The Human Digestive System
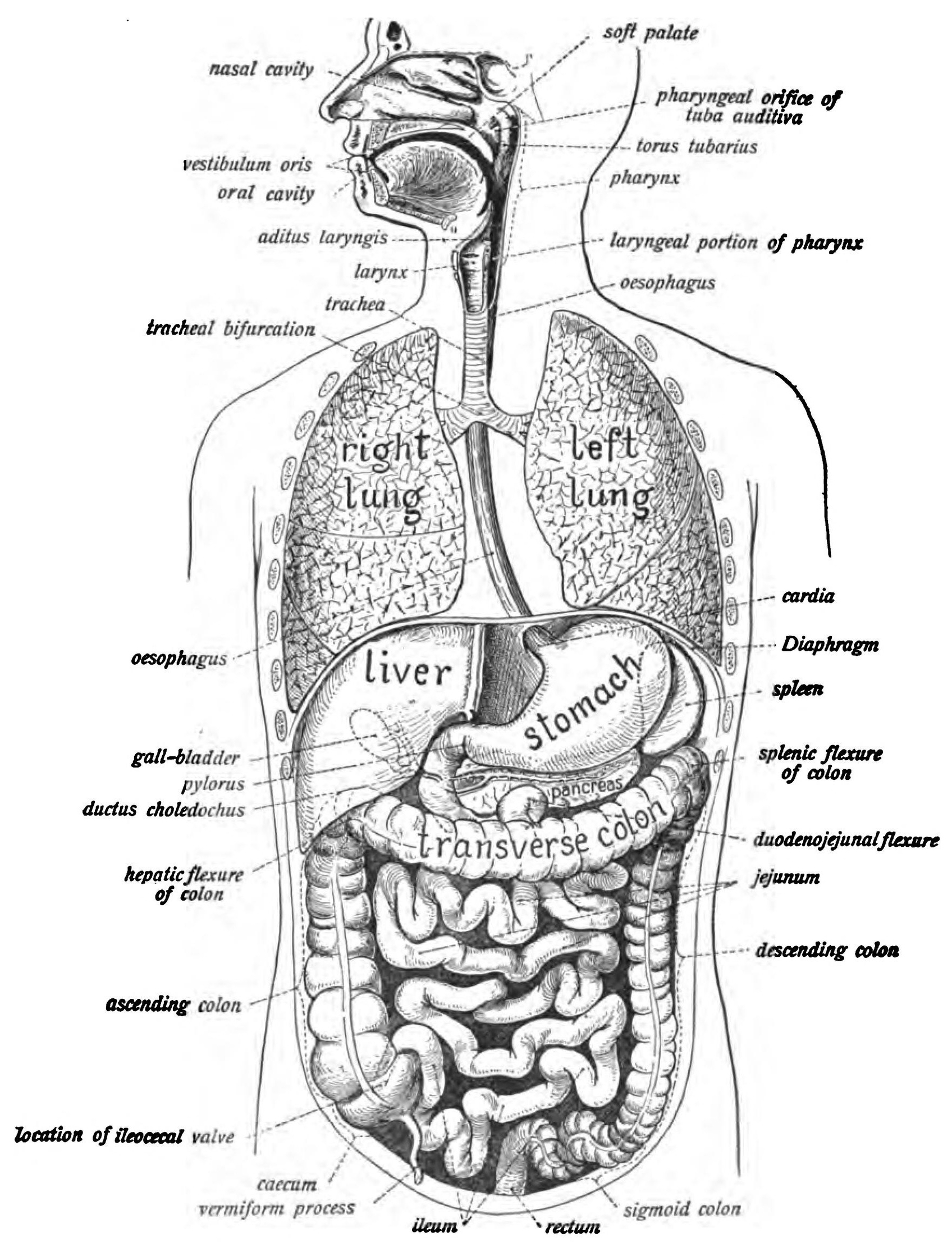
The human digestive system is a complex network of organs and structures that work together to break down food into nutrients, which the body uses for energy, growth, and cell repair. This system consists of the gastrointestinal tract and the accessory organs of digestion, including the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder.
1. Mouth and Salivary Glands
The process of digestion begins in the mouth. Here, food is broken down mechanically by chewing and chemically by digestive enzymes present in saliva. The tongue helps in kneading the food and mixing it with saliva, forming a bolus.
2. Esophagus
The bolus is then swallowed down the esophagus, a muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) to the stomach.
3. Stomach
In the stomach, the food is further broken down by mixing with gastric acid. The stomach’s muscular walls churn the food, turning it into a semi-liquid substance called chyme.
4. Small Intestine
The chyme then passes into the small intestine, which is divided into three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Here, it is mixed with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver. The small intestine is where most of the digestion and absorption of nutrients occur.
5. Large Intestine
The remaining undigested food material and water pass into the large intestine, where water and some minerals are reabsorbed into the bloodstream. The large intestine consists of the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon.
6. Rectum and Anus
The waste products of digestion, known as feces, are stored in the rectum before being eliminated from the body through the anus.
Accessory Organs
The accessory organs play a crucial role in digestion. The liver produces bile, which helps in the digestion and absorption of fats. The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile. The pancreas produces a variety of enzymes that help break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Conclusion
The human digestive system is a marvel of nature, efficiently converting the food we eat into the energy we need to live. It is a complex system that involves a range of organs working together to ensure our bodies receive the necessary nutrients for growth, energy, and repair. Understanding this system is key to maintaining good health and well-being..