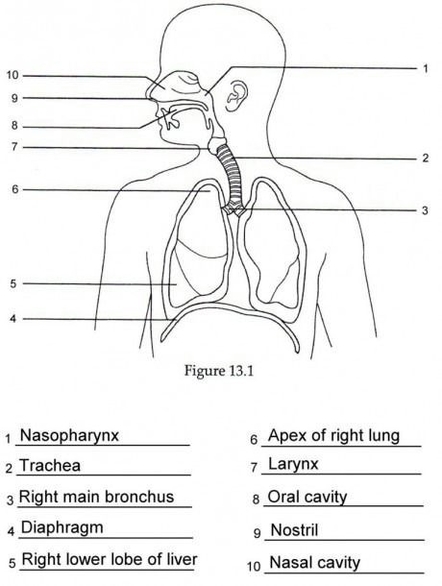
Human Respiratory System Visual
The Human Respiratory System
The human respiratory system is a complex network of organs and structures responsible for the vital process of respiration, which involves the exchange of gases between the air we breathe and our body’s cells.
Upper Respiratory System
The upper respiratory system comprises the nose, nasal cavities, and the paranasal sinuses. These structures provide airways for respiration. The pharynx, also part of the upper respiratory system, connects the nasal and oral cavities to the larynx and esophagus. The larynx and vocal cords allow us to breathe, talk, and sing.
Lower Respiratory System
The lower respiratory system consists of the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and the structures within the lungs, such as the bronchioles and alveolar ducts. The trachea is the main airway to the lungs, while the bronchi are passageways that facilitate the movement of air in and out of the lungs.
Lungs and Alveoli
The lungs, located in the thorax and protected by the bony and muscular thoracic cage, are responsible for gas exchange between the air we breathe and our bodies. The alveoli, microscopic air sacs within the lungs, are the site of this external respiration.
Diaphragm
The diaphragm, the main respiratory muscle, plays an essential role in the physical process of breathing. Under the control of the central nervous system, the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles of the chest wall generate a pumping action on the lung, expanding and contracting the internal space of the thorax.
Function of the Respiratory System
Through breathing, inhalation and exhalation, the respiratory system facilitates the exchange of gases between the air and the blood and between the blood and the bodys cells. The respiratory system also helps us to smell and create sound.
Conclusion
The human respiratory system is a marvel of biological engineering, efficiently facilitating the exchange of life-sustaining gases. Understanding its structure and function is crucial to comprehending how our bodies utilize oxygen and expel waste gases, maintaining the delicate balance necessary for life..
Human Respiratory System Visual Diagram - Human Respiratory System Visual Chart - Human anatomy diagrams and charts explained. This anatomy system diagram depicts Human Respiratory System Visual with parts and labels. Best diagram to help learn about health, human body and medicine.