The Human Body Skeletal System
The human skeletal system is a complex structure that serves as the body’s support framework. It consists of bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, all of which work together to provide support, protection, and movement.
Composition
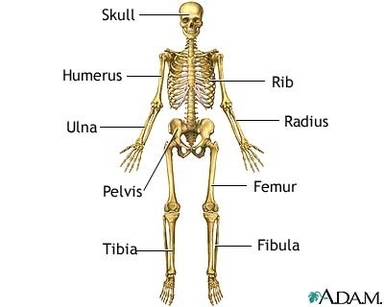
The human skeletal system consists of 206 bones in adults. Children’s skeletons contain more bones, which fuse together as they grow up. The skeletal system can be divided into two main parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
1. Axial Skeleton: The axial skeleton consists of 80 bones, forming the vertical axis of the body. It includes the bones of the head, neck, chest, and spine. The skull comprises 22 bones, further classified into cranial bones (8) and facial bones (14). The vertebral column is made up of 26 bones, including the cervical vertebrae (7), thoracic vertebrae (12), lumbar vertebrae (5), sacrum, and coccyx. The thoracic cage, composed of the sternum and 12 pairs of ribs, protects the organs of the upper torso.
2. Appendicular Skeleton: The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones. It includes the bones that make up the arms and legs, as well as the bones that attach them to the axial skeleton.
Functions
The skeletal system performs several crucial functions:
1. Support: The skeletal system provides the structural framework for the human body, giving it shape. The vertebral column, corresponding to the notochord in lower organisms, is the main support of the trunk.
2. Protection: The skeletal system protects our vital organs. The brain is well protected by the cranium, and the spinal cord by the vertebral column. The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs.
3. Movement: The skeletal system, in conjunction with the muscular system, facilitates body movement.
4. Blood Cell Production: The skeletal system is responsible for the production of blood cells.
5. Mineral Storage: The skeletal system stores minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus.
Differences in Male and Female Skeletons
The male skeleton is usually longer and has a higher bone mass, while the female skeleton has a broader pelvis to accommodate for pregnancy and childbirth.
Conclusion
The human skeletal system is a marvel of biological engineering. Its intricate design and multifunctionality enable us to perform a wide range of activities, from simple movements to complex athletic feats. Understanding its structure and functions can provide valuable insights into human health and physiology.