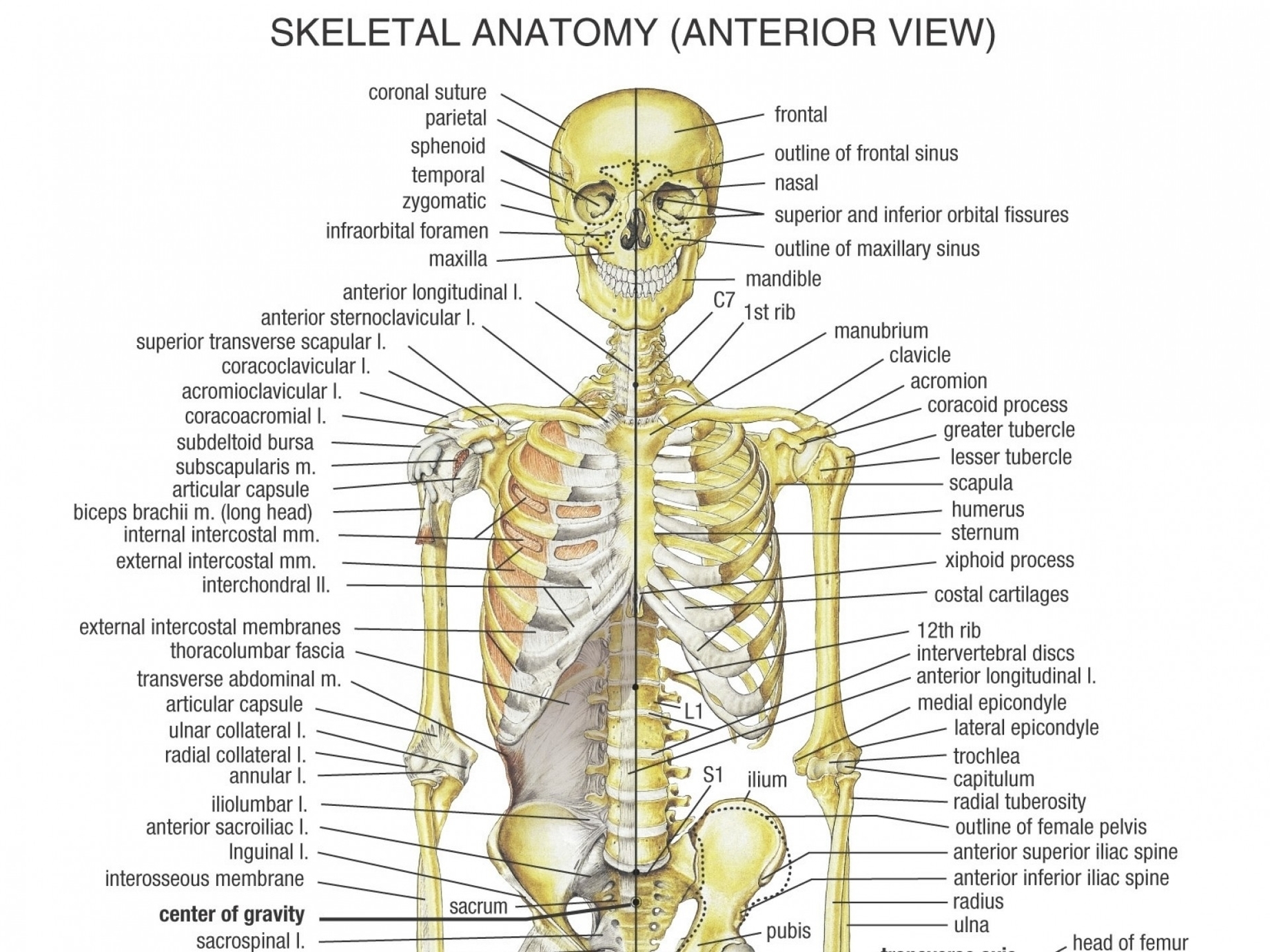
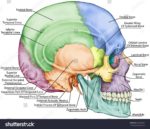
Human Bone Structure
The human bone structure, also known as the skeleton, serves as the framework for the body. It consists of many individual bones and cartilages, along with bands of fibrous connective tissue, including ligaments and tendons.
ubdivisions of the Skeleton
The human skeleton consists of two principal subdivisions:
1. Axial Skeleton: Comprises the vertebral column (the spine) and much of the skull.
2. Appendicular Skeleton: Includes the pelvic (hip) and pectoral (shoulder) girdles, and the bones and cartilages of the limbs.
Bone Tissue
Bone tissue, or osseous tissue, is a type of connective tissue consisting mainly of a collagen matrix that is mineralized with calcium and phosphorus crystals. This combination of flexible collagen and hard mineral crystals makes bone tissue hard, without making it brittle.
Gross Anatomy of Bones
A typical long bone has two main regions: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the hollow, tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The outer walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone. The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis, which is filled internally with spongy bone. Red bone marrow fills the spaces between the spongy bone in some long bones.
Compact and Spongy Bone
Compact bone is dense and forms the outer shell of the bone, while spongy bone is less dense and found inside the bone, providing a support structure for the marrow.
Periosteum and Endosteum
The periosteum forms the outer surface of bone, and the endosteum lines the medullary cavity. The periosteum contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels that nourish compact bone. Tendons and ligaments attach to bones at the periosteum.
Functions of the Skeleton
The functions of the skeleton are of three different types: support, protection, and motion. The vertebral column, corresponding to the notochord in lower organisms, is the main support of the trunk. The central nervous system lies largely within the axial skeleton, the brain being well protected by the cranium and the spinal cord by the vertebral column.
In conclusion, the human bone structure is a complex and dynamic system that not only provides support, protection, and facilitates movement, but also plays a crucial role in the production of blood cells and the storage of essential minerals..