The human body is a complex and intricate system, composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues, subsequently forming organs and organ systems. These systems work together to ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
1. Head and Neck: The head houses the brain, the control center of the body, along with sensory organs like the eyes and ears. The neck supports the head and contains the pathway for food and air.
2. Hair: Hair, made of a protein called keratin, serves various functions such as protection, regulation of body temperature, and facilitation of evaporation of perspiration.
3. Torso: The torso, which includes the thorax and abdomen, contains vital organs. The thorax houses the heart and lungs, while the abdomen contains the digestive and reproductive organs.
4. Arms and Hands: Arms and hands are essential for physical manipulation. They allow us to interact with our environment, perform tasks, and express ourselves.
5. Legs and Feet: Legs and feet provide mobility and balance. They support the body’s weight and enable movement.
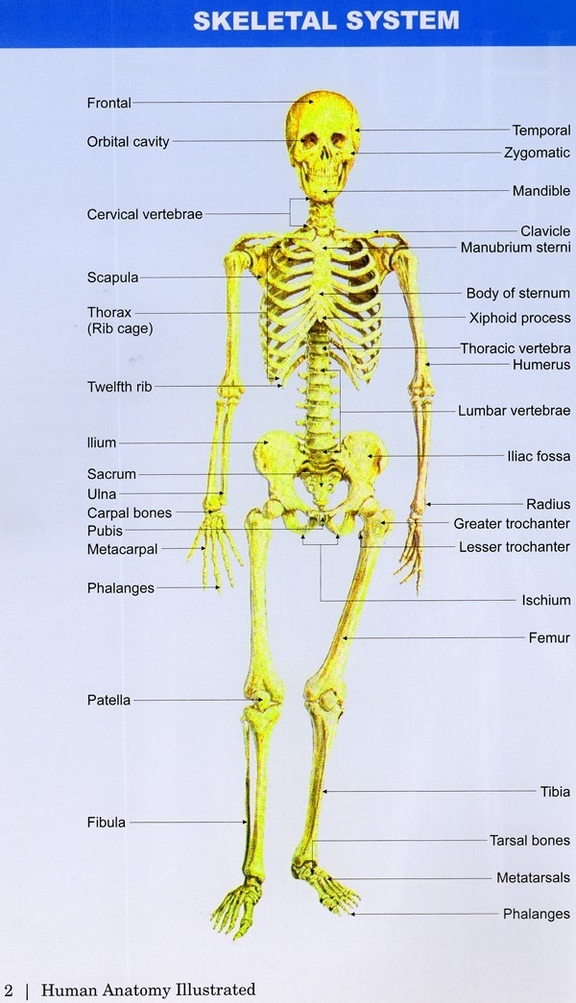
6. Skeletal System: Giving the body its shape is the skeleton, composed of cartilage and bone. It provides structure, protects internal organs, and facilitates movement.
7. Muscular System: Muscles, attached to bones by tendons, allow for a wide range of motion and flexibility. They also generate heat to maintain body temperature.
8. Cardiovascular System: This system, comprising the heart and blood vessels, circulates blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells.
9. Respiratory System: The respiratory system, including the lungs, exchanges gases. It takes in oxygen from the environment and expels carbon dioxide.
10. Digestive System: The digestive system breaks down food into nutrients, which are then absorbed into the body for energy, growth, and cell repair.
11. Nervous System: The nervous system, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, controls and coordinates the body’s activities.
12. Endocrine System: The endocrine system, made up of glands that produce hormones, regulates metabolism, growth, development, and body functions.
13. Reproductive System: The reproductive system allows for the production of offspring. It includes organs such as the ovaries in females and testes in males.
In conclusion, the human body is a marvel of biological engineering, with each part playing a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and function of the organism. Understanding the human body and its parts can provide valuable insights into human health and disease.