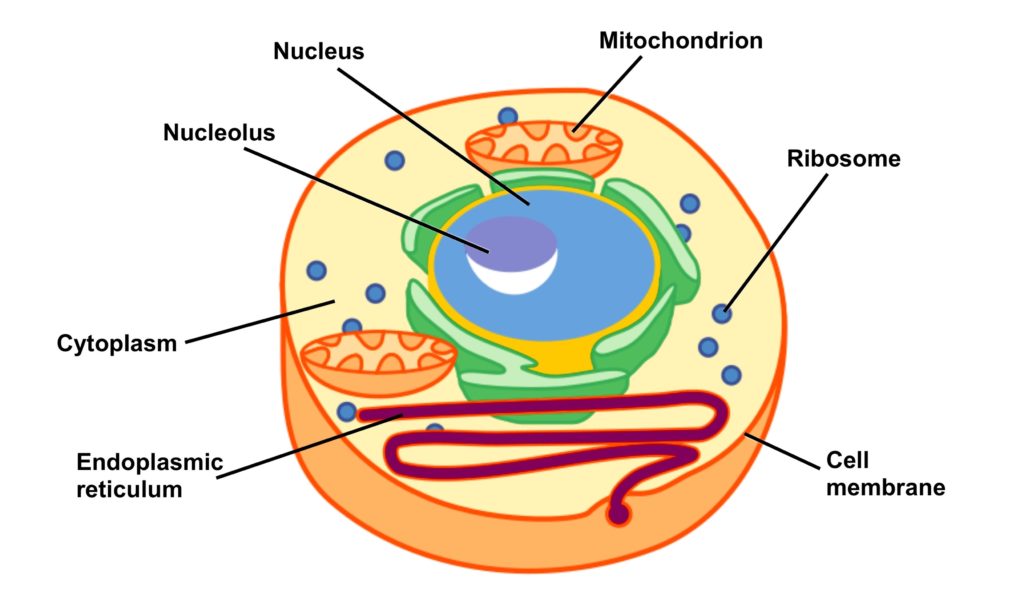
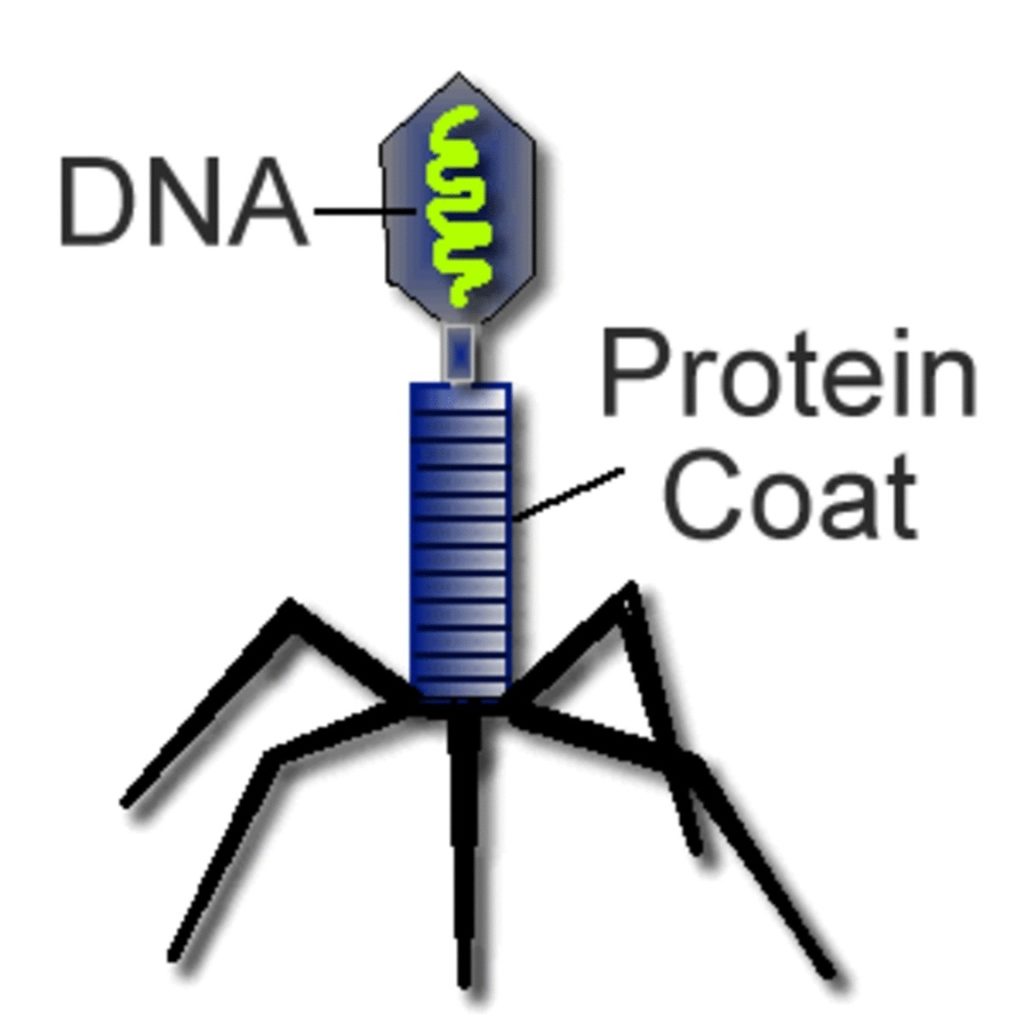
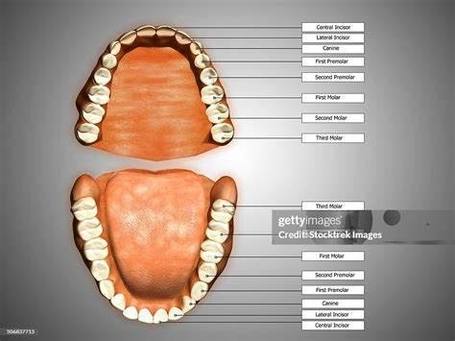
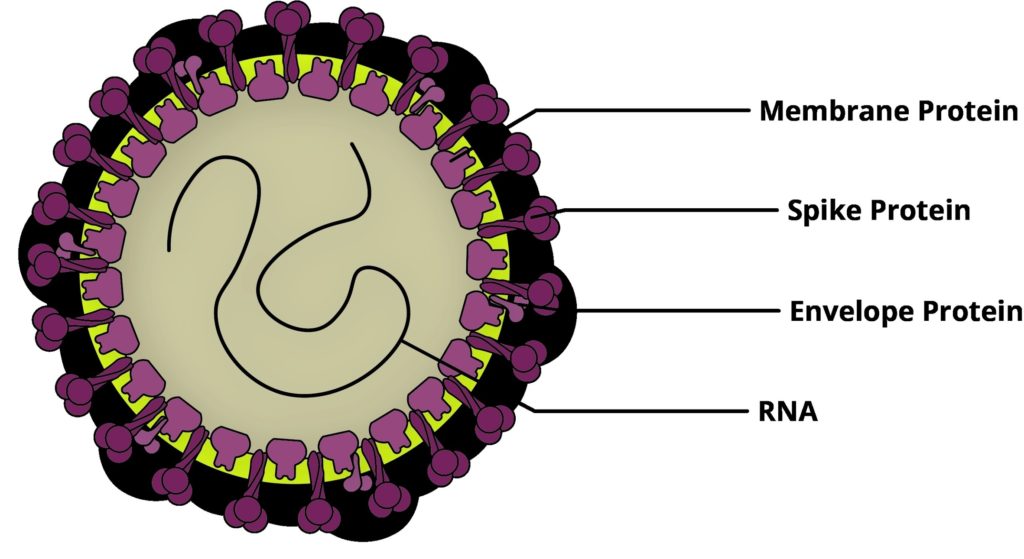
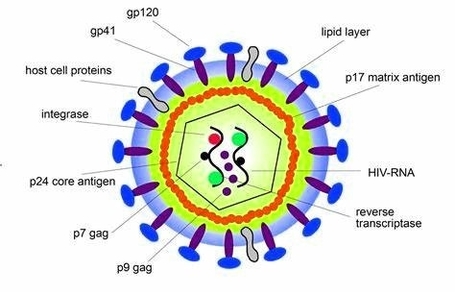
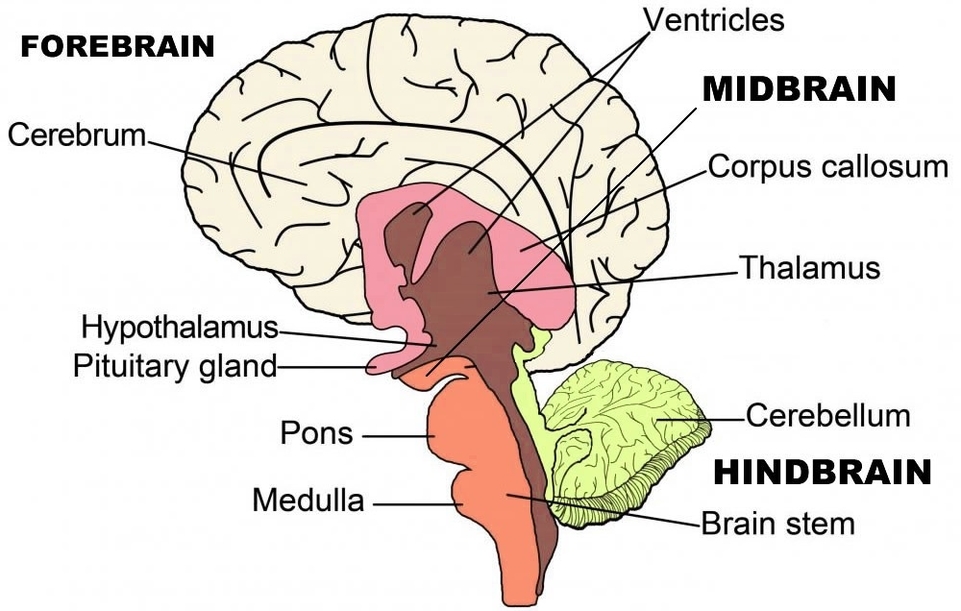
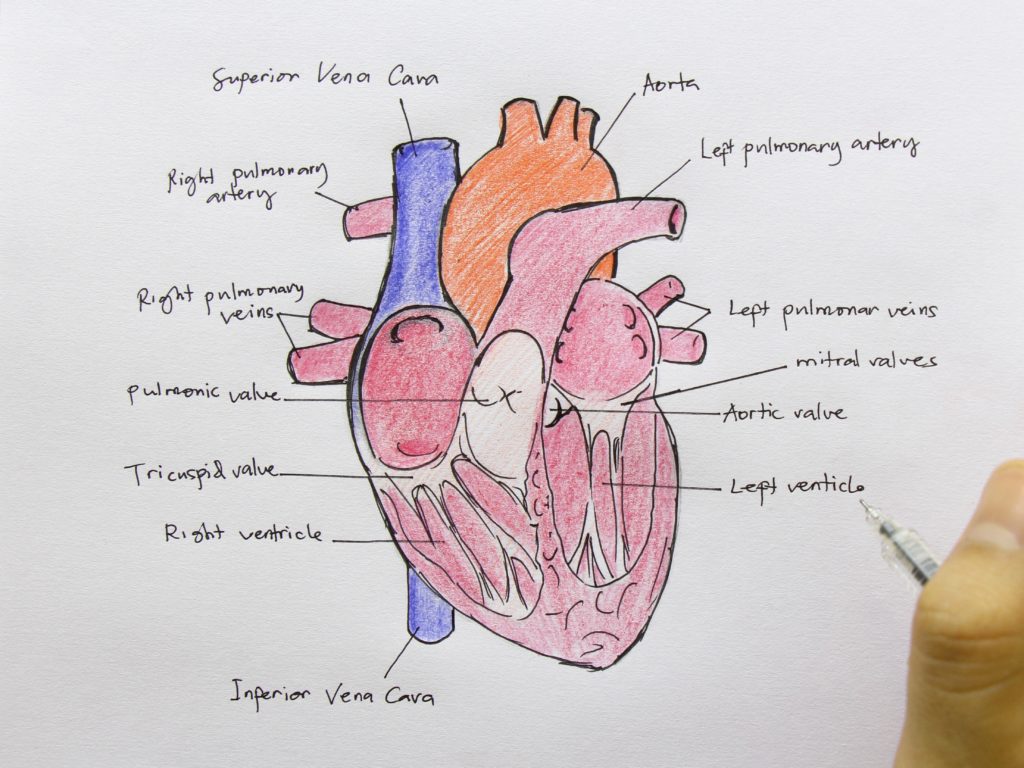
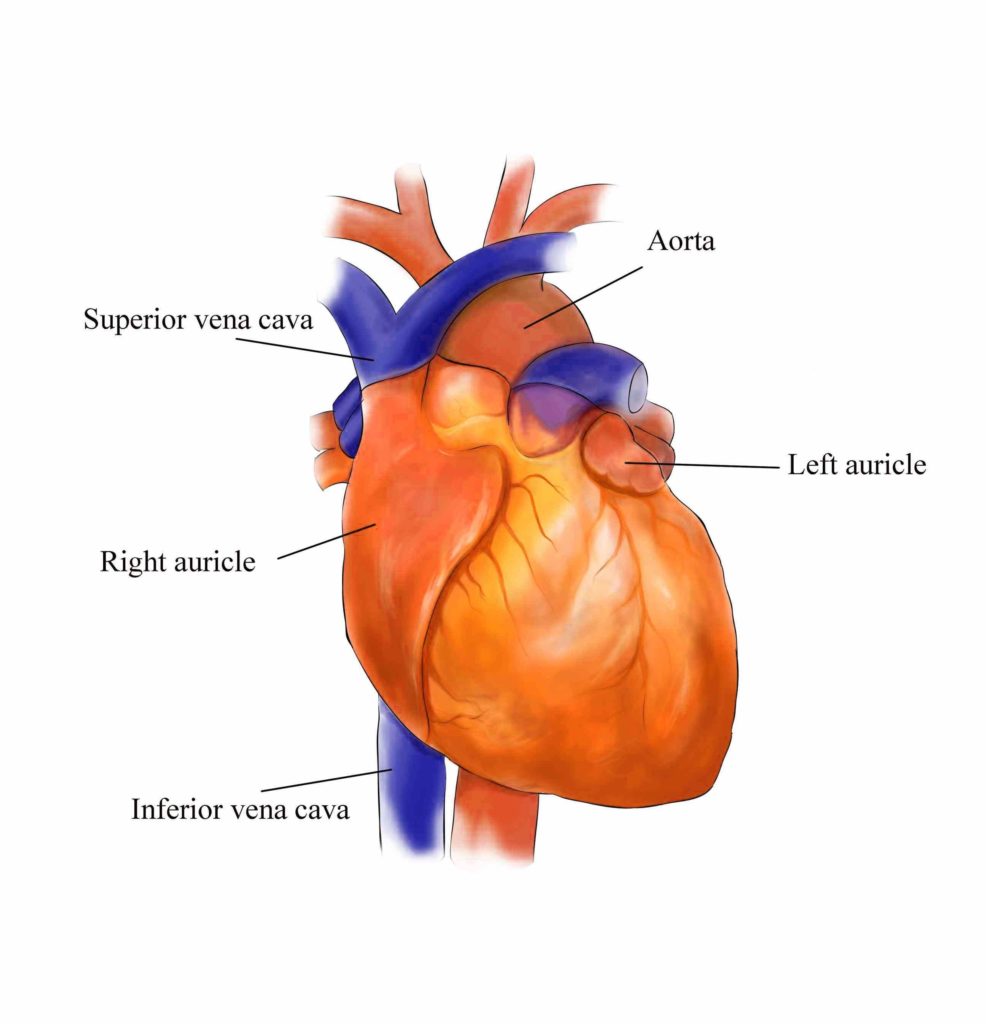
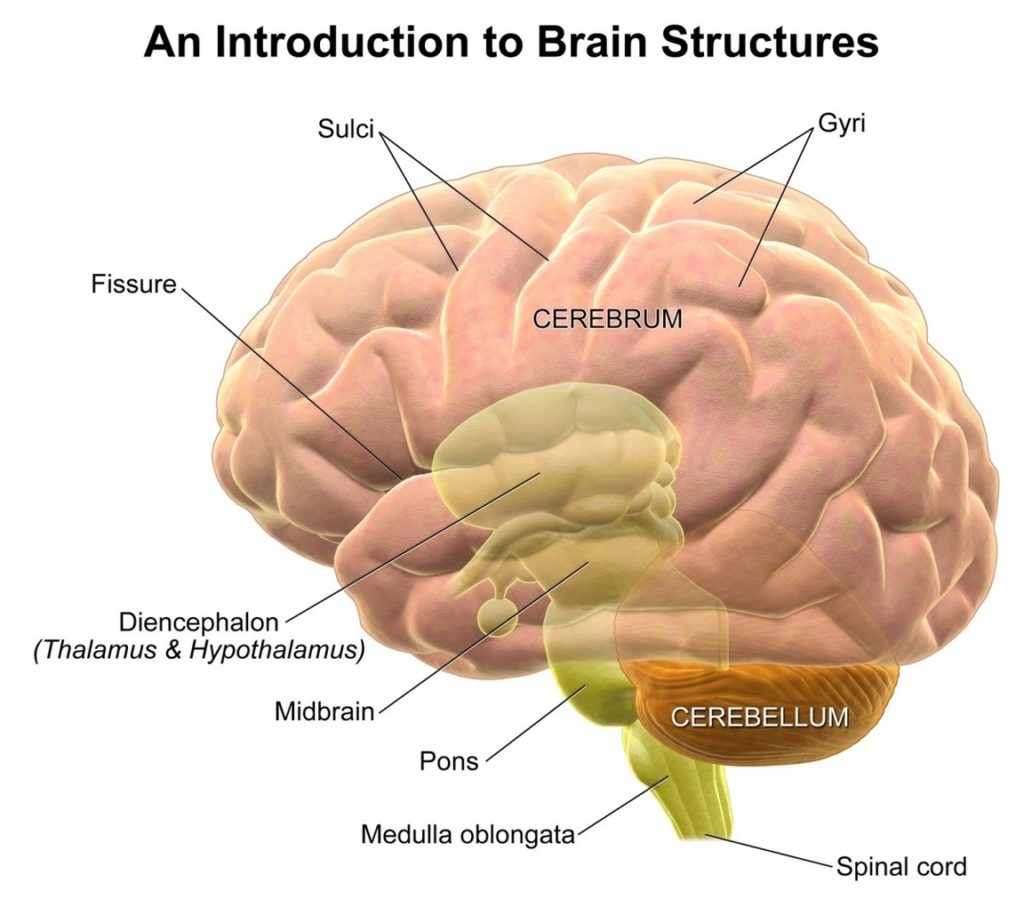
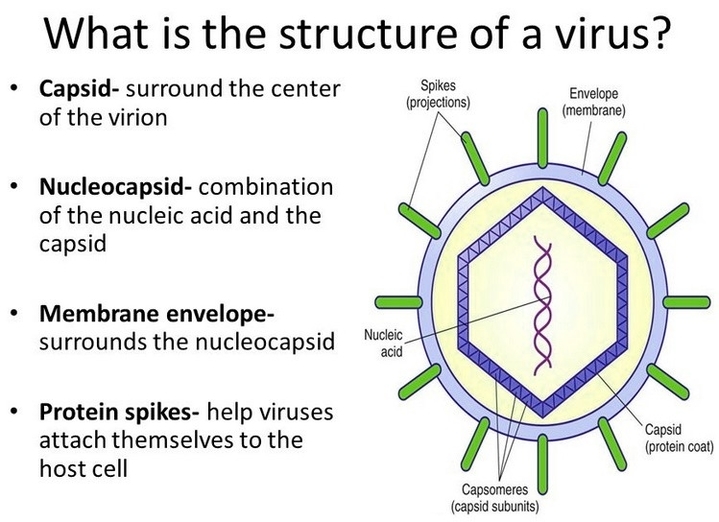
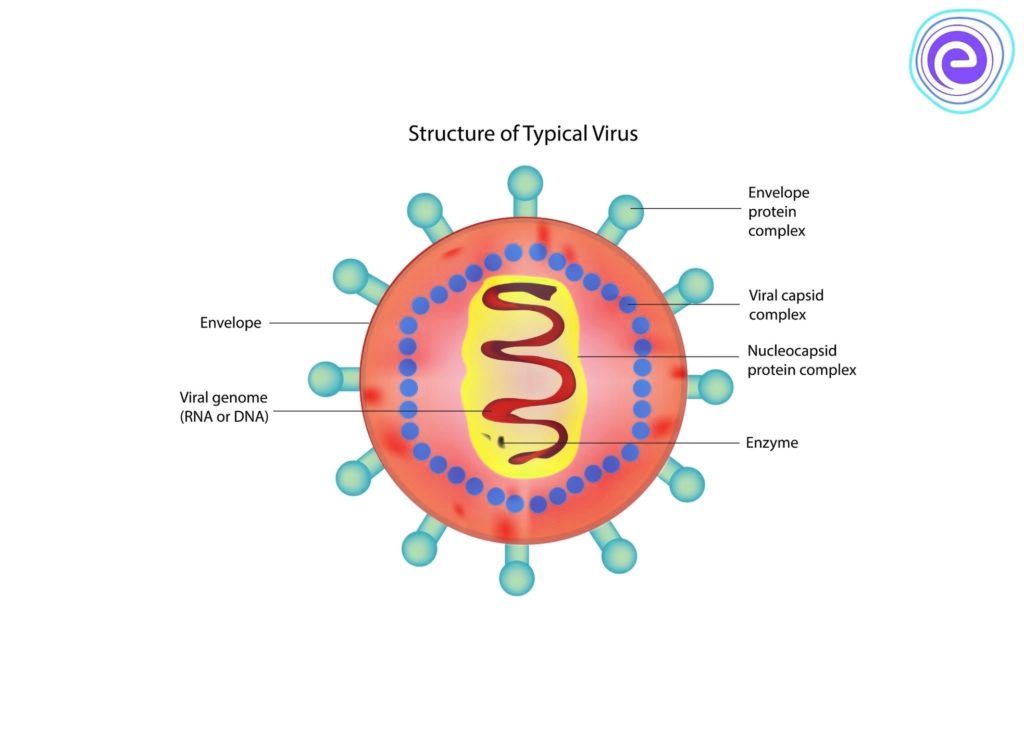
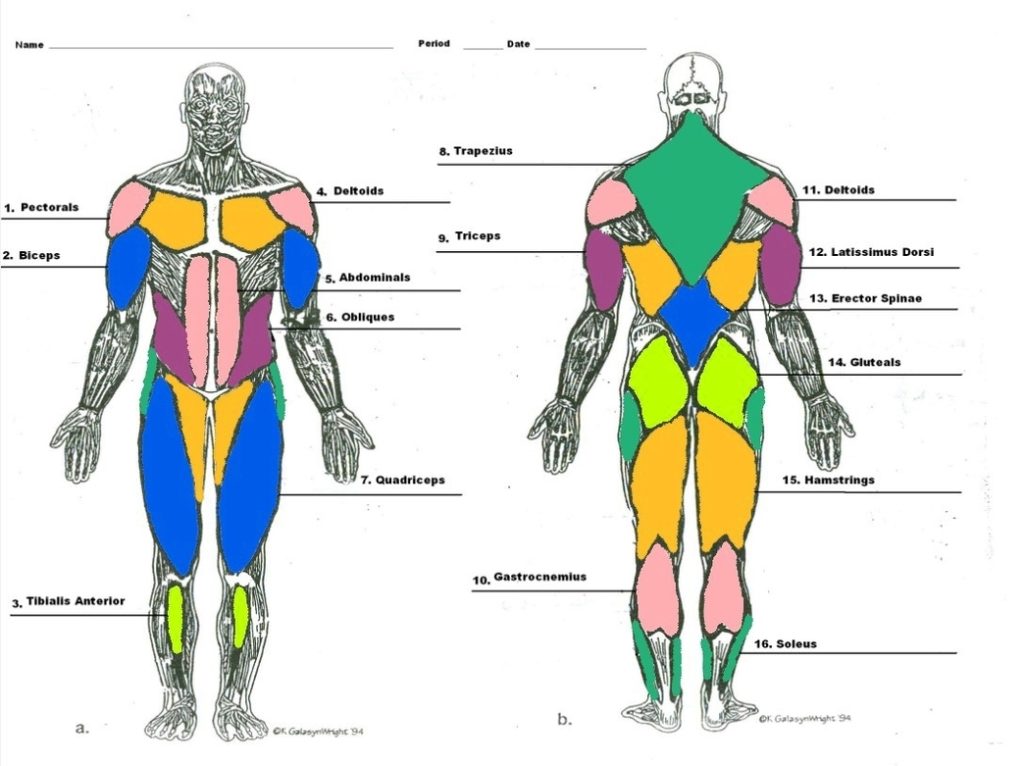
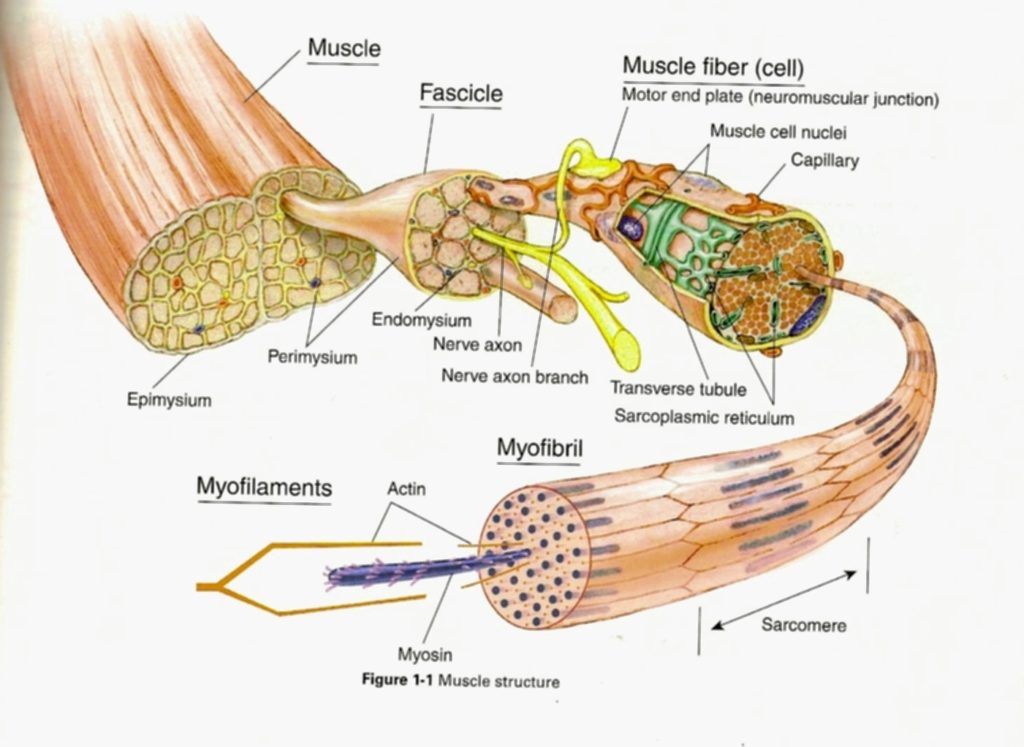
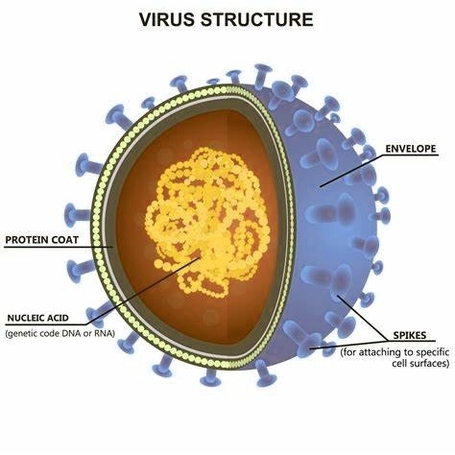
Posted inCell
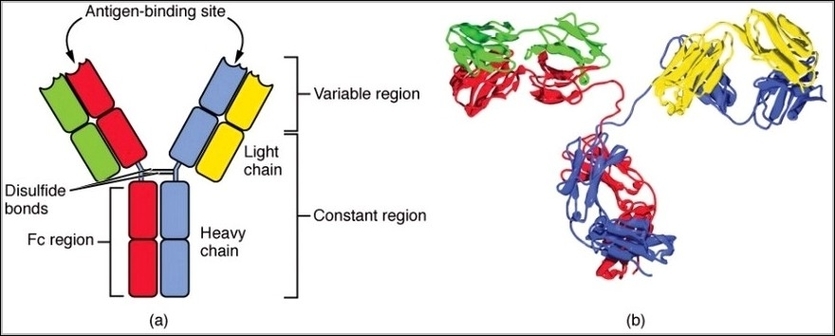
Four Chain Structure of a Generic Antibody IgG2 Structures
IgG antibodies consist of four polypeptide chains: two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains linked by disulfide bonds into a Y-shaped molecule. The heavy chains determine the classgamma…