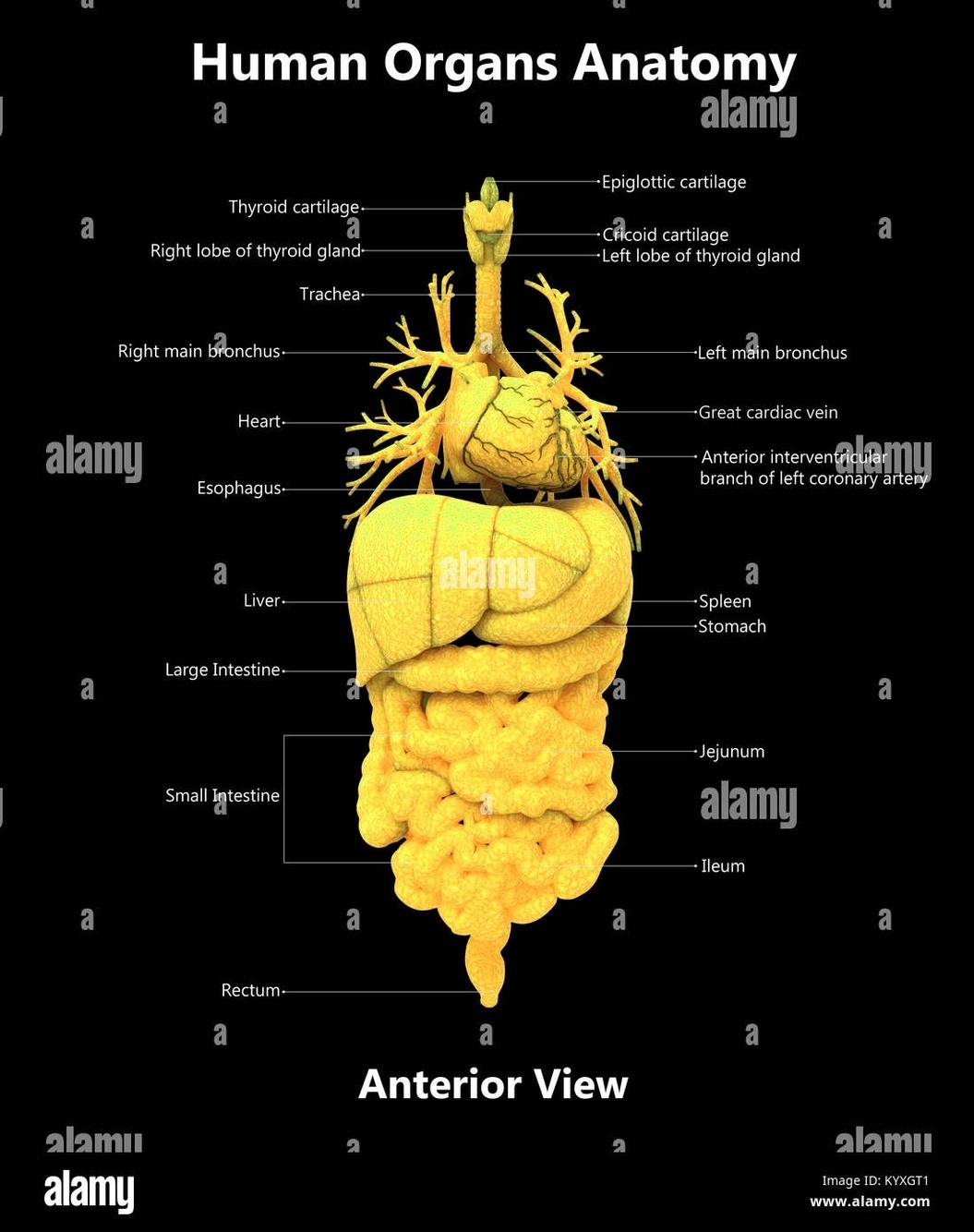
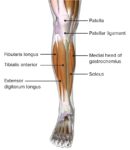
The human body is a complex system of interconnected organs, each with a specific structure and function. The anterior view of the human body provides a perspective that showcases several key organs. Here’s an overview of some of these organs:
1. Brain: The brain is the control center of the body, responsible for regulating all bodily functions, processing sensory information, and facilitating cognition and consciousness.
2. Heart: The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes.
3. Lungs: The lungs are responsible for gas exchange, taking in oxygen from the air we breathe and expelling carbon dioxide.
4. Liver: The liver performs numerous vital functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.
5. Kidneys: The kidneys filter the blood, removing waste products and converting them into urine. They also help regulate blood pressure and electrolyte balance.
6. Stomach: The stomach is a muscular organ involved in the digestion of food, breaking it down into a semi-liquid substance that can be further processed in the small intestine.
7. Intestines: The intestines are responsible for absorbing nutrients from digested food. The small intestine absorbs most nutrients, while the large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes, forming feces.
8. Muscles: Muscles allow for movement by contracting in response to nervous stimulation. In the anterior view, you can see major muscle groups like the pectorals (chest), abdominals (stomach), and quadriceps (thigh).
9. Bones: The skeletal system provides structural support for the body and protects internal organs. Key bones visible in the anterior view include the sternum, ribs, and pelvis.
10. Skin: The skin, the body’s largest organ, acts as a barrier against environmental damage, helps regulate body temperature, and allows for sensations of touch, heat, and cold.
This is a simplified overview and doesn’t cover all the organs or the complexity of their functions. Each organ is part of an organ system, a group of organs that work together to perform major functions or meet physiological needs of the body. For example, the heart and blood vessels form the circulatory system, which distributes oxygen and nutrients to the body’s cells.
In terms of anatomical terminology, the term “anterior” refers to the front side of the body in the standard anatomical position, where the person stands erect with their feet and palms facing forward. This is also known as the ventral side.
Understanding the human body’s anatomy and the functions of its organs is fundamental to medical and health-related fields. It allows healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat diseases more effectively and helps individuals make informed decisions about their health..