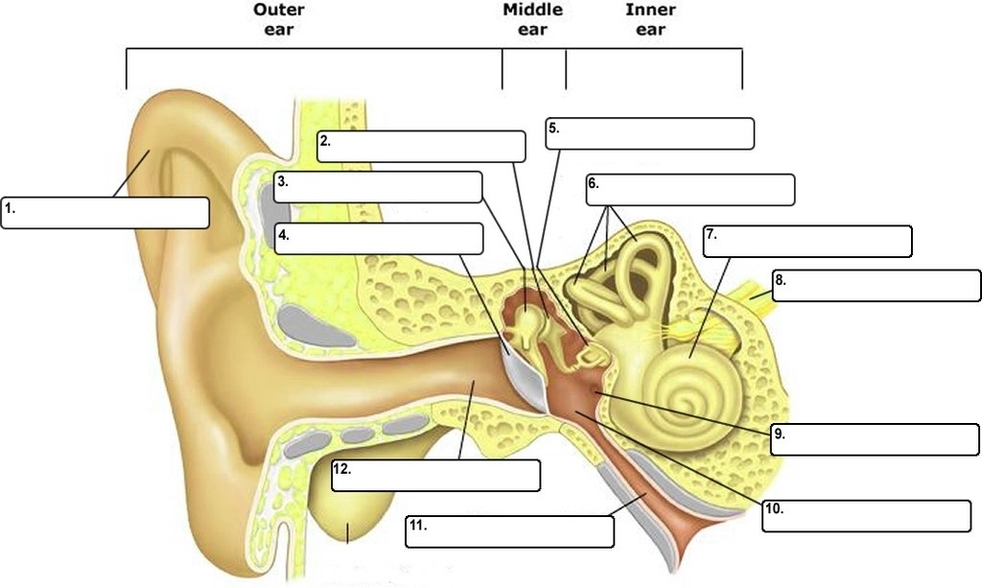
The human ear is a complex organ that serves two main functions: hearing and maintaining balance. Here are some key parts of the ear and their functions according to Quizlet:
1. Pinna: Also known as the auricle or outer ear, it’s the shell-shaped part surrounding the auditory canal.
2. Ceruminous Glands: These glands in the outer ear secrete a waxy yellow substance known as cerumen or earwax.
3. External Acoustic Meatus: Also known as the auditory tube, it’s a short narrow chamber carved into the temporal bone of the skull.
4. Tympanic Membrane: Also known as the eardrum, it’s a small, thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves hit it.
5. Tympanic Cavity: A small air-filled cavity within the temporal bone, flanked laterally by the eardrum.
6. Ossicles: These are three small bones located in the middle ear that transmit the vibratory motion of the eardrum. They include:
– Malleus (Hammer): One of the ossicles which increase or decrease vibrations from the eardrum.
– Incus (Anvil): Another ossicle which also helps in increasing or decreasing vibrations from the eardrum.
– Stapes (Stirrup): The last ossicle which presses on the oval window of the inner ear, setting the fluids of the inner ear into motion.
7. Pharyngotympanic Tube: Also known as the auditory tube, it links the nasopharynx to the middle ear.
8. Cochlea: A snail-shaped chamber within the inner ear, it changes the vibrations from the bones into electrical signals.
9. Vestibulocochlear Nerve: This is how the brain gets electrical messages from the inner ear.
10. Semicircular Canals: These are responsible for keeping you upright and maintaining balance.
11. Vestibule: The central part of the osseous labyrinth, situated medial to the tympanic cavity, behind the cochlea, and in front of the semicircular canals.
12. Osseous Labyrinth: A set of three parts in the ear (Cochlea, Vestibule, Semicircular Canals) filled with a bodily fluid called perilymph.
These components work together to convert sound waves into electrical signals that the brain can interpret as sound. Additionally, the ear plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and spatial orientation. Understanding the anatomy of the ear can provide insights into how hearing loss or balance disorders may occur..