Embryonic folding converts the flat trilaminar disc into a cylindrical body around weeks 3-4 through head, tail, and lateral folds that pinch the embryo off the yolk sac, incorporating endoderm into the gut tube, bringing amnion around, and establishing body cavities like pericardial and peritoneal. Cranial and caudal folds shape the brain and hindgut, lateral folds form the body wall closing ventral defects if incomplete like omphalocele; this crucial morphogenetic movement organizes scattered primordia into proper three-dimensional relationships essential for organ positioning.
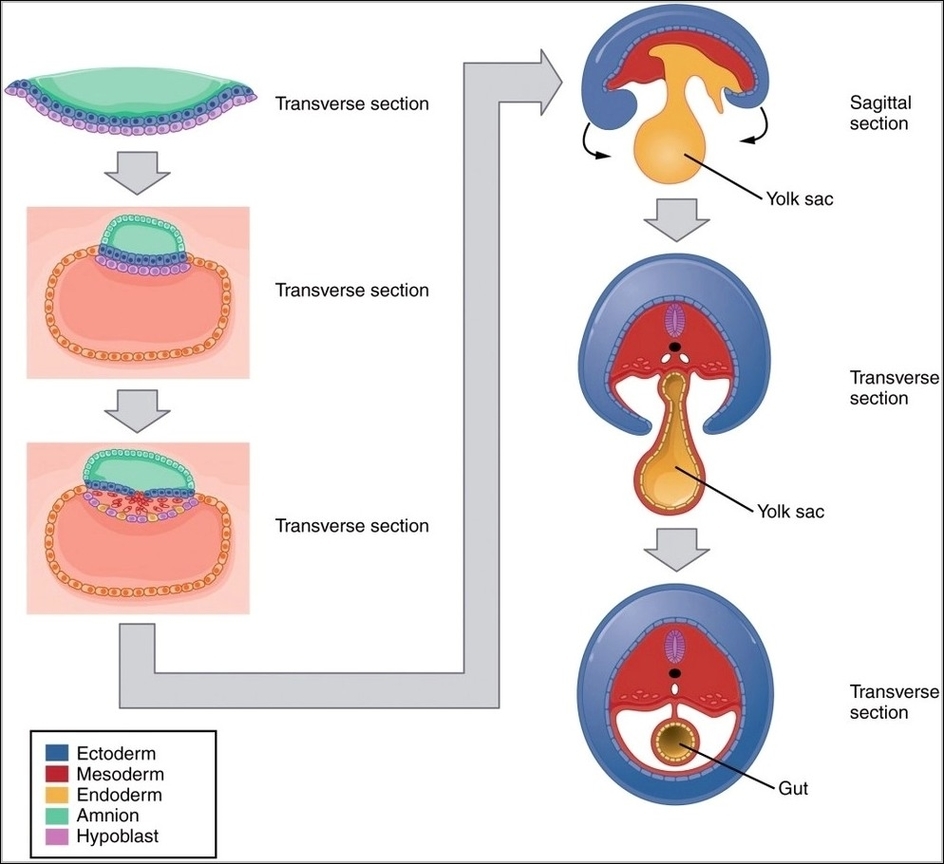
Embryonic Folding
Posted inMedical