The human skeleton, an intricate internal framework, provides essential support, protection, and mobility for our bodies. Comprising numerous individual bones and cartilages, it forms the structural basis upon which our muscles, organs, and other soft tissues rely. the human skeleton.
## Anatomy of the Human Skeleton
1. Axial Skeleton:
– The vertebral column, commonly known as the spine, constitutes the central axis of the axial skeleton. It serves as the primary support for the trunk and head.
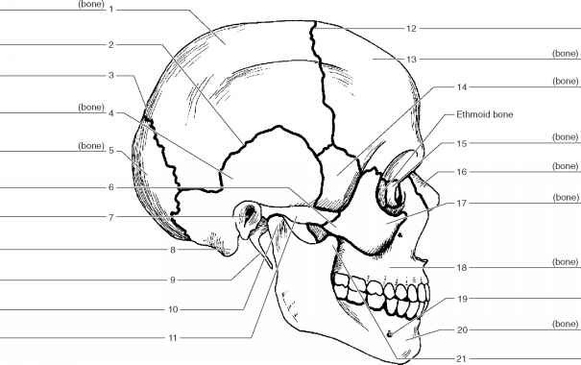
– Within the skull, the cranial bones encase and protect the brain. The facial bones form the framework for our facial features.
– The visceral skeleton includes the hyoid bone (associated with swallowing) and certain elements of the upper and lower jaws.
– These components collectively contribute to our upright posture and overall stability.
2. Appendicular Skeleton:
– The appendicular skeleton encompasses the bones of the limbs and their attachments.
– The pectoral girdle (shoulder) and pelvic girdle (hip) anchor the upper and lower limbs, respectively.
– Our arms consist of the humerus, radius, and ulna, while the legs include the femur, tibia, and fibula.
– The hands contain intricate arrangements of carpal, metacarpal, and phalangeal bones.
– Similarly, the feet house the tarsal, metatarsal, and phalangeal bones.
## Functions of the Skeleton
1. Support:
– The skeleton’s primary role is to provide a sturdy framework for the body.
– The vertebral column, akin to the notochord in simpler organisms, offers crucial support for the trunk.
– It allows us to maintain an upright posture and withstand gravitational forces.
2. Protection:
– Bones shield vital organs from harm.
– The skull safeguards the brain, while the rib cage shields the heart and lungs.
– Additionally, the vertebral column protects the spinal cord.
3. Motion:
– The appendicular skeleton facilitates movement.
– Muscles attach to bones via tendons, allowing coordinated motion.
– Joints, where bones meet, enable a wide range of movements.
– For instance, the ball-and-socket joint at the hip permits rotation, while the hinge joint at the elbow allows flexion and extension.
## Ligaments and Tendons
– Ligaments are fibrous connective tissues that link bones together. They stabilize joints and prevent excessive movement.
– Tendons connect muscles to bones, transmitting the force generated during muscle contraction.
– Together, ligaments and tendons ensure the integrity of the skeletal system.
## Fun Facts About the Human Skeleton
1. The human skeleton comprises over 200 bones, including the 32 teeth.
2. Beyond bones, it includes ligaments and cartilage.
3. The axial skeleton evolved first, with the vertebral column as its central feature.
4. The vertebral column corresponds to the notochord in simpler organisms.
5. Our skeleton adapts to various functions, from standing to dancing, lifting weights to playing musical instruments.
In summary, the human skeleton is a remarkable marvela silent architect that shapes our bodies, supports our endeavors, and allows us to explore the world. ??.