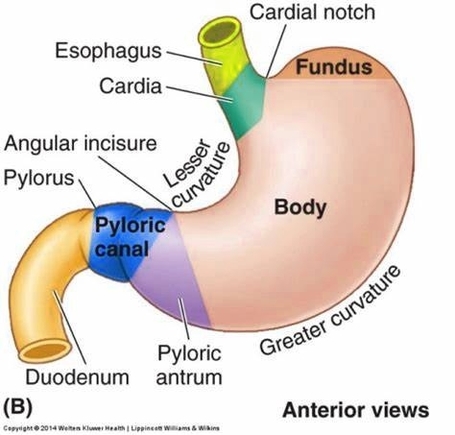
The stomach is a key organ in the human digestive system, responsible for breaking down food and preparing it for further digestion and absorption in the intestines. It is located in the upper abdomen on the left side of the body. The stomach is divided into five distinct sections:
1. Cardia: This is the top part of the stomach, which contains the cardiac sphincter. This sphincter prevents food from traveling back up the esophagus.
2. Fundus: This is a rounded section next to the cardia. It is often filled with gas.
3. Body (Corpus): This is the largest section of the stomach, located inferior to the fundus.
4. Antrum: This section lies below the body.
5. Pylorus: This is the bottom part of the stomach. It is a narrowing where the stomach joins the small intestine.
The stomach’s primary function is to digest food and send it to the small intestine. It temporarily stores food, contracts and relaxes to mix and break down food, and produces enzymes and other specialized cells to digest food. The stomach works with the rest of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which includes the mouth, esophagus, small and large intestine, and rectum, to break down food and liquid and carry it through the body.
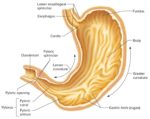
The stomach’s anatomy is quite complex; it consists of four parts, two curvatures, and receives its blood supply mainly from the celiac trunk. Innervation is provided via the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus. The stomach is capable of corroding metal due to the extremely potent hydrochloric acid it produces.
The stomach is the most dilated part of the digestive system, lying between the esophagus and duodenum. It is covered and connected to other organs by peritoneum. The lesser omentum connects the stomach to the liver and then extends around the stomach. The greater omentum then continues inferiorly from the stomach, hanging from it like a curtain.
In conclusion, the stomach plays a crucial role in the human digestive system. Its unique structure and function allow it to break down food effectively, preparing it for further digestion and absorption in the intestines. Understanding the anatomy and function of the stomach is essential for maintaining digestive health..