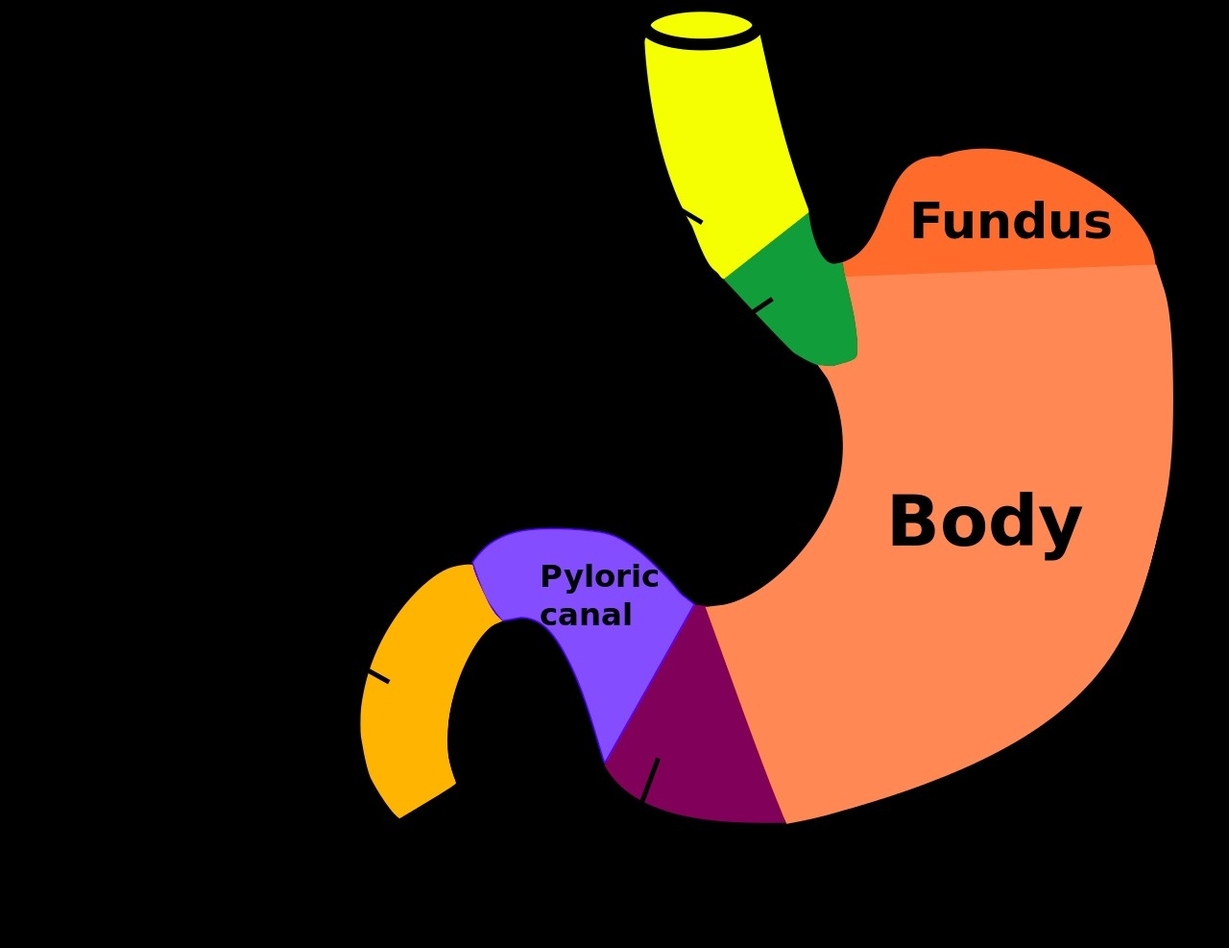
The stomach is a crucial organ in the digestive system, responsible for the accumulation and digestion of food. It has a complex anatomy, consisting of four main regions, each with its unique structure and function.
1. Cardia: This is the point where the esophagus connects to the stomach, and through which food passes into the stomach. It’s named after the Greek word ‘kardia’, which means heart, due to its proximity to the heart.
2. Fundus: Located superior to the diaphragm, above and to the left of the cardia, the fundus is the dome-shaped region of the stomach. It typically fills with air that is swallowed when eating or drinking, which can be seen in X-rays.
3. Body: This is the main part of the stomach, located below the fundus. It is where the majority of gastric glands are located, producing important substances like hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes.
4. Pylorus: This funnel-shaped region connects the stomach to the duodenum, which is the first part of the small intestine. The pylorus plays a crucial role in controlling the passage of gastric contents into the duodenum.
The stomach is located inside the abdominal cavity, spanning several regions of the abdomen, including the epigastric, umbilical, left hypochondriac, and left flank regions. It is connected to other organs by the peritoneum, a membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity.
The stomach’s primary function is to serve as a temporary holding chamber. It can ingest a meal far more quickly than it can be digested and absorbed by the small intestine. The stomach also plays several important roles in chemical digestion, including the continued digestion of carbohydrates and the initial digestion of proteins and triglycerides.
The stomach’s blood supply mainly comes from the celiac trunk, and it is innervated via the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus. Despite its robustness, the stomach is susceptible to various conditions, such as gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer.
In conclusion, the stomach is a complex and vital organ in the human body. Its unique structure and function allow it to play a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of food, contributing significantly to overall health and well-being..