Human Body Tissues Explained
Human Body Tissues Explained
The human body is a complex structure composed of four primary tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. These tissues, each with their unique structure and function, work together to maintain the overall health and functionality of the body.
1. Epithelial Tissue: This tissue type covers the exterior surfaces of the body, lines internal cavities and passageways, and forms certain glands. It is made of layers of cells that cover the surfaces of the body that come into contact with the exterior world.
2. Connective Tissue: As its name implies, connective tissue binds the cells and organs of the body together. It provides support and structure to the body and is essential for our overall health and well-being.
3. Muscle Tissue: Muscle tissue contracts forcefully when excited, providing movement. It is crucial for our ability to move and perform physical tasks.
4. Nervous Tissue: Nervous tissue is excitable, allowing for the generation and propagation of electrochemical signals in the form of nerve impulses that communicate between different regions of the body. It is essential for our ability to sense and respond to our environment.
These primary tissue types originate from the three germ layers formed during embryonic development: ectoderm (outer), mesoderm (middle), and endoderm (inner). The cells composing a tissue share a common embryonic origin.
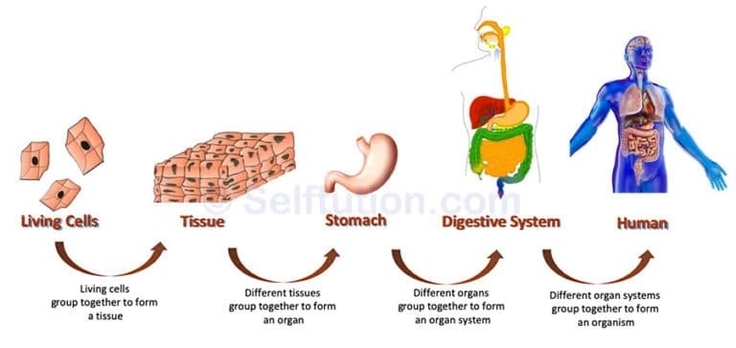
The organization of these tissues into organs and organ systems allows the body to function as a whole. For example, the digestive system is responsible for taking in and processing food, while the respiratory systemworking with the circulatory systemis responsible for taking up oxygen and getting rid of carbon dioxide. The muscular and skeletal systems are crucial for movement; the reproductive system handles reproduction; and the excretory system gets rid of metabolic waste.
In conclusion, understanding the various primary tissue types present in the human body is essential for understanding the structure and function of organs which are composed of two or more primary tissue types. The survival of the organism depends on the integrated activity of all the organ systems, often coordinated by the endocrine and nervous systems..
