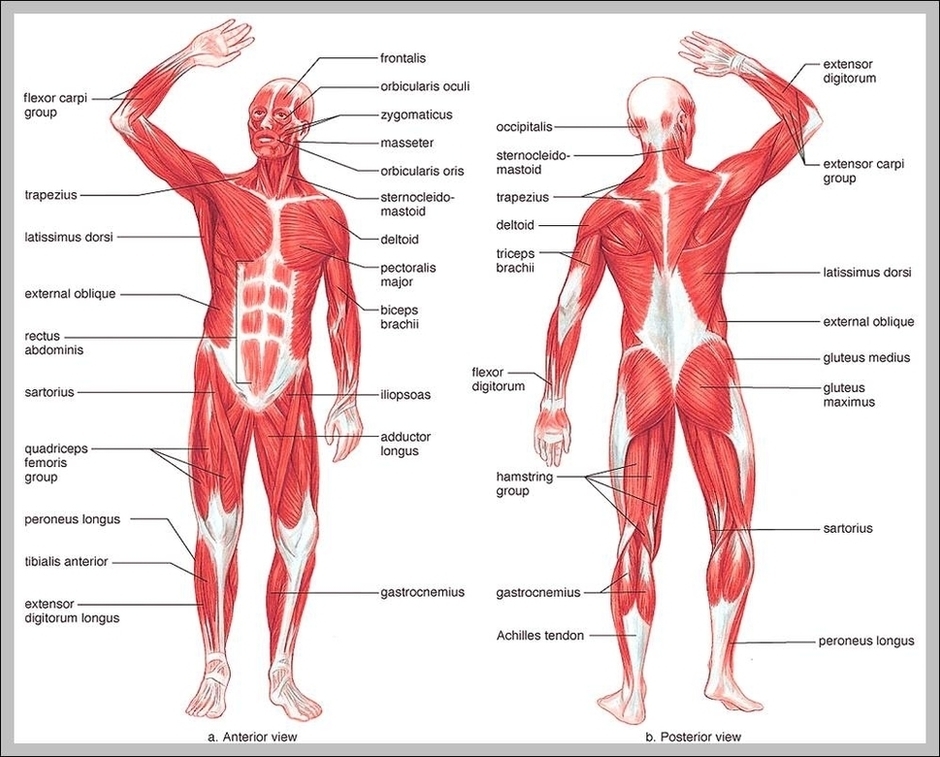
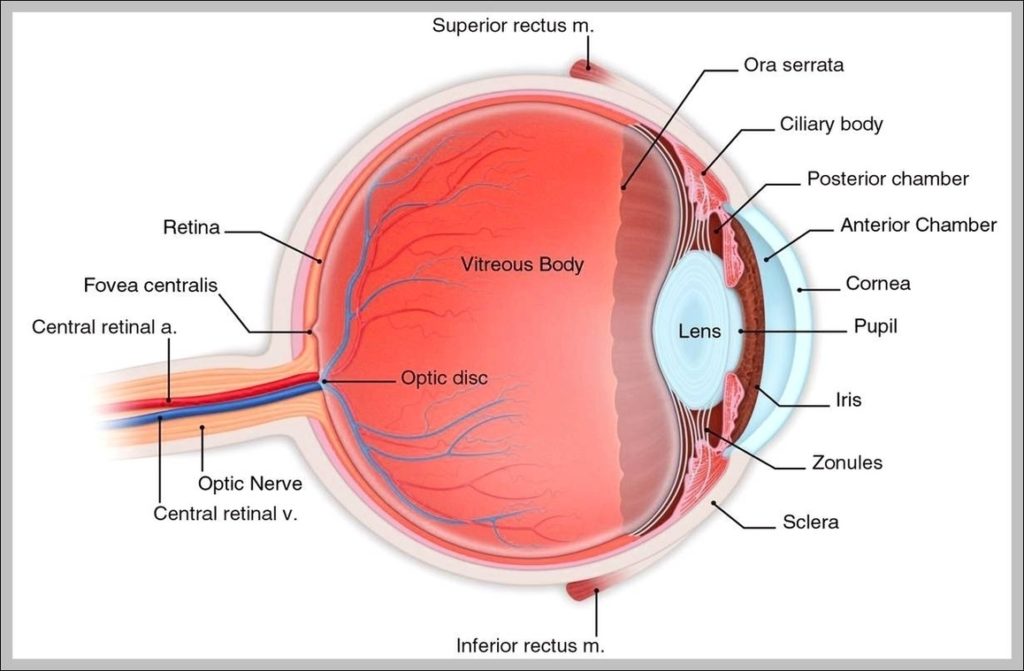
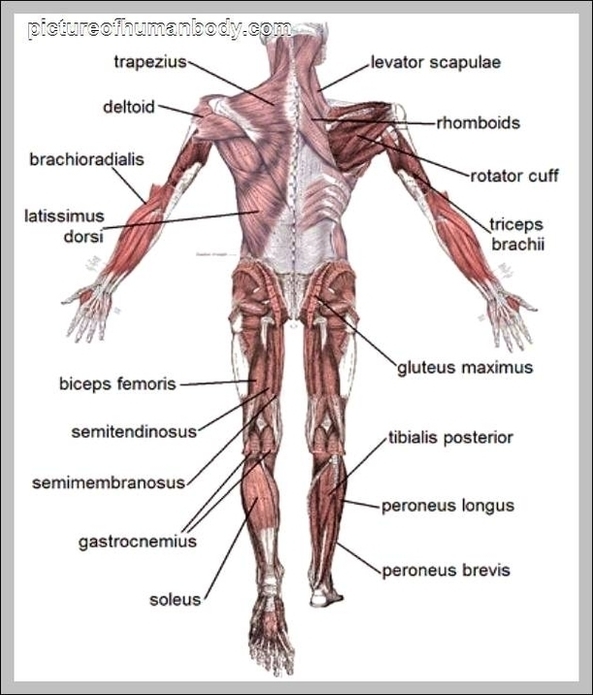
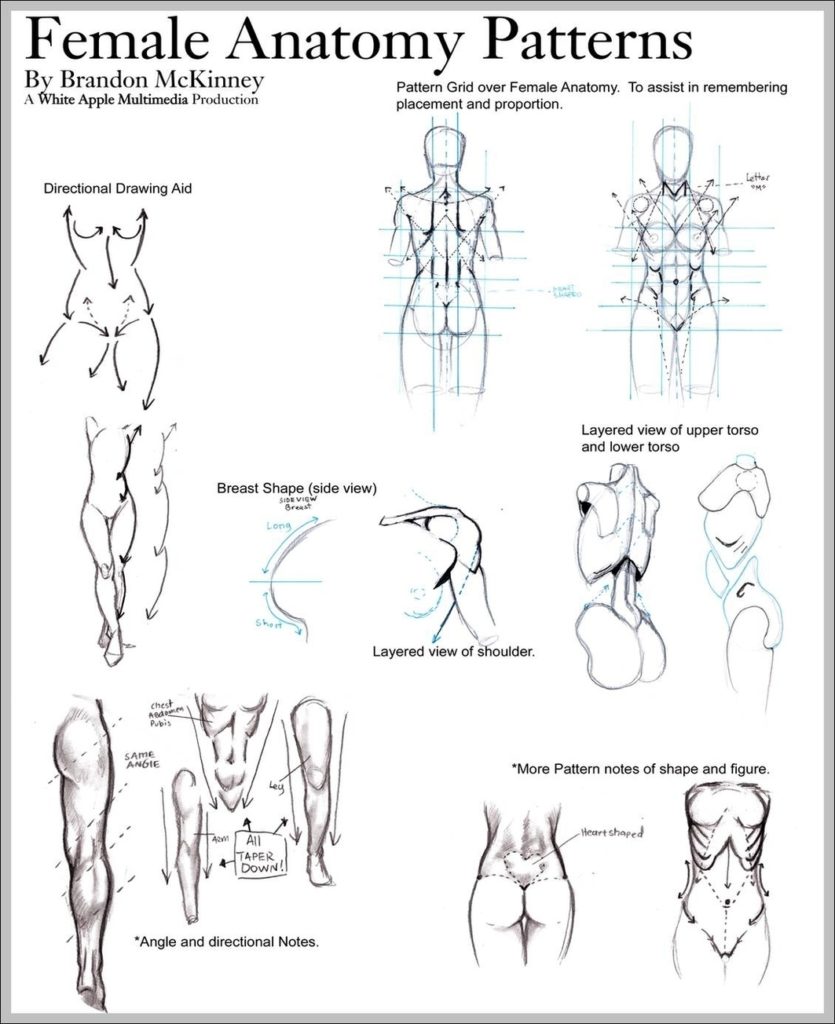
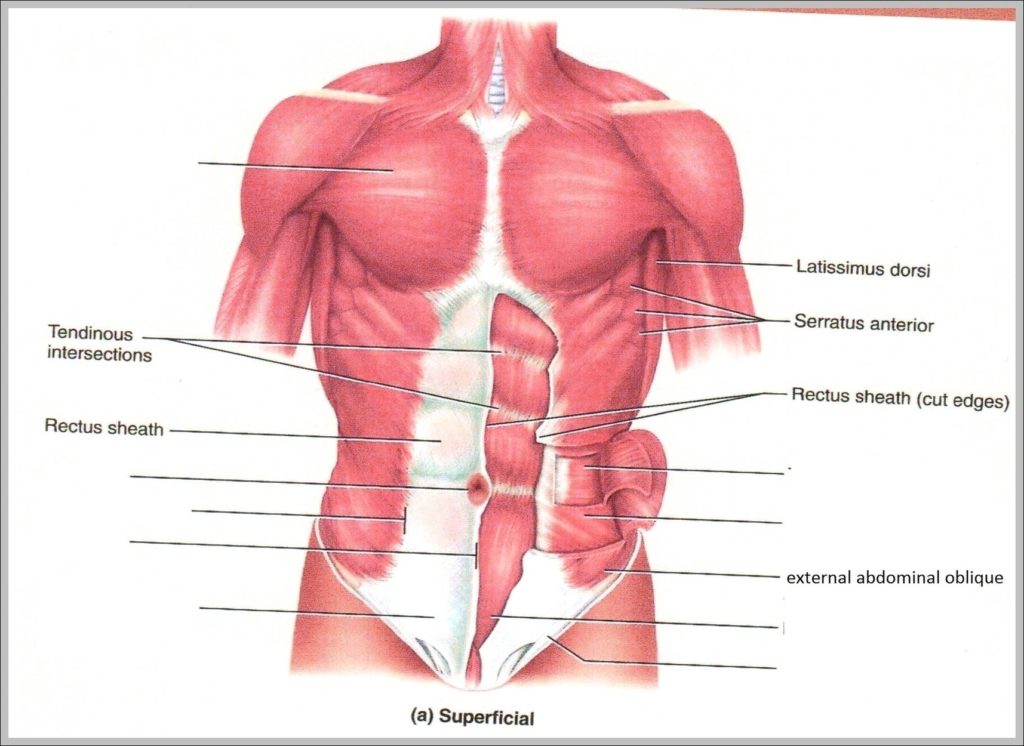
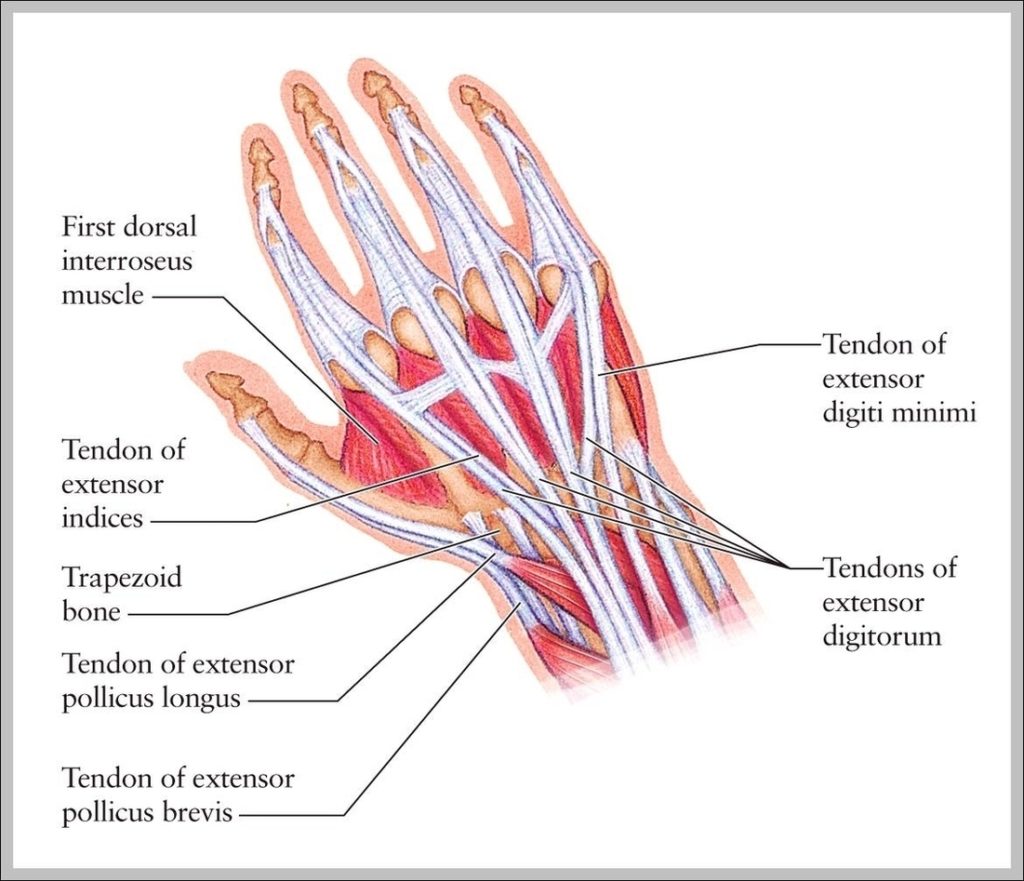
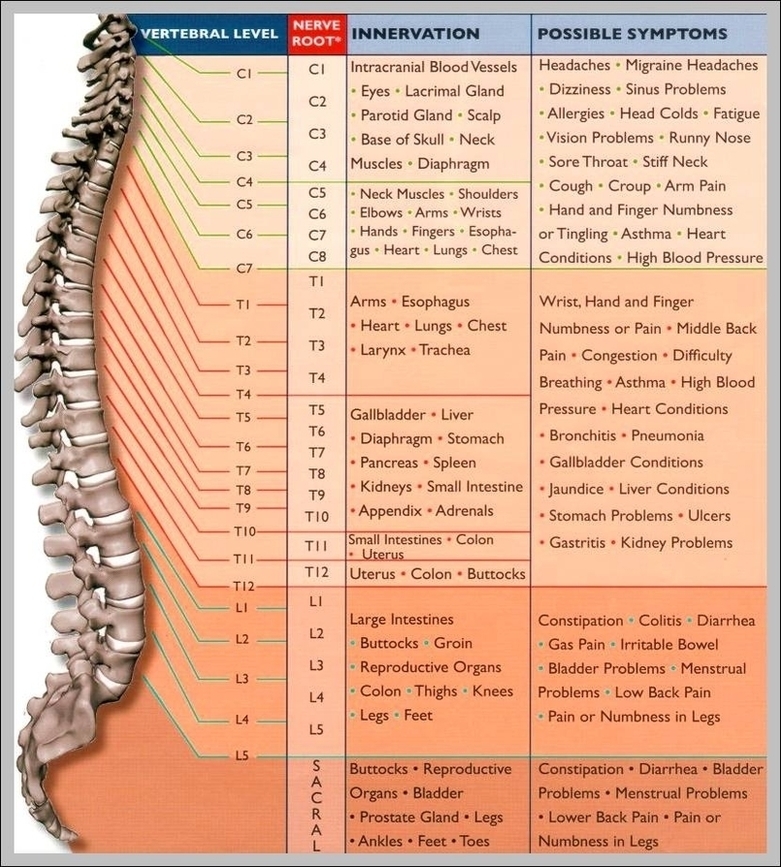
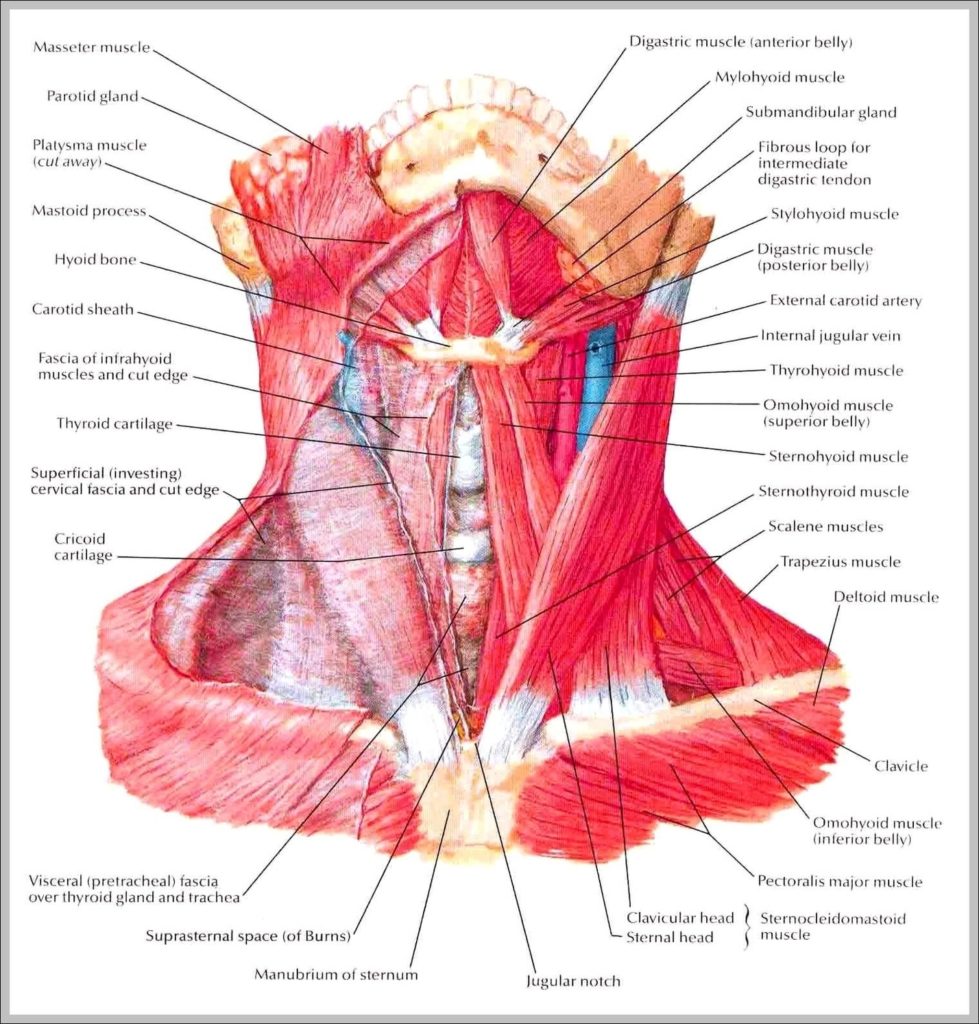
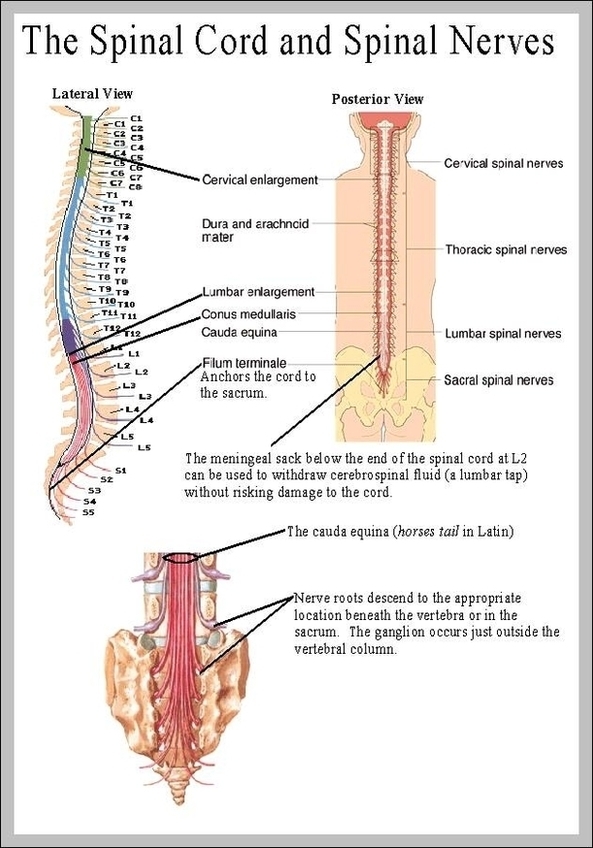
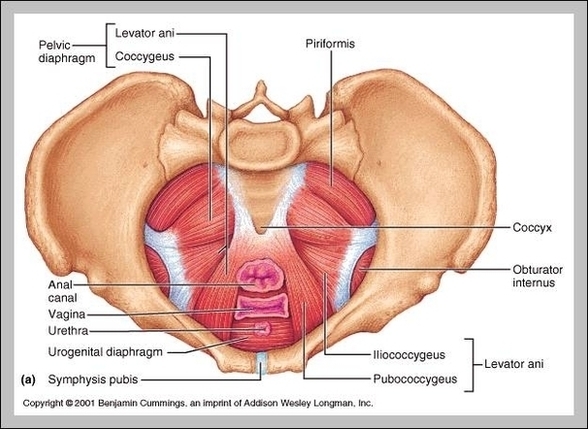
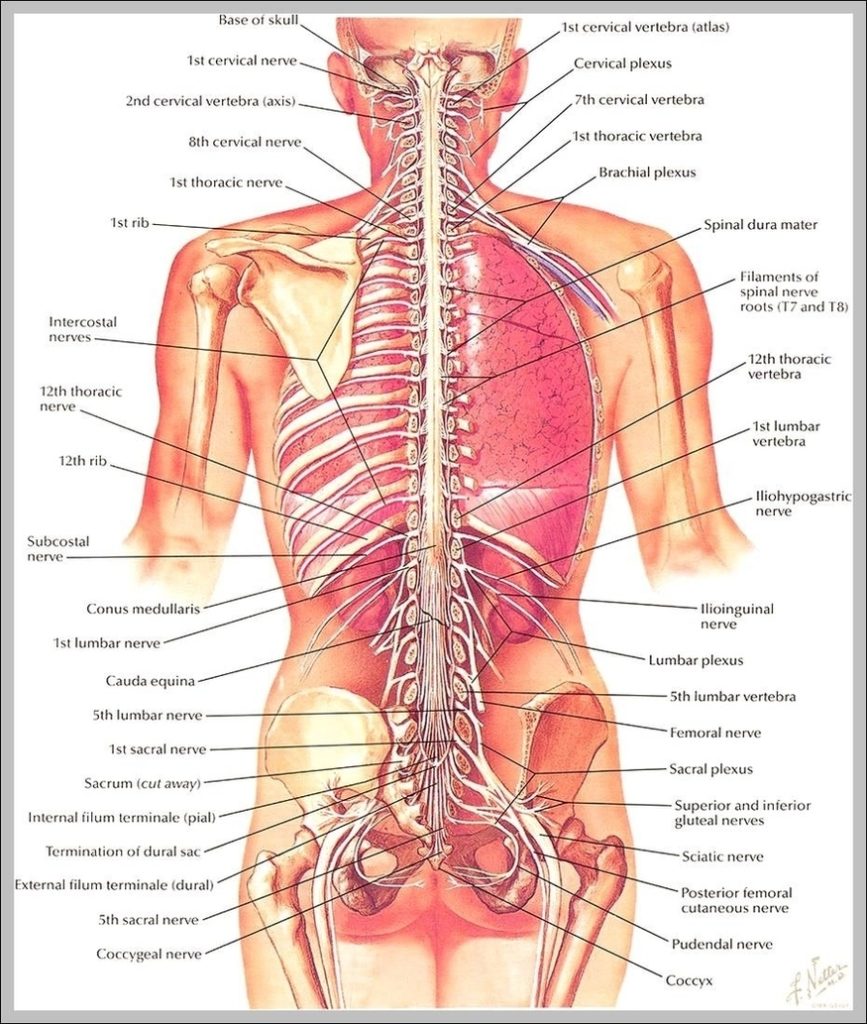
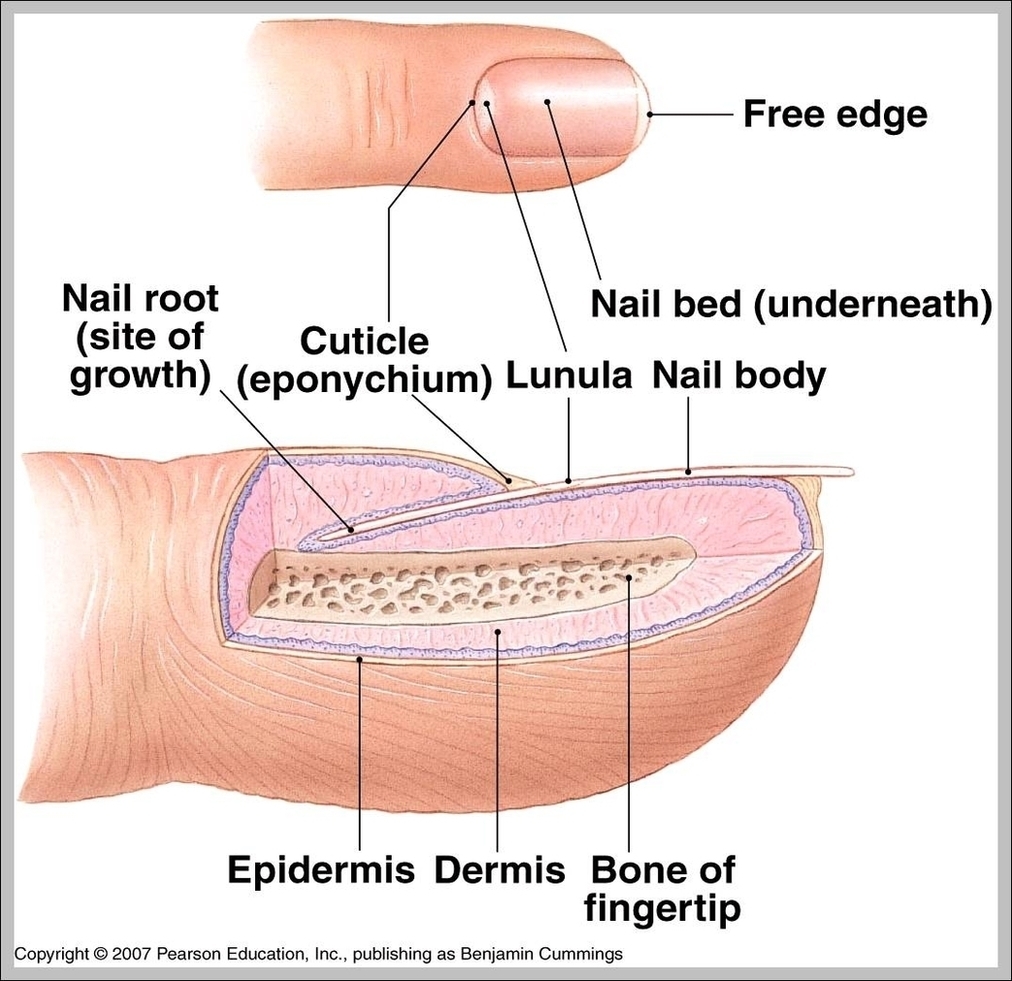
Posted inMedical
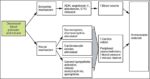
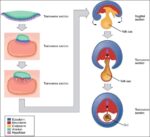
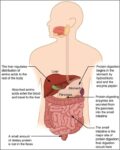
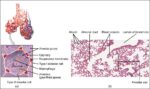
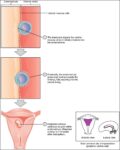
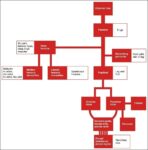
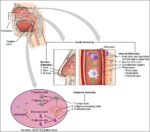
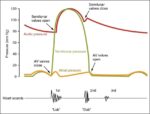
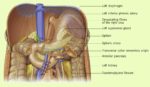
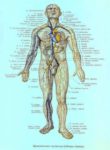
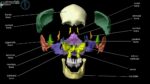
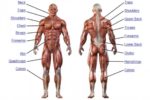
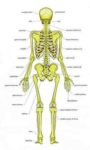
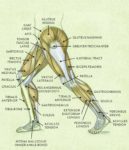
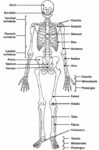
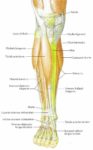
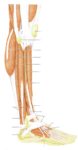
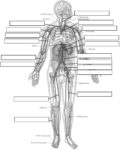
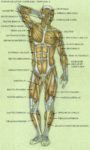
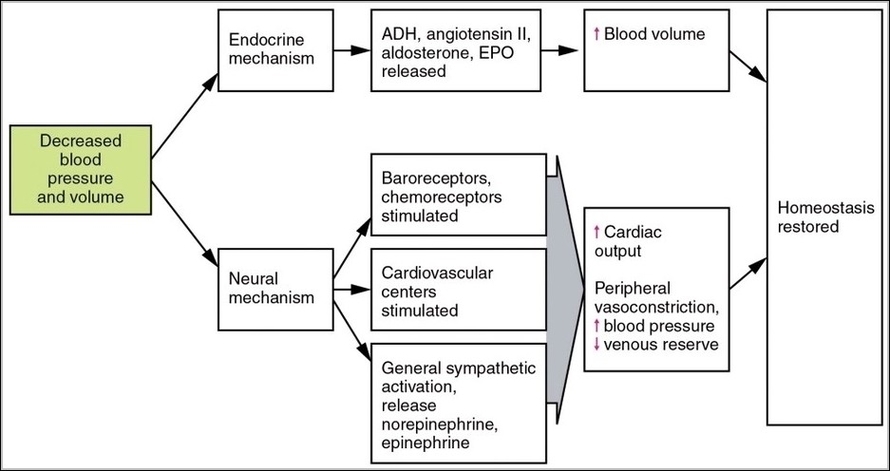
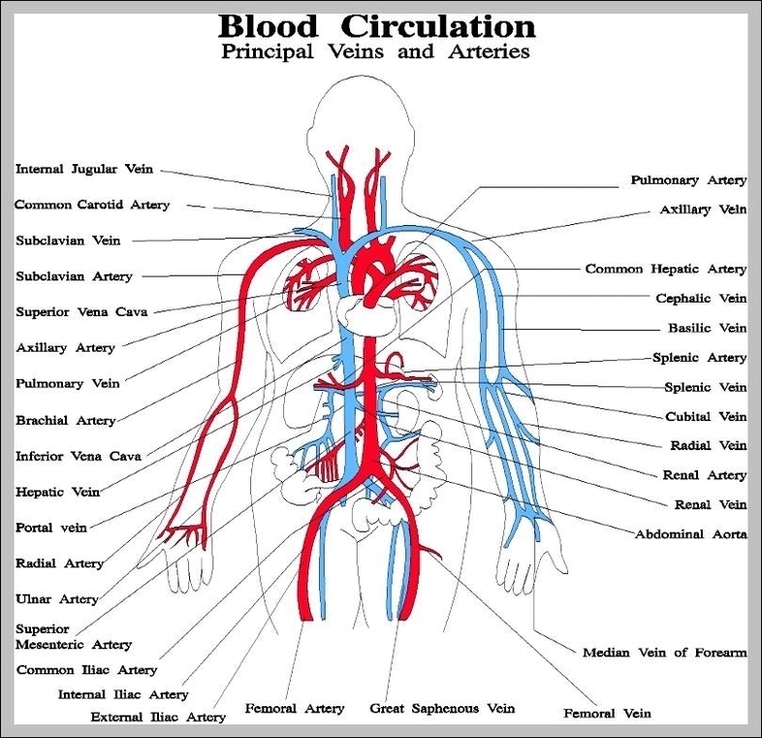
Blood Volume Loss and Homeostasis
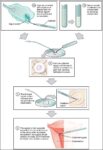
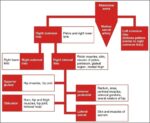
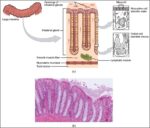
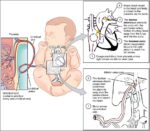
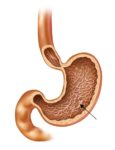
An illustration of blood volume loss and homeostasis explains how the body responds to bleeding or dehydration. It shows sensors detecting reduced volume or pressure, triggering responses such as increased…