Human Muscle Anatomy
The human muscle system is a complex network of tissues designed to provide movement and maintain posture. It consists of three types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
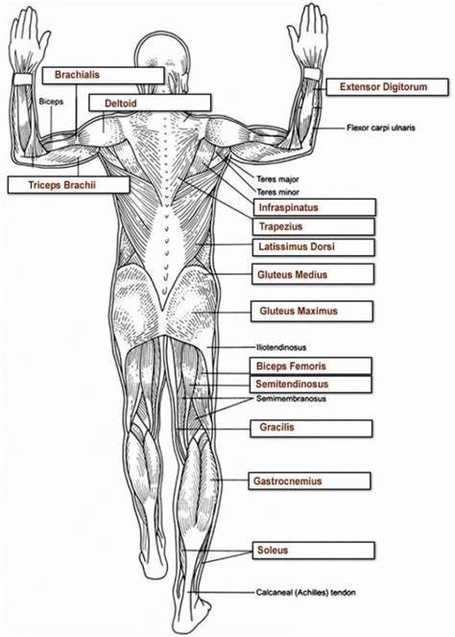
1. Skeletal Muscle: These muscles are attached to the bones by tendons and are under voluntary control. They work in groups to move the skeleton. Skeletal muscles are made of thousands of small fibers woven together. These fibers stretching and pressing together is what moves your body. There are more than 600 skeletal muscles, and they make up about 40 percent of a person’s body weight.
2. Smooth Muscle: Found in the walls of hollow organs, respiratory passageways, and blood vessels, smooth muscle is under involuntary control. Its wavelike movements propel things through the bodily system, such as food through your stomach or urine through your bladder.
3. Cardiac Muscle: This muscle type makes up the walls of the heart and is responsible for the rhythmic contractions of that vital pumping organ. It is under involuntary control and creates the steady, rhythmic pulsing that pumps blood through the body.
Each muscle consists of fibers of muscle cells surrounded by protective tissue, bundled together many more fibers, all surrounded in a thick protective tissue. A muscle uses ATP to contract and shorten, producing a force on the objects it is connected to.
Muscle movement happens when neurological signals produce electrical changes in muscle cells. During this process, calcium is released into the cells and brings about a short muscle twitch. Problems with the junction between the cells called a synapse can lead to neuromuscular diseases.
Muscle pain is a common issue that can signal numerous problems, even if it’s something as simple as overuse. Some muscular disorders and conditions that affect muscles include muscle pain, sprains and strains, bruising, cramping, myopathy, muscular dystrophy, Parkinsons disease, fibromyalgia, and multiple sclerosis.
Proper nutrition and exercise are important to keeping all muscles healthy, whether they are cardiac, smooth, or skeletal. Without muscle, humans could not live. The primary job of muscle is to move the bones of the skeleton, but muscles also enable the heart to beat and constitute the walls of other important hollow organs.