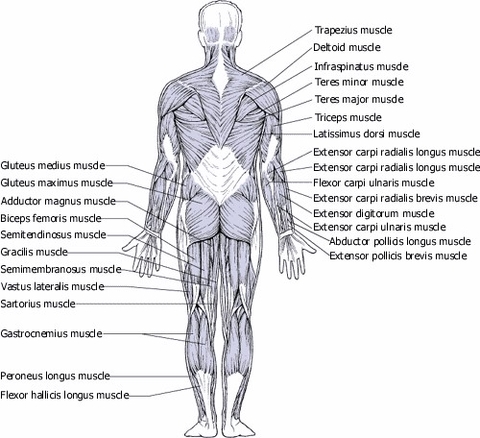
Human Muscles: Back View
The human back, a complex structure comprising bones, muscles, and nerves, plays a crucial role in body support, movement, and protection of vital organs.
pine
The spine, composed of 33 vertebrae, forms the spinal canal, protecting the spinal cord. The vertebrae are connected by facet joints, with fluid supporting their free movement. A disk sits between each vertebra, cushioning the bones from shocks. The spine consists of five sections:
1. Cervical Spine: The top part of the spine, running from the neck to the upper back. It consists of seven vertebrae.
2. Thoracic Spine: The middle part of the spine, connecting the cervical and lumbar spine. It has 12 vertebrae.
3. Lumbar Spine: The lower part of the back, made up of five larger vertebrae. These support most of the bodys weight.
4. Sacrum: The bottom part of the spine, which connects to the hip bones. The sacrum has five vertebrae fused together.
5. Coccyx: The base, or tailbone, of the spine. This consists of four vertebrae fused together.
pinal Cord
The spinal cord runs from the neck down to the lower back. It consists of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain. The spinal cord allows the body to move freely, have an awareness of the position of limbs, feel sensations, regulate body temperature, blood pressure, and heart rate, and carry out bodily functions.
Muscles in the Back
There are three different groups of muscles in the back:
1. Superficial Muscles: These are the muscles closest to the skin surface. They are primarily responsible for movements of the shoulder.
2. Intermediate Muscles: These muscles are involved in respiratory processes as they help move the ribs, facilitating breathing.
3. Intrinsic Muscles: These are deep muscles that directly attach to the spine. They maintain posture and control precise movements of the spine.
Each muscle group has specific muscles with unique roles in movement and stability. Understanding these muscles and their functions can help in maintaining back health and managing back-related issues.
Conclusion
The back’s complex structure, including its muscles, plays a vital role in daily activities, from walking and lifting to sitting and standing. Understanding the back’s anatomy can provide insights into how to maintain its health and manage potential issues. It’s a testament to the intricate design of the human body, where every component has a specific function contributing to the body’s overall performance.