The Human Brain
The human brain, the central organ of the human nervous system, is a complex structure that controls most of the body’s activities. It processes, integrates, and coordinates information received from the sense organs, and makes decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body.
Composition
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates, and salts. The brain is not a muscle but contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
tructure
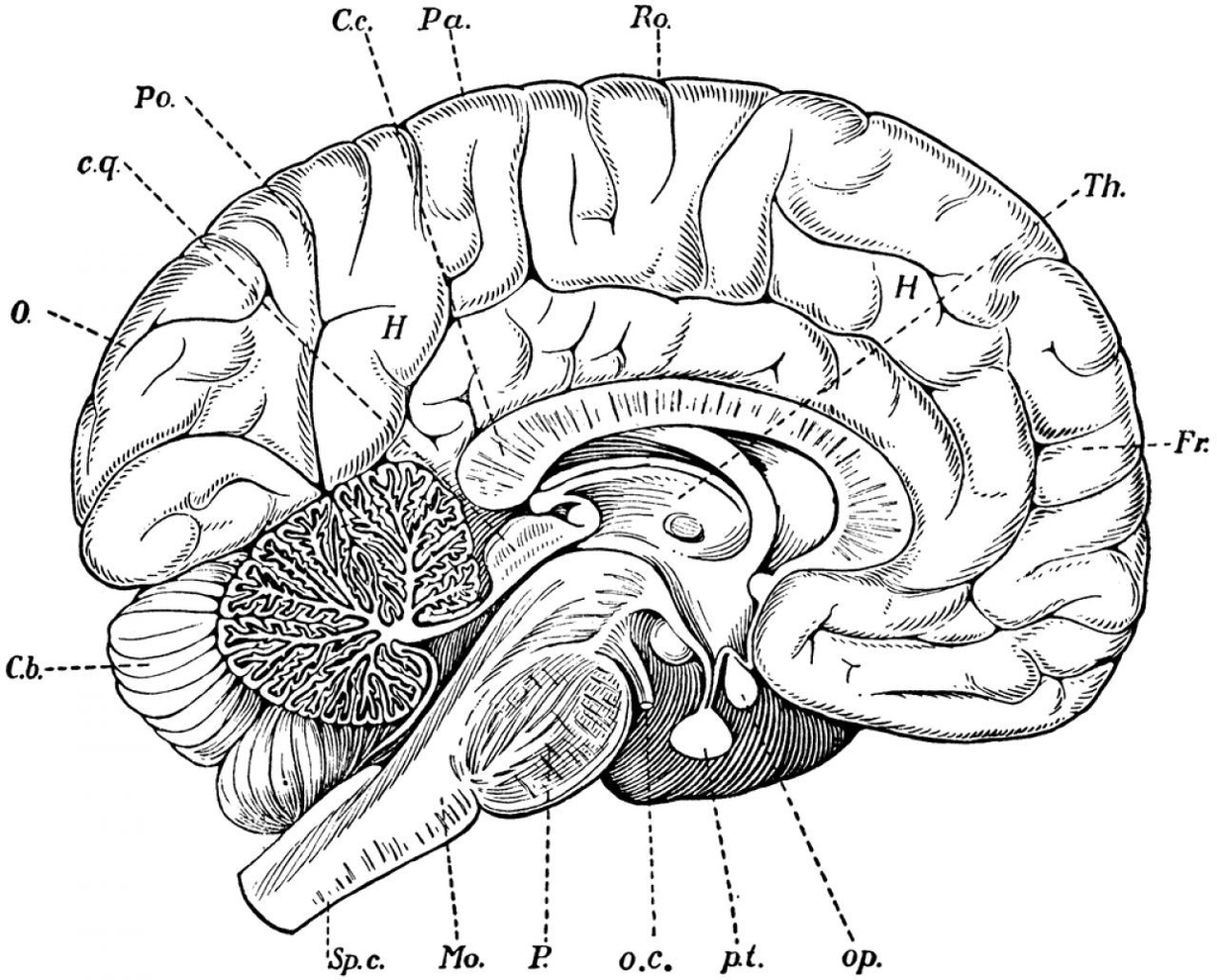
The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem, and the cerebellum. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface the cerebral cortex composed of grey matter.
Cerebral Cortex
The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four lobes the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes.
Functions
The frontal lobe is associated with executive functions including self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought, while the occipital lobe is dedicated to vision. Within each lobe, cortical areas are associated with specific functions, such as the sensory, motor, and association regions.
Hemispheres
Although the left and right hemispheres are broadly similar in shape and function, some functions are associated with one side, such as language in the left and visual-spatial ability in the right. The hemispheres are connected by commissural nerve tracts, the largest being the corpus callosum.
Brainstem and Cerebellum
The cerebrum is connected by the brainstem to the spinal cord. The brainstem consists of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The cerebellum is connected to the brainstem by three pairs of nerve tracts called cerebellar peduncles.
Other Structures
Underneath the cerebral cortex are several important structures, including the thalamus, the epithalamus, the pineal gland, the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, and the subthalamus; the limbic structures, including the amygdalae and the hippocampi, the claustrum, the various nuclei of the basal ganglia, the basal forebrain structures, and the three circumventricular organs.
Conclusion
The human brain, with its intricate structure and complex functions, is a marvel of nature. It is the command center for the human nervous system, receiving signals from the body’s sensory organs and outputting information to the muscles. Its study continues to be a fascinating field, offering insights into our behavior, cognition, and the very essence of what makes us human..