The Coronary Sinus: An Overview
The coronary sinus (CS) is a significant component of the heart’s circulatory system. It is the largest vein of the heart, responsible for draining over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. The CS plays a crucial role in life-saving heart treatments.
Anatomy and Location
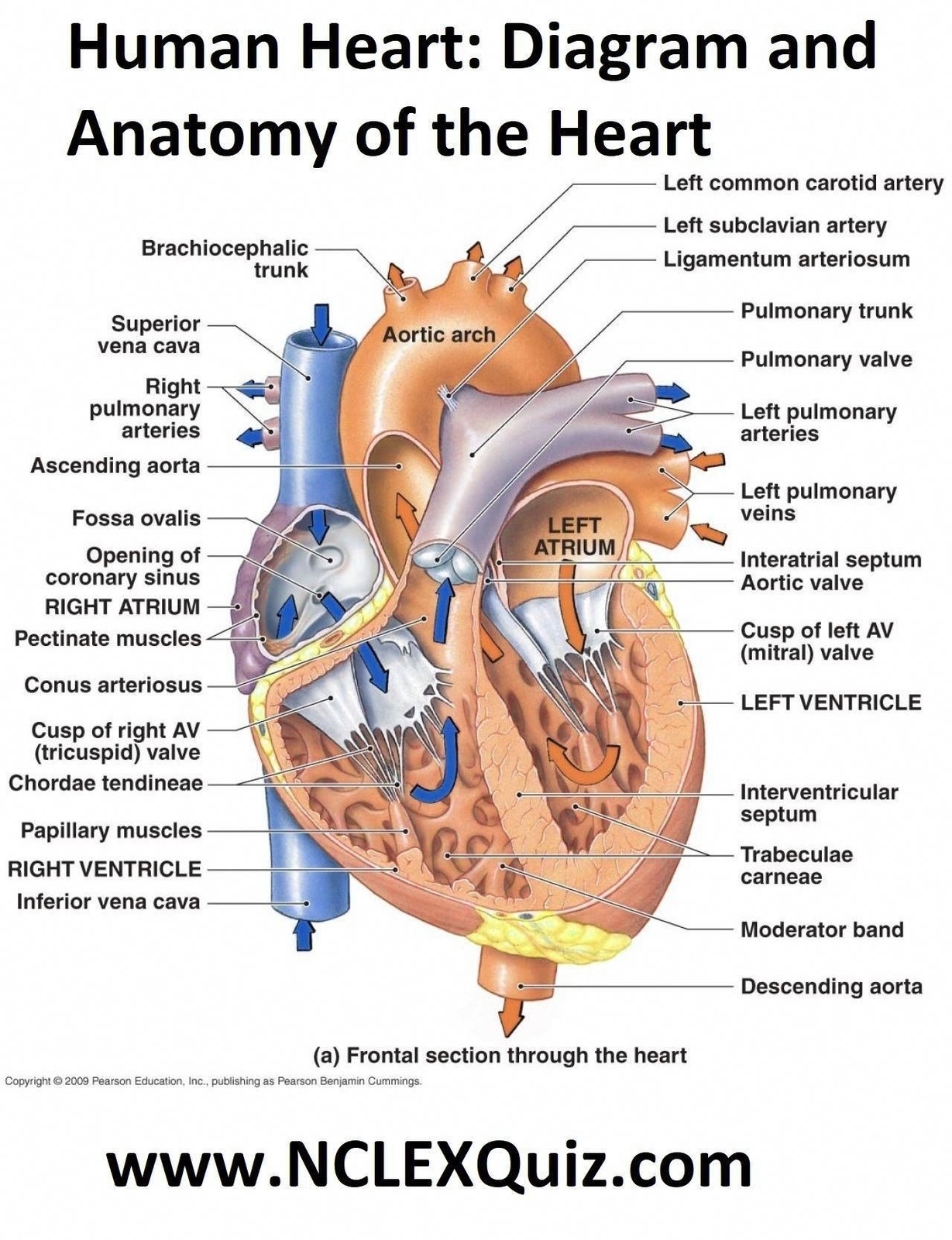
The CS is a large coronary vein that measures between 35 centimeters in length and 12 cm in diameter. It is located towards the posterior, or rear, of the heart, between the left atrium and the left ventricle. The starting point of the CS is often described as where the great cardiac vein and the oblique vein of the left atrium meet. The large blood vessel then continues between the left atrium and left ventricle, running along the interventricular groove, and finally empties into the right atrium.
Function
The primary function of the CS is to drain deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. This blood comes from most of the blood vessels of the heart muscle and wall. The CS is responsible for returning approximately 55% of the hearts deoxygenated blood supply into the right atrium.
Tributaries
Many tributaries, or smaller veins, feed into and form the CS, though the exact anatomy may differ among individuals. Some veins that may feed into and form the CS include the great cardiac vein, oblique vein of the left atrium, posterior vein of the left ventricle, middle cardiac vein, and small cardiac vein.
Anatomical Variations
There are many different anatomical variations of the CS ranging from size, the number of smaller veins that connect to it, and the shape, or form, of the valves that surround it. Most anatomical variations are harmless, although some may present clinical implications for cardiac procedures.
Clinical Significance
The anatomical location of the CS often serves as a landmark for surgeons when performing cardiac surgery. The presence of irregular valves in the CS may hinder some cardiac intervention techniques.
Conclusion
The coronary sinus is a vital part of the heart’s circulatory system. Its primary function is to drain deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. Understanding its anatomy, function, and clinical significance is crucial in the field of cardiology and cardiac surgery..