human anatomy. The human body, a marvel of biological engineering, is a complex and intricate system composed of living cells, tissues, and organs. Here, I’ll provide an overview of its organization, major components, and essential functions.
## Organization of the Human Body
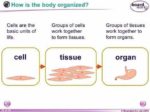
1. Cells and Tissues:
– Cells: The fundamental units of life, cells carry out vital functions. They vary in shape, size, and function. Examples include nerve cells (neurons), muscle cells (myocytes), and blood cells (erythrocytes).
– Tissues: Cells aggregate to form tissues. Four primary tissue types exist:
– Epithelial Tissues: These cover the body’s surfaces (skin) and line internal organs, cavities, and passageways.
– Muscle Tissues: Capable of contraction, they form the body’s musculature.
– Nerve Tissues: Conduct electrical impulses and constitute the nervous system.
– Connective Tissues: Support and connect various structures (e.g., bones, tendons, and ligaments).
2. Organs and Systems:
– Organs: Combinations of tissues with specific functions. Examples include the heart, lungs, liver, and brain.
– Systems: Organs collaborate to form systems, each serving a distinct purpose. Here are some major systems:
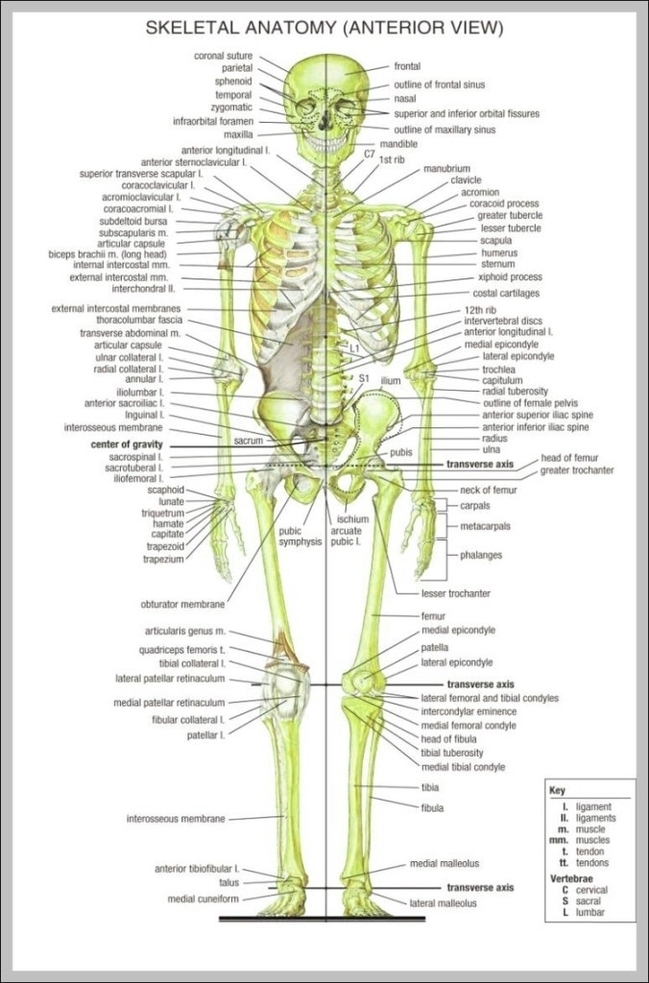
– Skeletal System: Provides structural support, protects organs, and enables movement.
– Muscular System: Facilitates movement, maintains posture, and generates heat.
– Cardiovascular System: Circulates blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients.
– Respiratory System: Enables gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out).
– Digestive System: Processes food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste.
– Nervous System: Coordinates body functions, processes sensory information, and controls movement.
– Endocrine System: Regulates hormones and maintains homeostasis.
– Urinary System: Filters blood, removes waste, and maintains fluid balance.
– Reproductive System: Ensures perpetuation of the species.
– Integumentary System: Comprises skin, hair, and nails, protecting against external threats.
3. Development and Aging:
– Embryonic Development: From conception to birth, the body undergoes intricate development. The notochord (dorsal supporting rod) and pharyngeal gill slits (present only during embryonic stages) play crucial roles.
– Growth: Throughout life, the body grows, adapts, and repairs itself.
– Aging: As we age, tissues and organs gradually change, affecting overall function.
4. Biochemical Constituents:
– Proteins: Essential for cell structure, enzymes, and signaling.
– Carbohydrates: Provide energy and structural support.
– Lipids: Form cell membranes and store energy.
– Nucleic Acids: Encode genetic information (DNA and RNA).
– Vitamins and Hormones: Regulate various processes.
## Conclusion
The human body’s intricate design allows us to thrive, adapt, and experience life. From the microscopic interactions within cells to the coordinated efforts of organs and systems, our bodies are a testament to the wonders of nature.
For more detailed information on specific structures or functions, explore resources on human anatomy and physiology..