Communicable Diseases
Communicable diseases, also known as infectious or transmissible diseases, are illnesses that spread from one person or animal to another or from a surface to a person. They are caused by pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa.
Types of Pathogens
1. Viruses: These are tiny pathogens that contain genetic material. They lack the complex structure of a cell and must enter the cells of other living beings to replicate.
2. Bacteria: These are microscopic, single-celled organisms. They exist in almost every environment on earth, including inside the human body. While many bacteria are harmless or even beneficial, some can cause infections.
3. Fungi: This type of organism includes yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. Of the millions of different fungi, only around 300 cause harmful illnesses. Fungal infections commonly affect the skin and mucus membranes.
4. Protozoa: These are microscopic organisms that typically consist of a single cell. Some protozoa are parasitic, meaning they live on or inside another organism and use the organisms nutrients for their own survival.
Transmission
Communicable diseases can transmit through various means, including contact with bodily fluids, insect bites, contaminated surfaces, water, and foods, or through the air.
ymptoms
Once a pathogen has entered a persons body, it often begins replicating, and the individual may start to experience symptoms. These symptoms will vary depending on the disease. Some people will not experience any symptoms but can still transmit the pathogen.
Prevention and Treatment
Prevention and treatment methods vary depending on the specific disease. Common preventive measures include practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. Treatment may involve medication, rest, hydration, and in some cases, hospitalization.
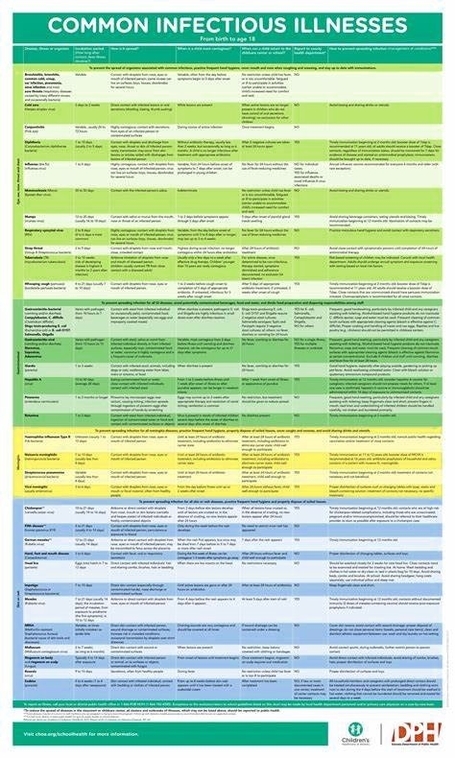
Common Communicable Diseases
Common communicable diseases include colds, flu, HIV, malaria, measles, tuberculosis, cholera, hepatitis, and many others. In Canada, the Public Health Agency lists numerous infectious diseases, including COVID-19, influenza, hepatitis, HIV/AIDS, and Lyme disease.
Conclusion
Communicable diseases pose significant challenges to global health. Understanding these diseases, their causes, transmission methods, and prevention strategies is crucial in controlling their spread and minimizing their impact on public health. Despite the challenges, advancements in medical science continue to provide new ways to prevent and treat these diseases..