The human leg, a marvel of biological engineering, is powered by a complex network of muscles. These muscles, working in harmony, enable us to perform a wide range of movements, from walking and running to jumping and standing on our toes.
Upper Leg Muscles
The upper leg, or thigh, houses some of the body’s strongest muscles, including the quadriceps and hamstrings.
1. Quadriceps: These are the major extensors of the knee and are composed of four muscles:
– Vastus lateralis: The largest of the quadriceps, it extends from the top of the femur to the kneecap.
– Vastus medialis: A teardrop-shaped muscle of the inner thigh that attaches along the femur and down to the inner border of the kneecap.
– Vastus intermedius: Located between the vastus medialis and the vastus lateralis at the front of the femur, it is the deepest of the quadriceps muscles.
– Rectus femoris: This muscle attaches to the kneecap and has the least effect on flexion of the knee among the quadriceps muscles.
2. Hamstrings: These are three muscles at the back of the thigh that affect hip and knee movement:
– Biceps femoris: This long muscle flexes the knee. It begins in the thigh area and extends to the head of the fibula near the knee.
– Semimembranosus: This long muscle extends from the pelvis to the tibia. It extends the thigh, flexes the knee, and helps rotate the tibia.
– Semitendinosus: This muscle also extends the thigh and flexes the knee.
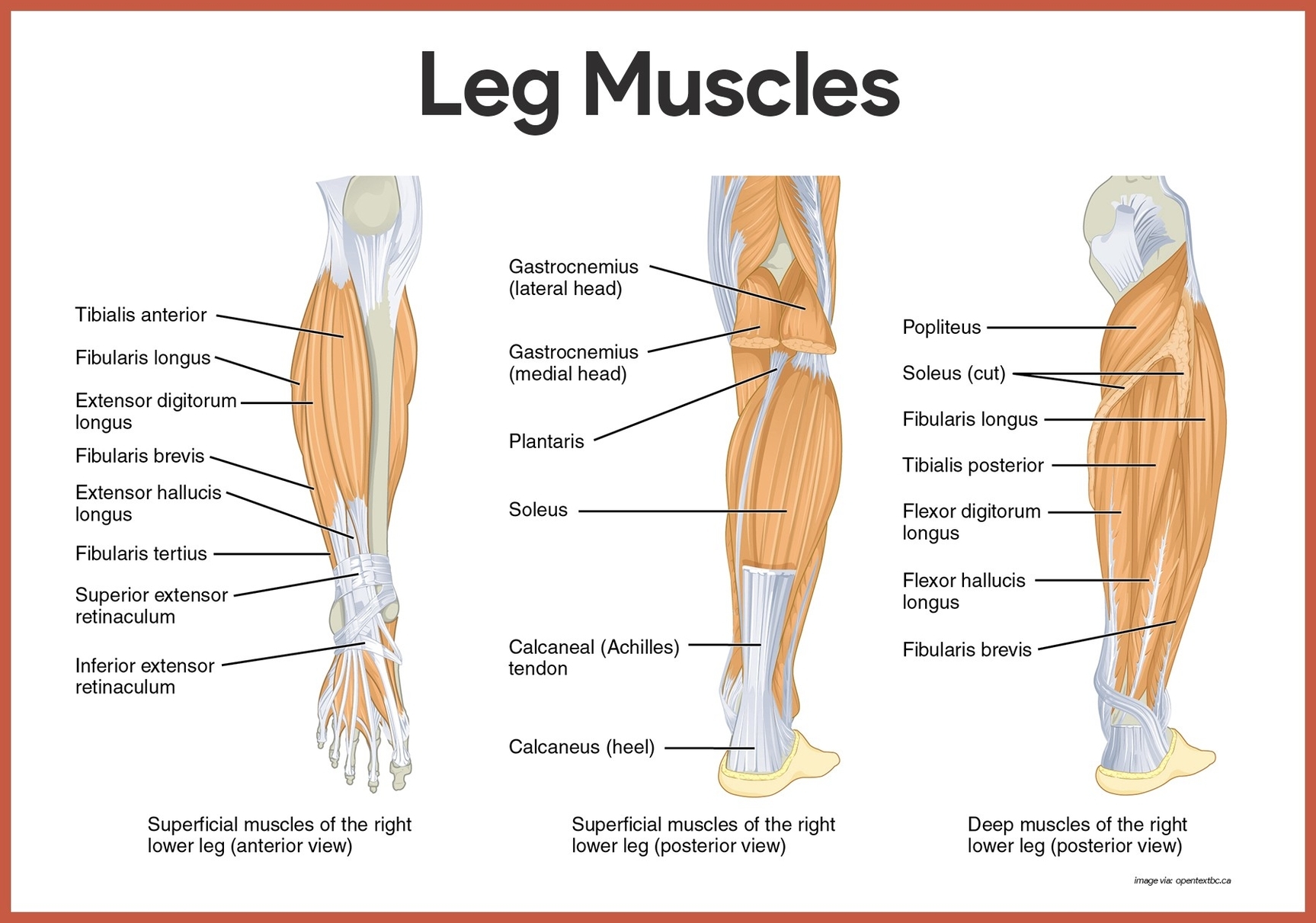
Lower Leg Muscles
The lower leg muscles, particularly the calf muscles, are pivotal to the movement of the ankle, foot, and toes.
1. Gastrocnemius (calf muscle): One of the large muscles of the leg, it connects to the heel. It flexes and extends the foot, ankle, and knee.
2. Soleus: This muscle extends from the back of the knee to the heel. It is important in walking and standing.
3. Plantaris: This small, thin muscle is absent in about 10 percent of people. The gastrocnemius muscle supersedes its function.
The Achilles tendon, which connects the plantaris, gastrocnemius, and soleus muscles to the heel bone, is possibly the most important tendon in terms of mobility. It stores the elastic energy needed for running, jumping, and other physical activity.
In conclusion, the muscles of the human leg, from the powerful quadriceps and hamstrings to the pivotal calf muscles, play a crucial role in our mobility. They not only enable a wide range of movements but also support our weight and stabilize our body, allowing us to stand up straight and maintain good posture..