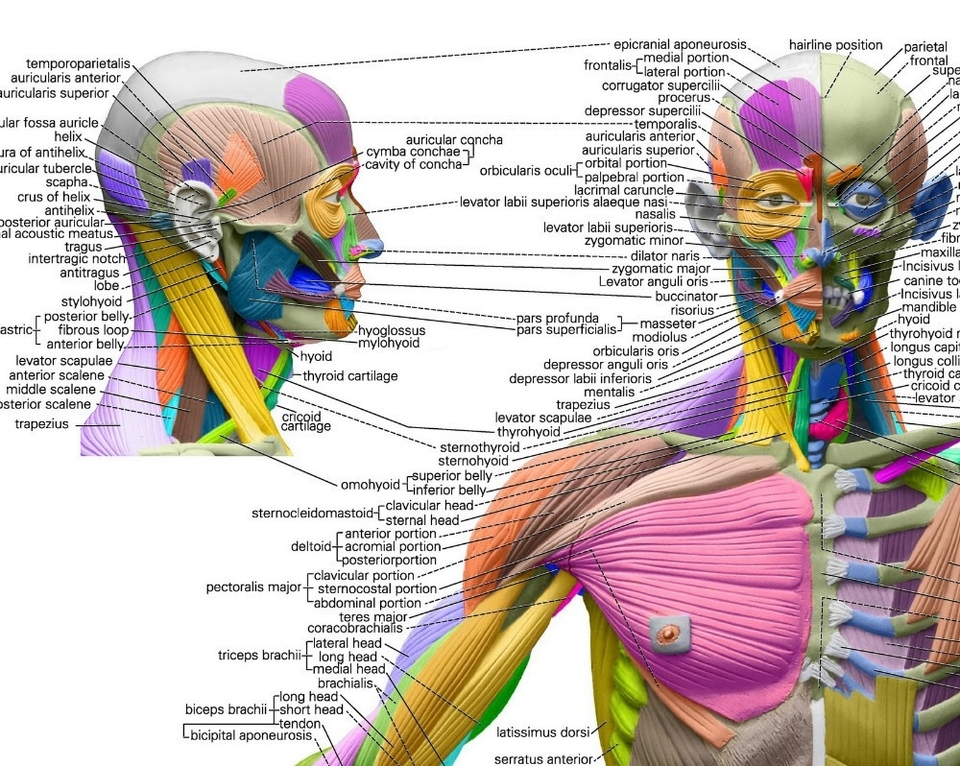
The Human Anatomical Muscular System
The human anatomical muscular system is a complex network of muscles that enables movement, stability, and support. It is an organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. This system permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates blood throughout the body.
Types of Muscles
1. Skeletal Muscles: These muscles are attached to the bones by tendons and are under voluntary control. They work together to move the skeleton when the nervous system signals the muscle to contract. There are more than 600 skeletal muscles, making up about 40 percent of a persons body weight.
2. Cardiac Muscles: This type of muscle makes up the mass of the heart and is responsible for the rhythmic contractions of that vital pumping organ. It is under involuntary control and creates the electrical impulses that produce the hearts contractions.
3. Smooth Muscles: These muscles are found in the walls of internal organs and control involuntary processes like digestion and constriction of blood vessels. They are also found in the walls of hollow organs, respiratory passageways, and blood vessels.
Muscle Movement
Muscle movement happens when neurological signals produce electrical changes in muscle cells. During this process, calcium is released into the cells and brings about a short muscle twitch. Problems with the junction between the cells called a synapse can lead to neuromuscular diseases.
Muscle Disorders
ome muscular disorders and conditions that affect muscles include muscle pain, sprains and strains, bruising, cramping, myopathy, muscular dystrophy, Parkinsons disease, fibromyalgia, and multiple sclerosis.
Maintaining Muscle Health
Proper nutrition and exercise are important for keeping