The Inner Ear
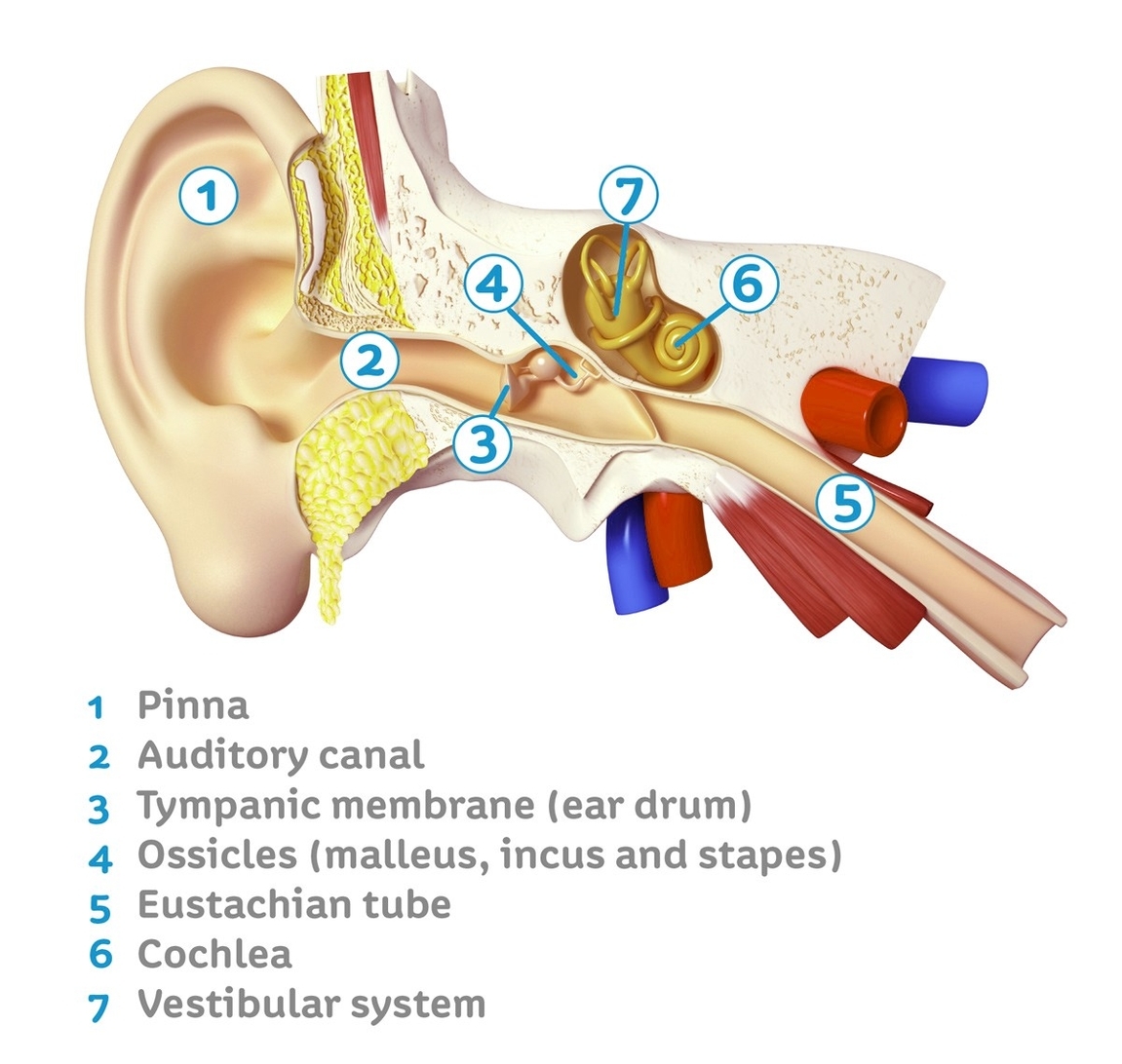
The inner ear, also known as the labyrinth, is the deepest part of the ear. It is located at the end of the ear canals, resting in a cavity in the temporal bone. The inner ear plays a crucial role in our ability to hear and maintain balance.
Anatomy
The inner ear consists of three main parts:
1. Cochlea: The cochlea is the auditory area of the inner ear that changes sound waves into nerve signals. It is shaped like a snail’s shell and filled with fluid. Inside the cochlea is a smaller, sensitive structure called the organ of Corti, which acts like the body’s “microphone.” It contains four rows of tiny hairs that pick up the vibrations from the sound waves.
2. Semicircular Canals: These canals sense balance and posture to assist in equilibrium. They are filled with liquid and lined with fine hairs, just like in the cochlea, except these hairs pick up body movements instead of sounds.
3. Vestibule: This is the area of the inner ear cavity that lies between the cochlea and semicircular canals, also assisting in equilibrium.
Function
The inner ear has two main functions: hearing and balance.
*Hearing*: The cochlea works with parts of the outer and middle ear to help you hear sounds. The cochlea is filled with liquid and contains the organ of Corti. This structure acts like the body’s “microphone.” It contains four rows of tiny hairs that pick up the vibrations from the sound waves. These hairs convert the movement from sound waves into electrical signals, which are sent to the brain through the hearing (auditory) nerves.
*Balance*: The balance parts of the inner ear are the vestibule and the semicircular canals. The three semicircular canals are loop-shaped tubes in the inner ear. They’re filled with liquid and lined with fine hairs, just like in the cochlea, except these hairs pick up body movements instead of sounds. The hairs act like sensors that help you with your balance.
Health Conditions
everal conditions can impact the inner ear and result in hearing loss and balance issues. Problems with this part of the ear can result in hearing loss and balance issues. Inner ear problems are one of the primary causes of vertigo.
In conclusion, the inner ear is a complex and vital part of our auditory and balance systems. Its intricate structure and function allow us to perceive and interact with our environment in a coordinated and meaningful way..