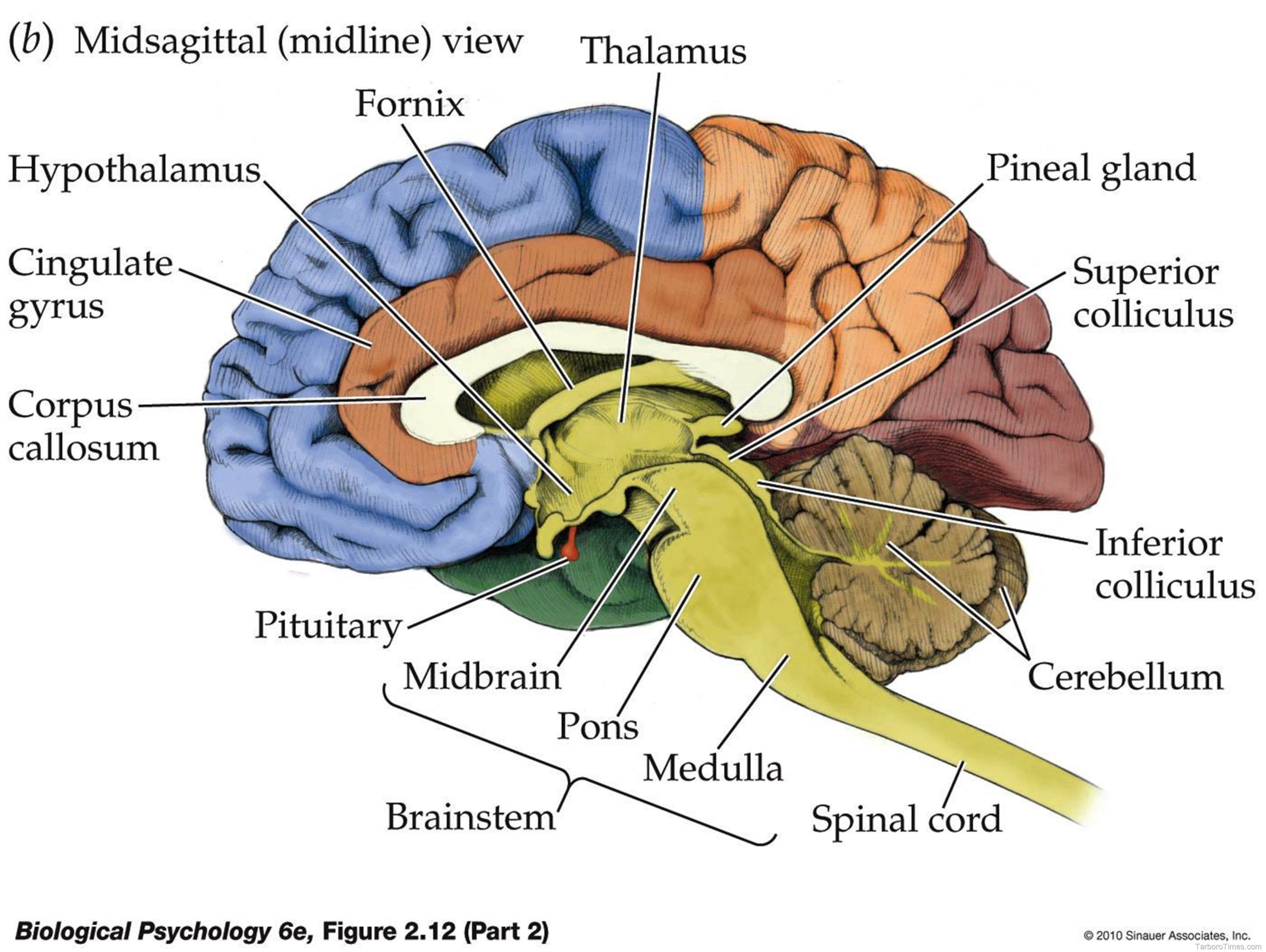
The human skeleton, an intricate framework of bones and cartilage, provides essential support, protection, and mobility for our bodies. Comprising 206 bones in adults, the skeleton is a remarkable system that plays a crucial role in maintaining our physical form and enabling various functions.
## 1. Structure and Composition:
– The human skeleton consists of two main divisions: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
– Axial Skeleton:
– Forms the central axis of the body.
– Includes the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage.
– The skull comprises the cranium (protecting the brain) and the facial bones.
– The vertebral column (or spine) consists of 33 vertebrae, providing flexibility and support.
– The rib cage safeguards vital organs like the heart and lungs.
– Appendicular Skeleton:
– Attaches to the axial skeleton.
– Includes the limbs, shoulder girdle, and pelvic girdle.
– The shoulder girdle connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton.
– The pelvic girdle supports the lower limbs and protects reproductive organs.
## 2. Bone Types:
– Bones are classified into five types based on shape and function:
1. Long Bones:
– Longer than they are wide.
– Examples: femur (thigh bone), humerus (upper arm bone).
2. Short Bones:
– Cube-shaped.
– Provide stability and support.
– Examples: carpals (wrist bones), tarsals (ankle bones).
3. Flat Bones:
– Thin and flat.
– Protect internal organs and provide attachment points.
– Examples: scapula (shoulder blade), sternum (breastbone).
4. Irregular Bones:
– Complex shapes.
– Serve specific functions.
– Examples: vertebrae, facial bones.
5. Sesamoid Bones:
– Develop within tendons.
– Reduce friction and enhance mechanical advantage.
– Example: patella (kneecap).
## 3. Bone Tissue:
– Bones consist of compact bone (dense and strong) and spongy bone (trabecular bone with a porous structure).
– Osteocytes, embedded in the bone matrix, maintain bone health.
– Haversian canals contain blood vessels and nerves, ensuring nutrient supply.
## 4. Joints:
– Joints connect bones and allow movement.
– Types of joints:
– Fibrous Joints: Immovable (e.g., sutures in the skull).
– Cartilaginous Joints: Slightly movable (e.g., intervertebral discs).
– Synovial Joints: Freely movable (e.g., ball-and-socket, hinge joints).
– Examples: shoulder joint, hip joint, knee joint.
## 5. Bone Development and Growth:
– Ossification:
– Process of bone formation.
– Intramembranous ossification: Forms flat bones directly from mesenchymal tissue.
– Endochondral ossification: Converts cartilage into bone (long bones).
– Bone Remodeling:
– Ongoing process of resorption and deposition.
– Maintains bone strength and adapts to stress.
## 6. Common Bones:
– Skull Bones:
– Cranium (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid).
– Facial bones (maxilla, mandible, zygomatic, nasal, etc.).
– Vertebral Column:
– Cervical (neck), thoracic (mid-back), lumbar (lower back), sacral, and coccygeal vertebrae.
– Upper Limb Bones:
– Humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges.
– Lower Limb Bones:
– Femur, tibia, fibula, patella, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges.
## 7. Clinical Significance:
– Osteoporosis: Bone density loss.
– Fractures: Breaks in bones.
– Arthritis: Joint inflammation.
– Scoliosis: Abnormal spinal curvature.
In summary, the human skeleton is a marvel of engineering, providing both strength and flexibility. Its intricate design ensures our survival, movement, and protection throughout life..