Medical Anatomy of Vertebrae
The vertebral column, also known as the spine or backbone, is a curved structure composed of approximately 33 bones called vertebrae. These vertebrae are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs. The vertebral column is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx.
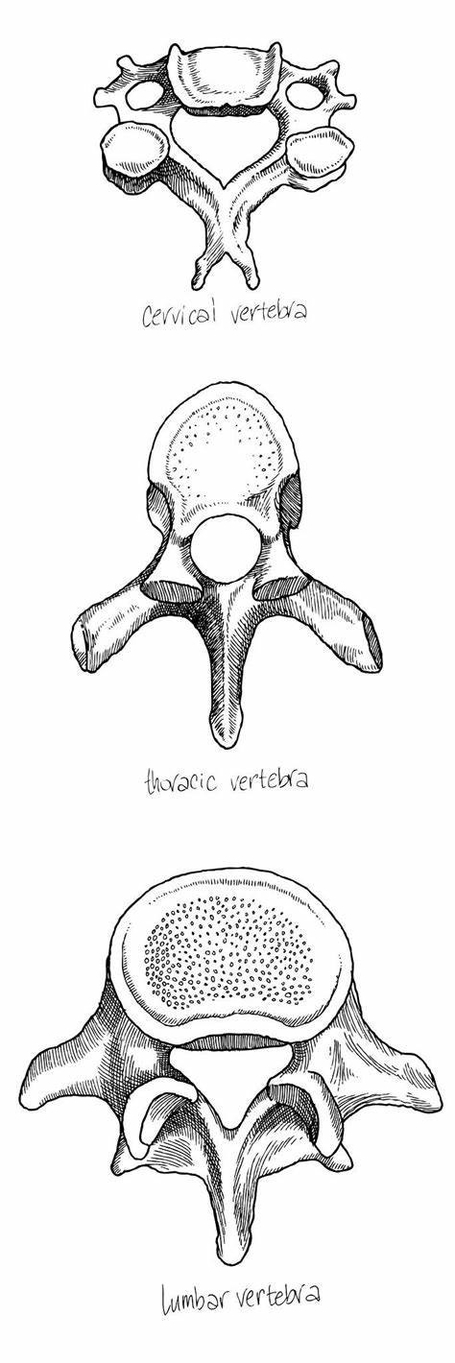
tructure of Vertebrae
Each vertebra consists of an anterior vertebral body and a posterior vertebral arch. The vertebral body forms the anterior part of each vertebra and is the weight-bearing component. Vertebrae in the lower portion of the column have larger bodies than those in the upper portion to better support the increased weight. The superior and inferior aspects of the vertebral body are lined with hyaline cartilage. Adjacent vertebral bodies are separated by a fibrocartilaginous intervertebral disc.
The vertebral arch forms the lateral and posterior aspect of each vertebra. In combination with the vertebral body, the vertebral arch forms an enclosed hole the vertebral foramen. The foramina of all the vertebrae line up to form the vertebral canal, which encloses the spinal cord.
Functions of the Vertebral Column
The vertebral column has four main functions:
1. Protection: It encloses and protects the spinal cord within the spinal canal.
2. Support: It carries the weight of the body above the pelvis.
3. Axis: It forms the central axis of the body.
4. Movement: It has roles in both posture and movement.
Clinical Relevance
Intervertebral discs are fibrocartilaginous cylinders that lie between the vertebrae, joining them together. They permit the flexibility of the spine and act as shock absorbers. In the lumbar and thoracic regions, they are wedge-shaped, supporting the curvature of the spine.
Conclusion
The vertebral column is a complex structure that plays a crucial role in the human body. Its intricate design allows it to perform a variety of functions, from providing structural support and facilitating movement to protecting the spinal cord. Understanding the anatomy of the vertebrae is essential in the medical field, particularly in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the spine..