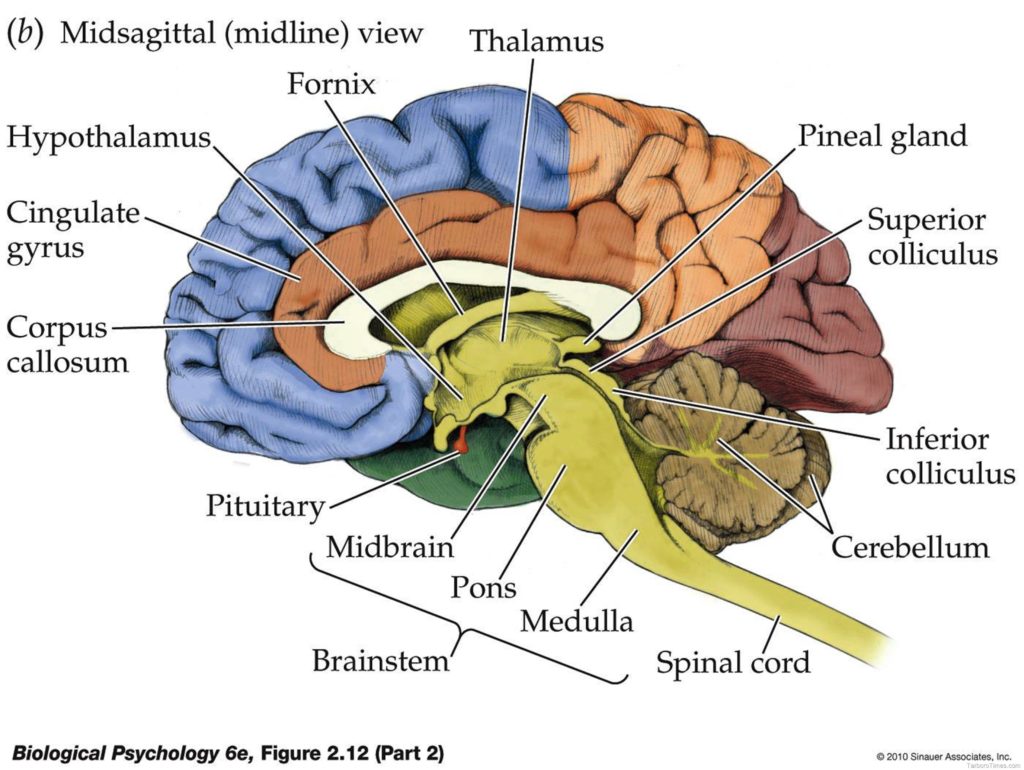
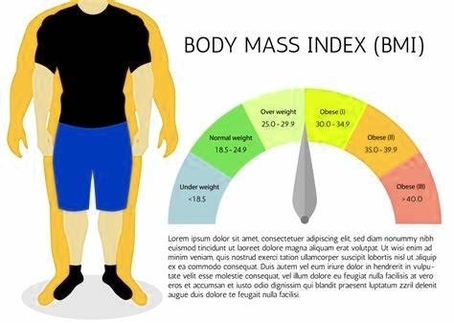
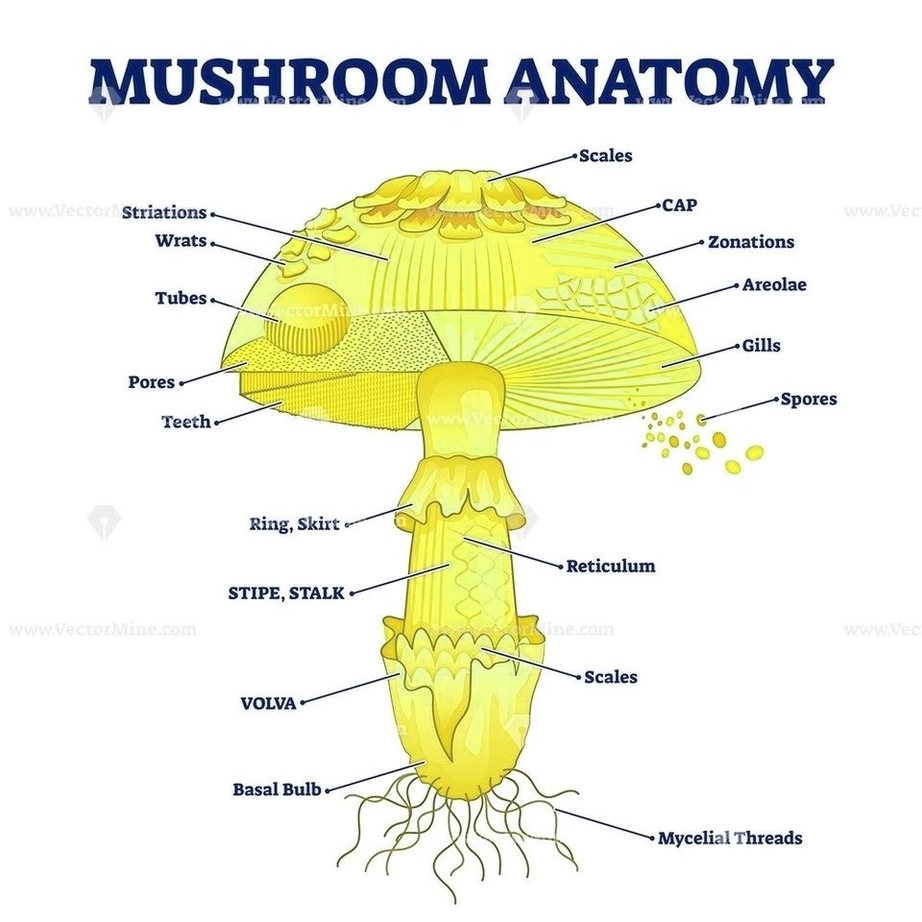
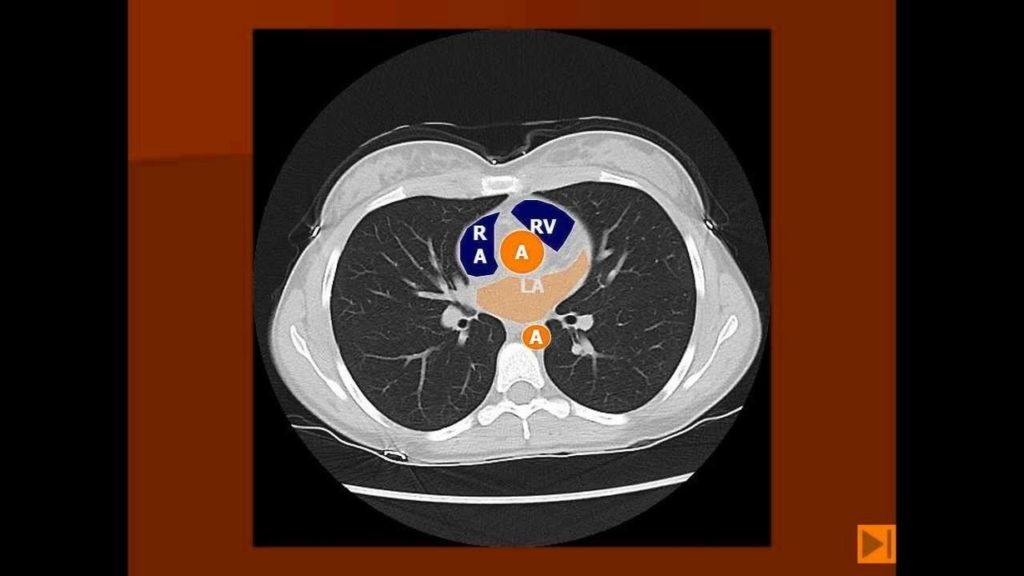
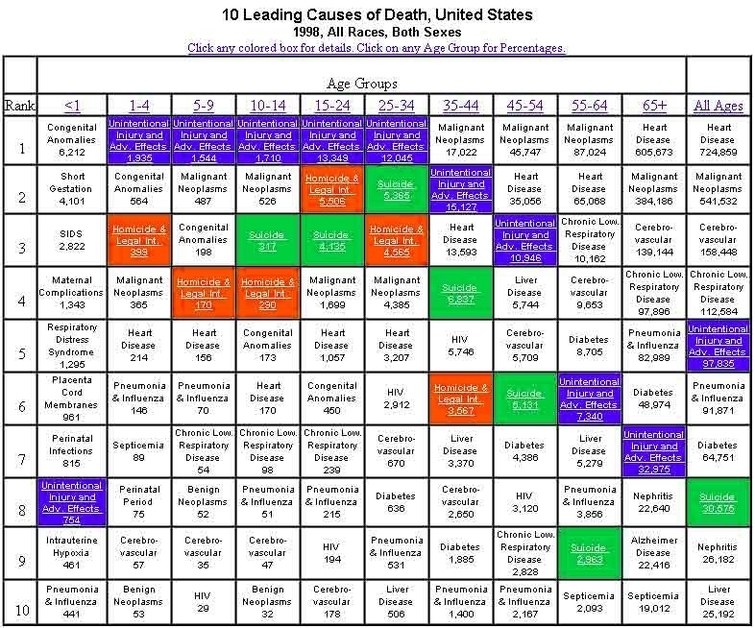
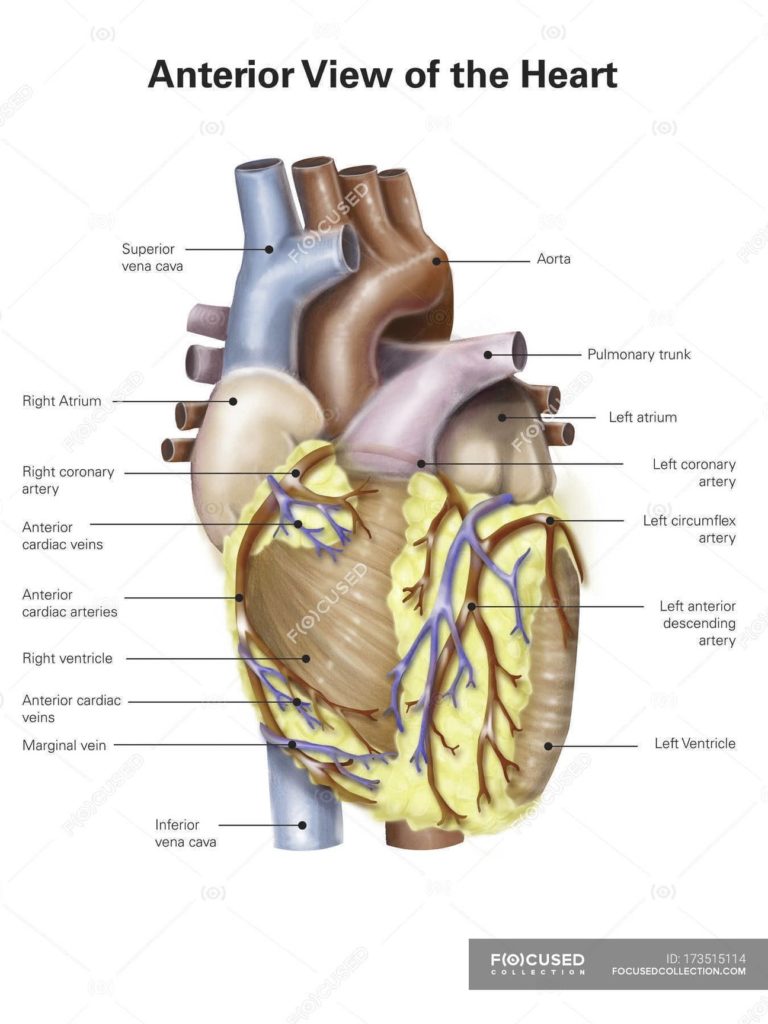
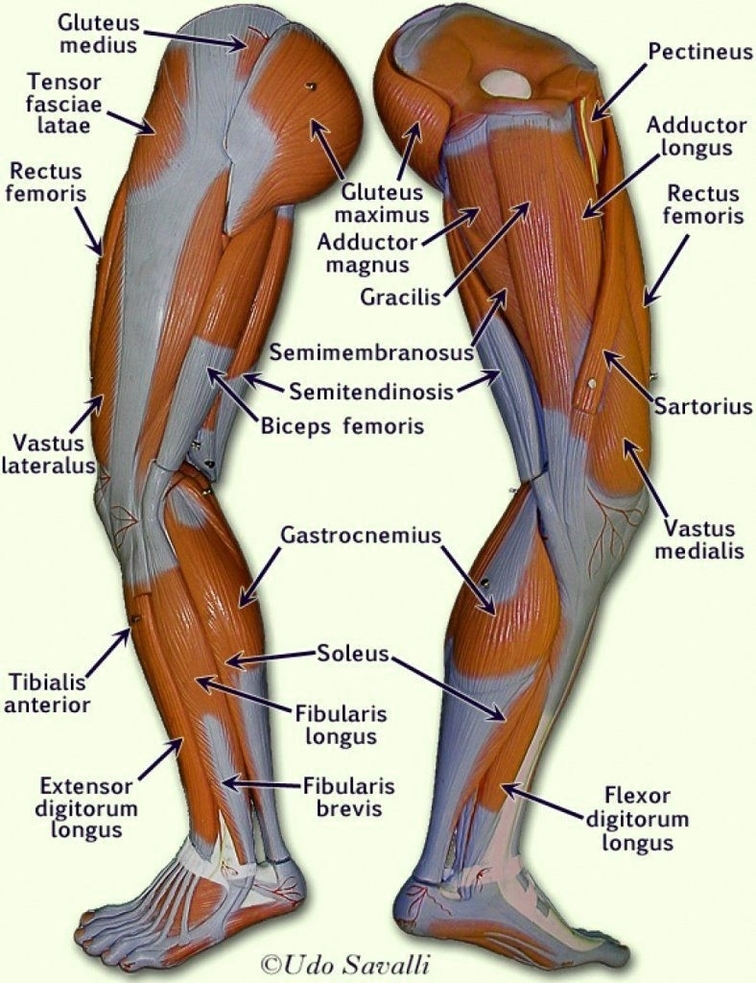
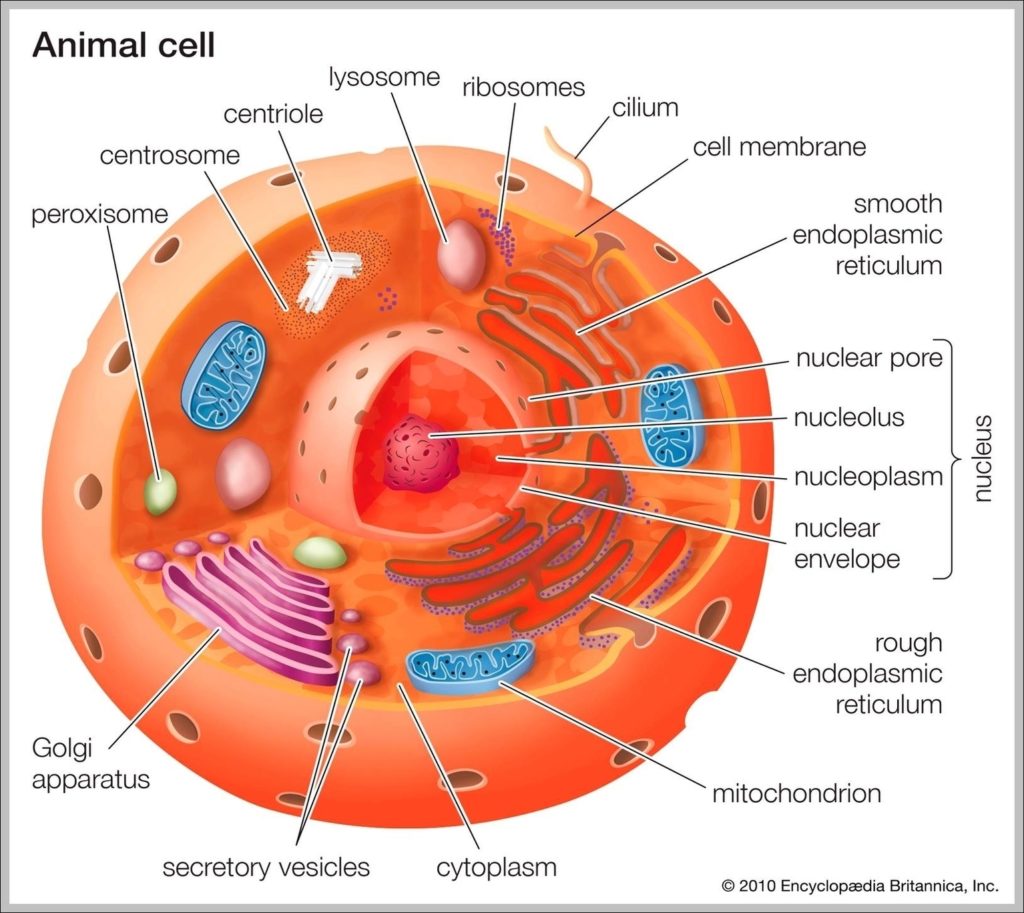
Posted inDiagrams
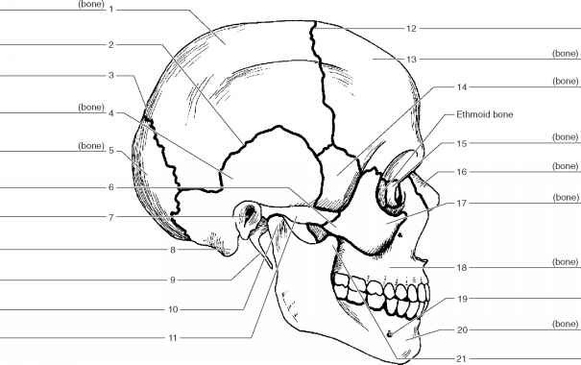
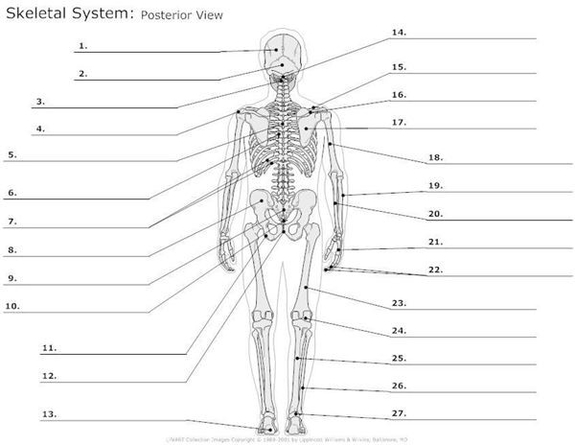
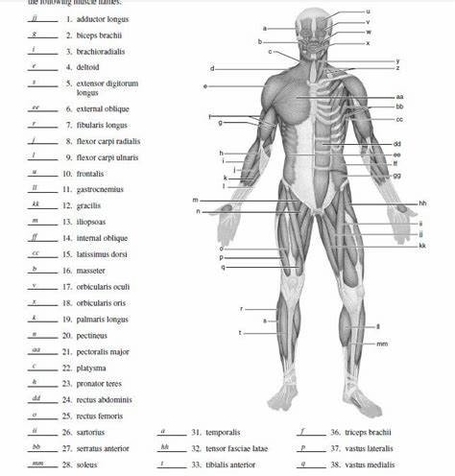
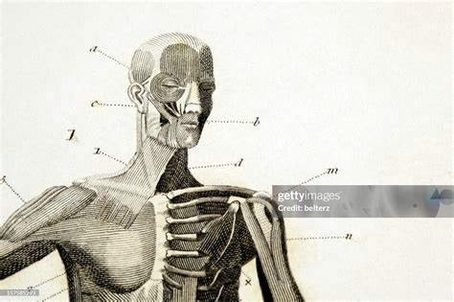
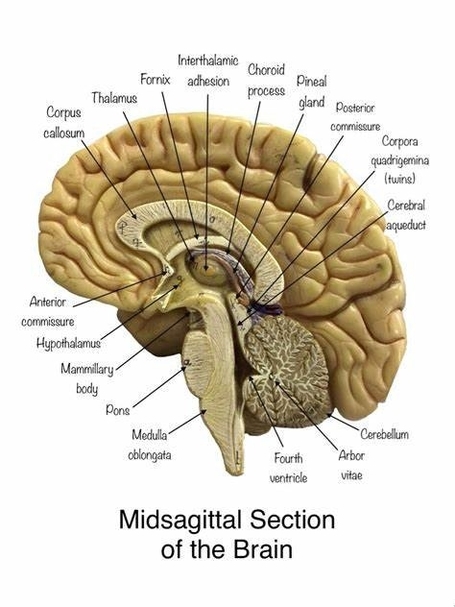
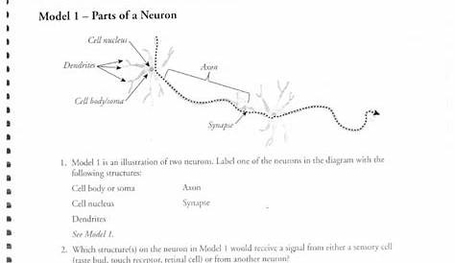
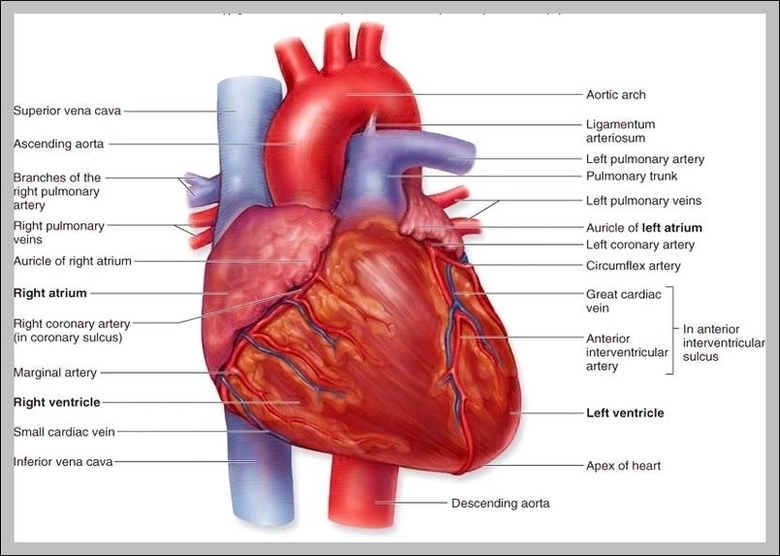
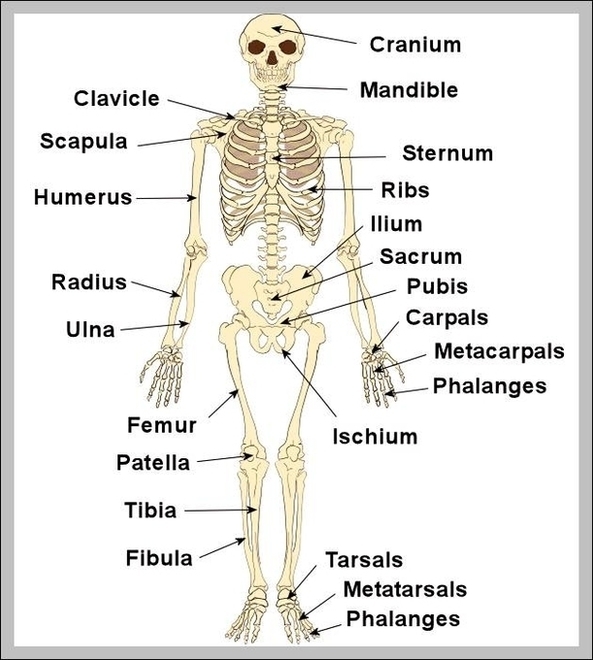
A Skeleton With Labelshuman Skeleton Diagram With Labels Example Of
The human skeleton, an intricate internal framework, serves as the architectural basis for our bodies. Comprising numerous individual bones and cartilages, it provides support, protection, and facilitates movement. Let's delve…