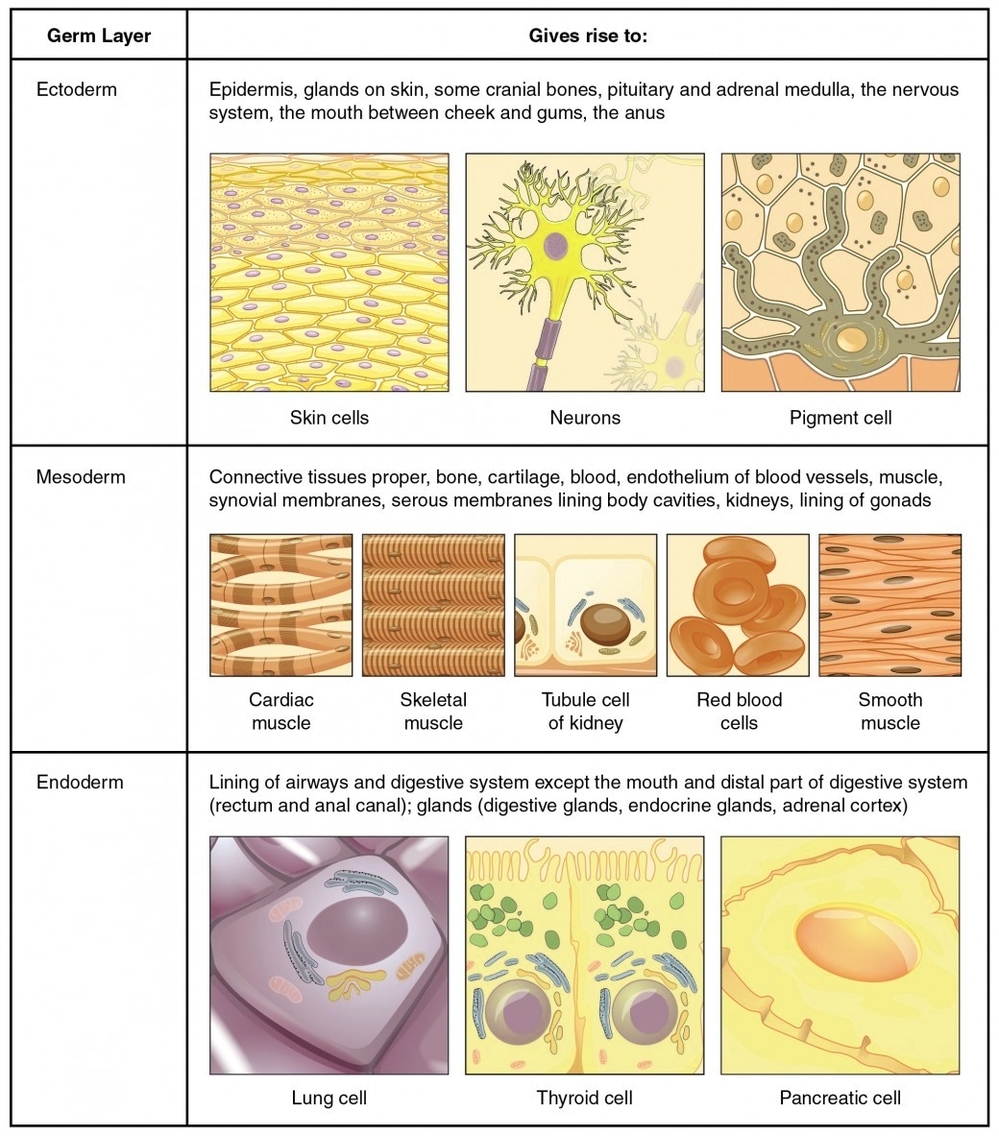
The human body is a complex system that is made up of different types of tissues. These tissues are organized into four broad categories: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous.
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue refers to groups of cells that cover the exterior surfaces of the body, line internal cavities and passageways, and form certain glands. They provide the bodys first line of protection from physical, chemical, and biological wear and tear. The cells of an epithelium act as gatekeepers of the body controlling permeability and allowing selective transfer of materials across a physical barrier. All substances that enter the body must cross an epithelium.
Connective Tissue
As its name implies, connective tissue binds the cells and organs of the body together. It is a diverse collection of tissues that support and connect other tissues, but also have protective functions. Connective tissues include blood, bone, adipose (fat), and cartilage.
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue contracts forcefully when excited, providing movement. It is responsible for the contractile power of the human body, enabling us to move and perform physical tasks.
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is also excitable, allowing for the generation and propagation of electrochemical signals in the form of nerve impulses that communicate between different regions of the body. It plays a crucial role in transmitting signals and information throughout the body, enabling us to respond to stimuli.
Each of these tissue types has a specific function that contributes to the overall health and maintenance of the human body. Any disruption in the structure of a tissue can lead to injury or disease. Understanding the various primary tissue types present in the human body is essential for understanding the structure and function of organs which are composed of two or more primary tissue types..