Structure of Viruses
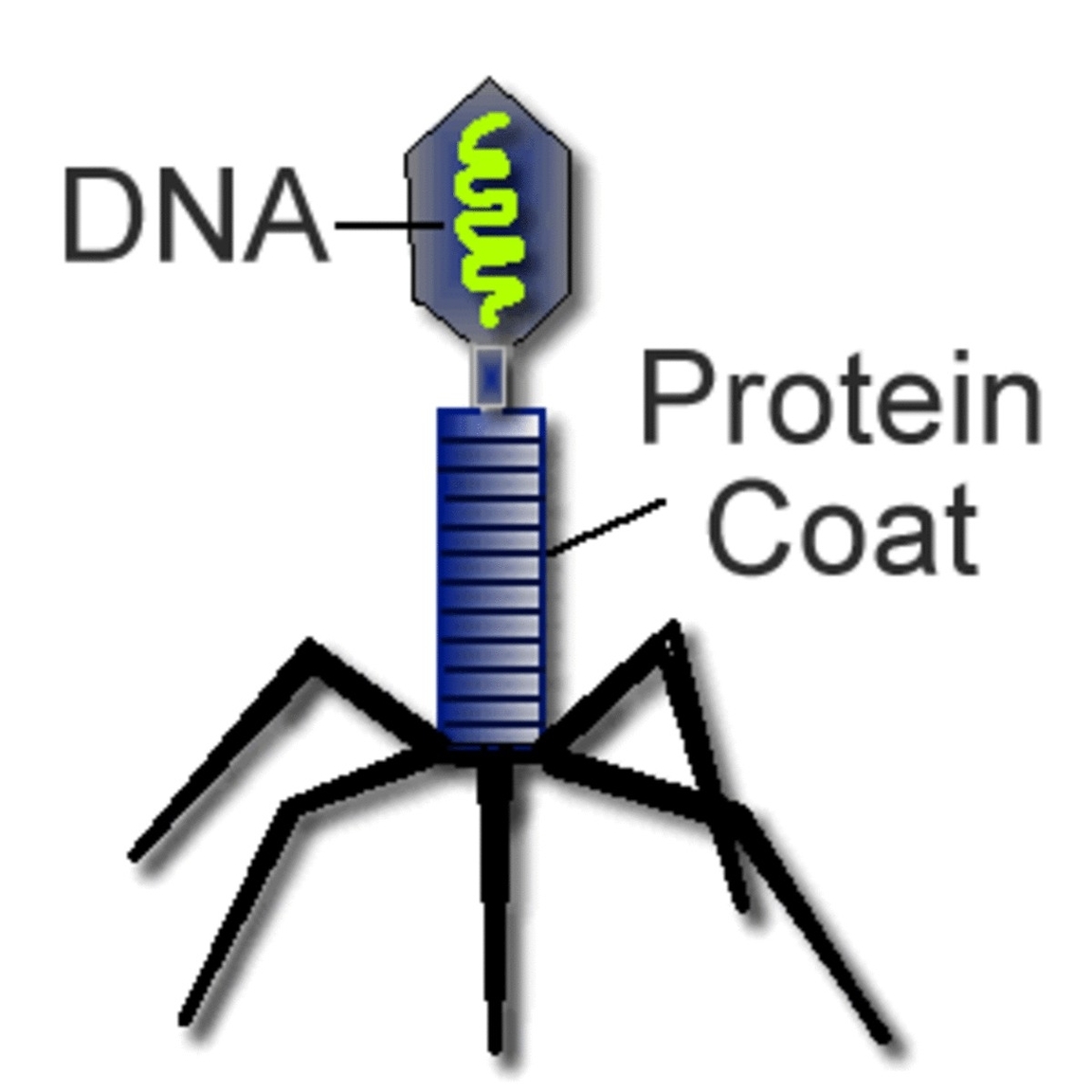
Viruses are biological structures that have a nucleic acid genome surrounded by protein and lipids. They are much smaller than bacteria and consist of a single- or double-stranded nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein shell called a capsid. Some viruses also have an outer envelope composed of lipids and proteins. They vary in shape and the two main classes are RNA viruses and DNA viruses.
Virology
Virology is the scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy.
Molecular Virology
Molecular virology is the study of viruses at the level of nucleic acids and proteins. The methods invented by molecular biologists have all proven useful in virology. Their small sizes and relatively simple structures make viruses an ideal candidate for study by these techniques.
Infection Process
A virus is an infectious particle that reproduces by “commandeering” a host cell and using its machinery to make more viruses. A virus is made up of a DNA or RNA genome inside a protein shell called a capsid. Some viruses have an external membrane envelope. Viruses reproduce by infecting their host cells and reprogramming them to become virus-making “factories”.
Diversity of Viruses
Viruses are very diverse. They come in different shapes and structures, have different kinds of genomes, and infect different hosts. Scientists estimate that there are roughly 10^31 viruses at any given moment. Most of these viruses are found in oceans, where they attack bacteria and other microbes. It may seem odd that bacteria can get a virus, but scientists think that every kind of living organism is probably host to at least one virus.
Conclusion
The study of viruses is a vast field that covers biology, health, animal welfare, agriculture, and ecology. Understanding the structure of viruses is crucial as it provides insights into how they function, how they cause diseases, and how they can be combated. Despite their small size and simple structure, viruses have a significant impact on all forms of life..