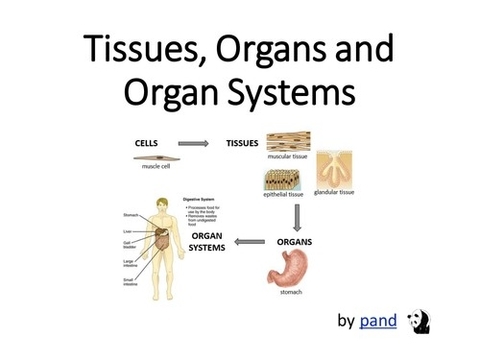
Organs and Tissues: An Explanation
The human body, a marvel of biological engineering, is composed of a complex network of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. This intricate organization allows the body to perform a multitude of functions, from simple to complex, ensuring our survival.
Cells
The fundamental unit of life, cells, are the building blocks of all living organisms. In humans, there are over 30 trillion cells, each performing specific functions.
Tissues
A tissue is a group of similar, specialized cells that work together to perform a specific function. For instance, muscle tissue comprises cells that contract and relax to facilitate movement, while nervous tissue contains cells that transmit electrical signals to relay information.
Organs
An organ is a structure composed of two or more types of tissues organized to carry out a particular function. For example, the heart, an organ, is made up of muscle tissue that pumps blood, nervous tissue that controls the heartbeat, and connective tissue that provides structure.
Organ Systems
Groups of organs with related functions form organ systems. Each organ system performs a specific role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis. For instance, the digestive system processes food, the respiratory system handles oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion, and the circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cells and removes waste products.
Interdependence
The function of an organ system depends on the integrated activity of its organs, and the survival of the organism depends on the integrated activity of all the organ systems. For example, cells of the digestive, muscular, skeletal, reproductive, and excretory systems all need oxygen from the respiratory system to function.
Nationalism
The rise of nationalism in the Ottoman Empire disrupted the traditional millet system. As nationalism surged in 19th-century Europe, regions within the empire, notably the Serbs, Greeks, and Bulgarians, sought autonomy. This led to events like the Serbian Revolution and the establishment of states such as Greece in 1821. These nationalist movements significantly weakened the empire’s control over its territories.
Conclusion
The human body’s organization, from cells to organ systems, is a testament to the complexity and efficiency of biological systems. This organization allows the body to perform a wide range of functions, ensuring our survival and well-being. Understanding this organization is crucial in fields like medicine and biology, where knowledge about the body’s structure and function can lead to advancements in healthcare and disease treatment.