The human hand is a marvel of evolution and one of the most complex and versatile structures in the body. It consists of 27 bones that work together to provide the dexterity and strength necessary for our daily activities.
Carpal Bones
The carpal bones are a set of eight irregularly shaped bones located in the wrist area. They are organized into two rows: proximal and distal.
*Proximal Row (from lateral to medial)*:
– Scaphoid
– Lunate
– Triquetrum
– Pisiform (a sesamoid bone, formed within the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris)
*Distal Row (from lateral to medial)*:
– Trapezium
– Trapezoid
– Capitate
– Hamate (has a projection on its palmar surface, known as the hook of hamate)
These bones form an arch in the coronal plane. A membranous band, the flexor retinaculum, spans between the medial and lateral edges of the arch, forming the carpal tunnel.
Metacarpal Bones
There are five metacarpals, each one related to a digit. They articulate proximally with the carpals, and distally with the proximal phalanges. They are numbered, and each associated with a digit:
– Metacarpal I Thumb
– Metacarpal II Index finger
– Metacarpal III Middle finger
– Metacarpal IV Ring finger
– Metacarpal V Little finger
Each metacarpal consists of a base, shaft, and a head. The medial and lateral surfaces of the metacarpals are concave, allowing attachment of the interossei muscles.
Phalanges
The phalanges are the bones of the fingers. Each finger has three phalanges, except for the thumb, which has two. They are referred to as:
– Proximal phalanx
– Middle phalanx
– Distal phalanx
Clinical Relevance
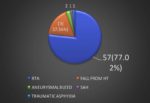
The scaphoid bone of the hand is the most commonly fractured carpal bone, typically by falling on an outstretched hand (FOOSH). In a fracture of the scaphoid, the characteristic clinical feature is pain and tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox.
In conclusion, the bones of the hand, including the carpal, metacarpal, and phalanges, play a crucial role in the hand’s function. Their unique arrangement and articulation allow for the hand’s remarkable dexterity and strength..