The human body is a complex and intricate system, composed of various organs, tissues, and cells, all working in harmony to maintain life. Here’s an overview of the labeled anatomy of the human body:
1. Vital Organs
These are organs that a person needs to survive. Any problem with these organs can quickly become life-threatening:
– Brain: The body’s control center, creating, sending, and processing nerve impulses, thoughts, emotions, physical sensations, and more.
– Heart: The most important organ of the circulatory system, which helps deliver blood to the body.
– Lungs: Essential for respiration, allowing oxygen in the air to be taken into the body while also enabling the body to get rid of carbon dioxide.
– Liver: Performs various functions such as detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.
– Kidneys: Responsible for filtering waste products, excess water, and other impurities from the blood.
2. Non-Vital Organs
These organs are not necessary for survival, but they do have a role in bodily functions. Examples include the gallbladder, pancreas, and stomach.
3. Organ Systems
These are groups of organs that work together to perform complex functions. For example, the nervous system supports the brain and other organs.
4. Tissues, Cells, and Extracellular Materials
The human body is composed of living cells and extracellular materials, organized into tissues, organs, and systems.
5. Biochemical Constituents
The body’s biochemical constituents include proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, vitamins, and hormones.
6. Development
The human body undergoes various stages of development, from conception through old age.
7. Sensory Reception
The human body has a complex sensory reception system that allows us to interact with our environment.
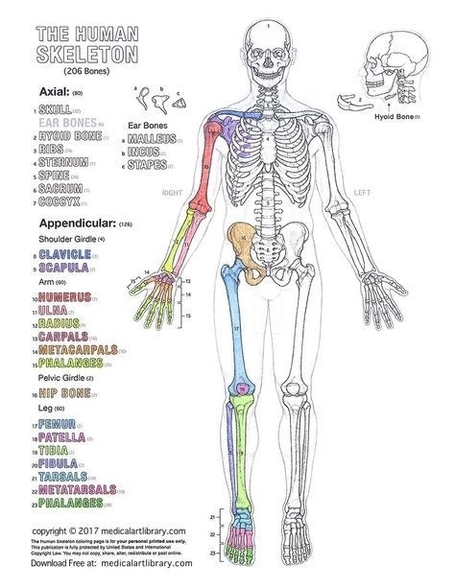
8. Muscular and Skeletal Systems
The human muscle system allows for movement and the skeletal system provides the structural framework for the body.
9. Reproductive System
The human reproductive system enables reproduction and the continuation of our species.
10. Respiratory System
The human respiratory system allows for the intake of oxygen and the expulsion of carbon dioxide.
11. Endocrine System
The human endocrine system regulates the body’s growth, metabolism, and sexual development and function.
12. Digestive System
The human digestive system breaks down food into nutrients that the body can use.
13. Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system circulates blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
In conclusion, the human body is a marvel of biological engineering, with each part playing a crucial role in maintaining overall health and function. Understanding the labeled anatomy of the human body is fundamental to appreciating the complexity and beauty of human life..