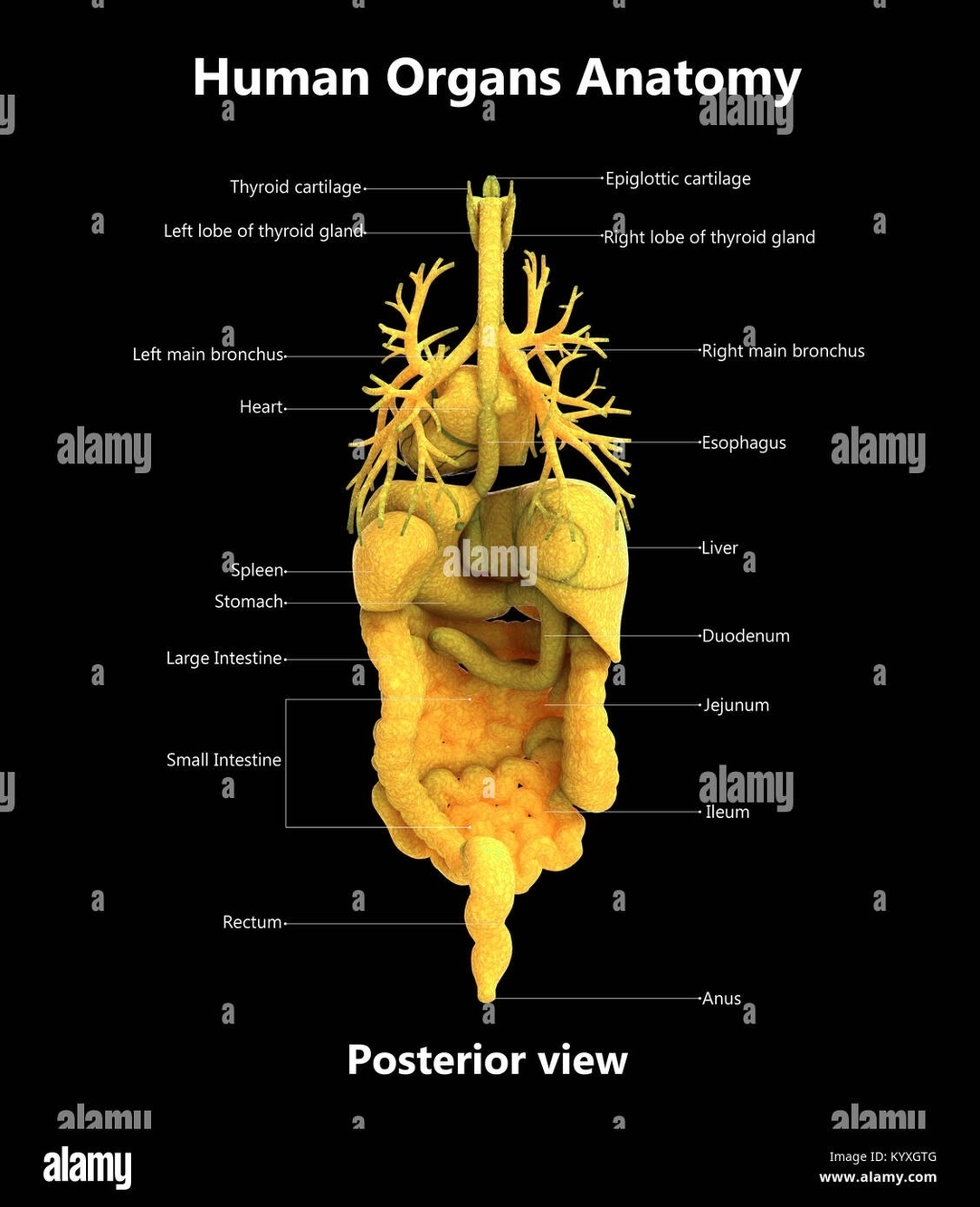
The human body is a complex system of organs, each with its unique function. When viewed from the posterior (back), several key organs are visible. Here’s an overview of these organs and their functions:
1. Brain: The brain is the bodys control center. It forms the core of the central nervous system by creating, sending, and processing nerve impulses, thoughts, emotions, physical sensations, and more. The major areas of the brain include:
– The medulla: Helps control heart and lung function.
– The pons: Helps control eye and facial movement.
– The parietal lobe: Supports identifying objects and doing spatial reasoning.
– The frontal lobe: Plays a role in many conscious functions, including personality and movement.
– The occipital lobes: Primarily interprets vision signals.
– The temporal lobes: Play a role in numerous functions, including speech, scent recognition, and short-term memory.
2. Heart: The heart is the most important organ of the circulatory system, which helps deliver blood to the body. It has four chambers: two upper chambers called atria, and two lower chambers called ventricles. Blood flows into the right atrium from the veins of the heart and body (except the lungs) and then flows into the right ventricle. From there, it flows into the pulmonary artery, which has branches that reach the lungs. The lungs then oxygenate the blood.
3. Lungs: The lungs are vital for respiration. They oxygenate the blood and remove carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. In the case of the paired lungs, a person can live without one of the pair.
4. Liver: The liver is a large organ that sits on the right side of the belly. It detoxifies chemicals and metabolizes drugs. The liver also makes proteins important for blood clotting and other functions.
5. Kidneys: The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They are located just below the rib cage, one on each side of the spine. The kidneys filter out wastes, extra water, and salt through the urine. In the case of the paired kidneys, a person can live without one of the pair.
These organs are vital for survival, and any problem with these organs can quickly become life-threatening. The posterior view of the human body also includes the spine, which provides structural support and houses the spinal cord, an extension of the brain that communicates with the rest of the body. The posterior view also shows the muscles and bones that support these organs and enable movement.
In conclusion, the posterior view of the human body reveals a complex interplay of organs, each with its unique function, working together to maintain the body’s overall health and vitality..