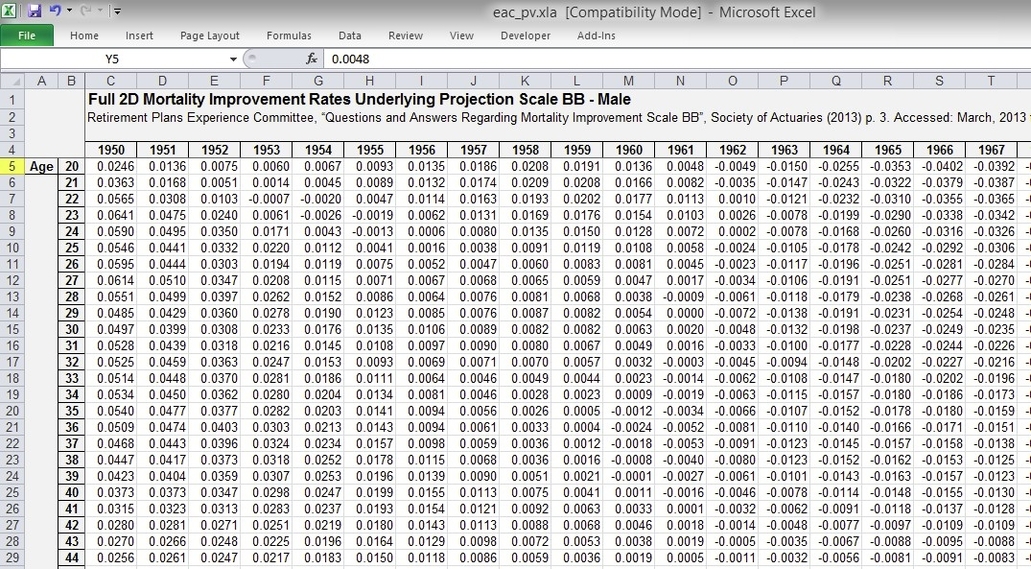
Mortality Tables and Life Expectancy
Mortality tables, also known as life tables, actuarial tables, or death tables, are statistically based tables that illustrate the probability of mortality at each age for a given population. They are fundamental tools in the field of actuarial science and are crucial for various applications, including insurance, pension plans, and public health planning.
Life expectancy, a key output from these tables, is the average number of years a person is expected to live based on their current age. It’s a statistical measure that reflects the overall mortality level of a population.
tructure of Mortality Tables
Mortality tables typically contain the following columns:
1. Age (x): This is the age at which the mortality rate is calculated.
2. Number of survivors (lx): This is the number of individuals surviving to age x.
3. Number of deaths (dx): This is the number of individuals expected to die between age x and x+1.
4. Probability of dying (qx): This is the probability that an individual of age x will die before reaching age x+1.
Life Expectancy Calculation
Life expectancy is calculated using the data in a life table. For any age, it is computed as the total number of years that a person of that age can expect to live, on average.
Factors Influencing Mortality Rates and Life Expectancy
everal factors influence the mortality rates used in life tables and, consequently, life expectancy. These include lifestyle factors (like diet and exercise), access to healthcare, socioeconomic status, and environmental factors.
Trends in Life Expectancy
Globally, life expectancy has increased significantly over the past century due to advancements in healthcare, nutrition, and living conditions. For instance, global life expectancy increased by more than 6 years between 2000 and 2019.
Mortality Tables and Insurance
Insurance companies use mortality tables to estimate future liabilities. For example, life insurance premiums are calculated based on the probability of a policyholder’s death, as determined by the mortality table.
Limitations of Mortality Tables and Life Expectancy
While mortality tables and life expectancy are useful tools, they have limitations. They provide averages and probabilities, not certainties. Individual health and longevity can vary widely from the averages due to genetic factors and personal habits.
In conclusion, mortality tables and life expectancy are powerful tools in understanding population health and planning for future needs. They provide valuable insights into the health outcomes of different populations and are essential for various sectors, including public health, insurance, and social security planning..