Connective Tissue Anatomy
Connective tissue is a fundamental component of our body, providing support and structure to other tissue types. It is the most abundant and widely distributed primary tissue. Here’s an overview of its characteristics and types:
Characteristics
Connective tissue consists of cells immersed in an extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM is composed of fibers and ground substance. The properties of each connective tissue are determined by the ratio of these components. The primary cell of connective tissue is the fibroblast, which produces and maintains the ECM.
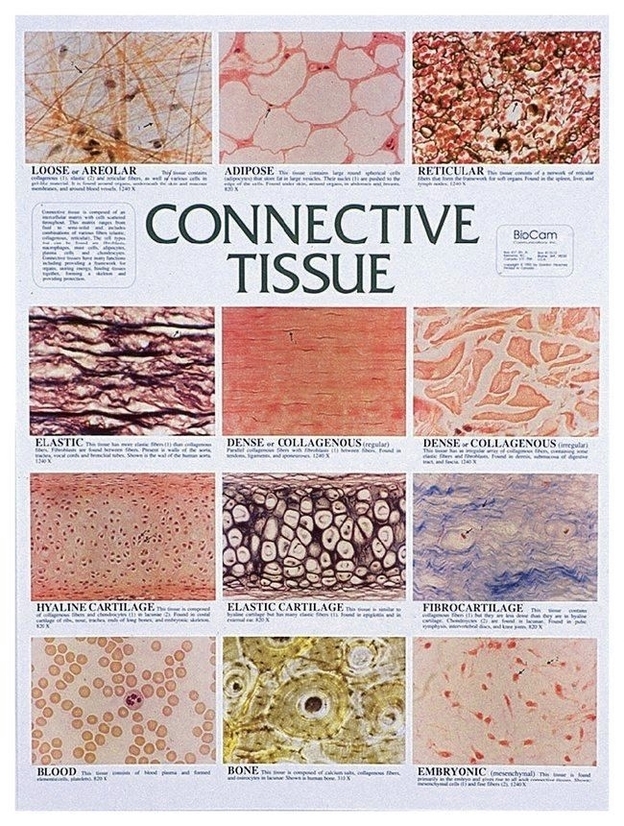
Types of Connective Tissue
1. Connective Tissue Proper: This is further divided into loose and dense connective tissues.
– Loose Connective Tissue: It has fibroblasts and collagen fibers loosely scattered in the ECM.
– Dense Connective Tissue: It contains fibroblasts and heavily packed collagen fibers in the ECM.
2. Specialized Connective Tissue: This includes reticular, blood, bone, cartilage, and adipose tissues.
– Reticular Connective Tissue: It has reticular cells and fibers organized in delicate networks.
– Cartilage: It contains chondrocytes and collagen II (hyaline cartilage), elastic fibers (elastic cartilage), or collagen I (fibrocartilage) in the ECM.
– Bone: It has osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts, and calcified lamellae in the ECM.
– Blood: It contains erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets, and blood plasma in the ECM.
– Adipose Tissue: It contains white and brown adipocytes.
3. Embryonic Connective Tissue: This includes mesenchyme (mesenchymal cells in reticular fibers rich ECM) and mucoid tissue (mesenchymal cells in collagen rich ECM).
Functions
Connective tissue plays many essential roles, including conferring stability, aiding in defense, and organizing and differentiating surrounding tissue. It maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support. The entire body is supported from within by a skeleton composed of bone, a type of connective tissue.
In conclusion, connective tissue is a crucial component of our body’s structure and function. Its diverse types and functions make it an integral part of our body’s anatomy..