IgG antibodies consist of four polypeptide chains: two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains linked by disulfide bonds into a Y-shaped molecule. The heavy chains determine the classgamma for IgGand form the Fc region that binds immune cells and complement, while the light chains pair with the variable regions of heavy chains to create two identical antigen-binding Fab sites. Flexibility at the hinge region allows the arms to spread or close for bivalent binding. Subclasses like IgG2 differ slightly in hinge length and disulfide arrangement, affecting complement activation and effector functions.
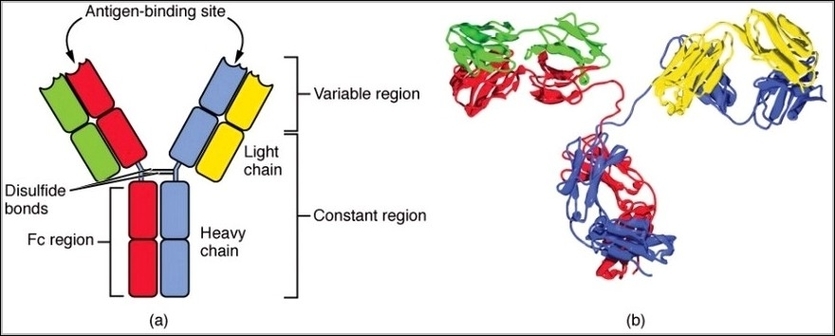
Four Chain Structure of a Generic Antibody IgG2 Structures
Posted inCell