Anticoagulant Drugs
Anticoagulant drugs, commonly known as blood thinners, are a class of medications that increase the time it takes for blood to clot. They work by preventing blood from coagulating to form a clot in vital organs such as the heart, lungs, and brain.
Uses of Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants are used to treat and prevent blood clots, reducing the risk of life-threatening conditions such as heart attack, stroke, and pulmonary embolism. They are often prescribed for conditions where the risk of blood clots is increased, such as:
– Atrial fibrillation
– Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
– Hip or knee replacement surgery
– Ischemic stroke
– Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
– Pulmonary embolism
– Unstable angina
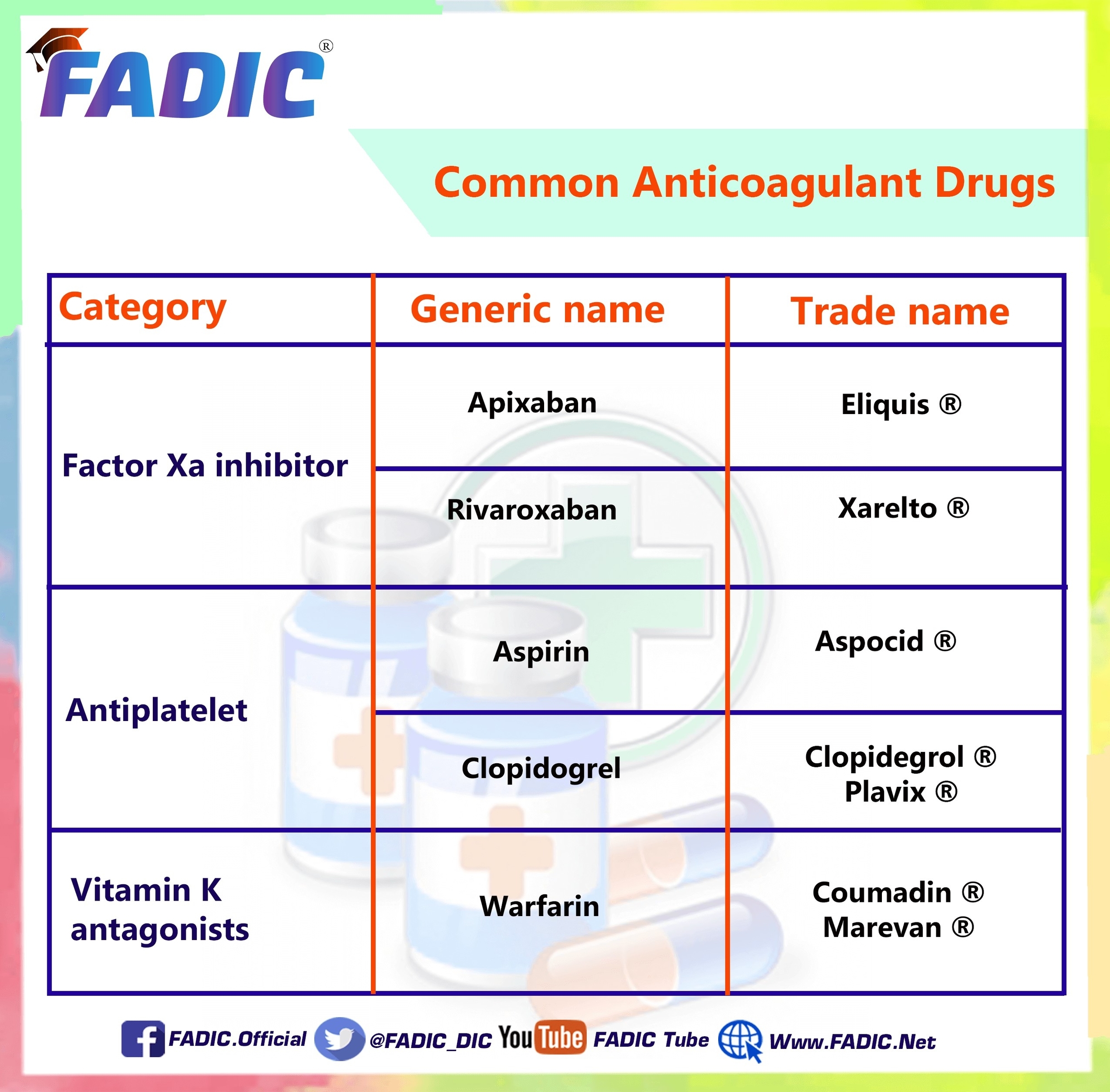
Types of Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants can be divided into four main groups: coumarins and indandiones, factor Xa inhibitors, heparins, and direct thrombin inhibitors.
1. Coumarins and Indandiones: Warfarin is a coumarin and the only one available in the U.S for human use. It works by limiting the availability of vitamin K, a vitamin necessary for the blood coagulation pathway to produce clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X.
2. Factor Xa Inhibitors: These work on factor Xa in the coagulation cascade, which is responsible for converting the protein prothrombin into thrombin. Factor Xa inhibitors can affect factor Xa within the blood and also within a pre-existing clot.
3. Heparins: The heparins are a group of anticoagulants that consist of unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparins, and heparinoids.
4. Direct Thrombin Inhibitors: These drugs directly inhibit thrombin, an enzyme that plays a central role in the process of blood clot formation.
ide Effects of Anticoagulants
The most common side effect of anticoagulant treatment is bleeding. Other side effects may include abdominal pain, flatulence (intestinal gas), headache, lethargy, dizziness, fever, local injection site reactions, and nausea.
Conclusion
Anticoagulant drugs play a crucial role in the prevention and treatment of conditions associated with blood clots. However, like all medications, they must be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider due to their potential side effects and interactions with other drugs. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized medical advice..