Anatomy of the Bone
The human skeleton is a complex structure composed of 206 bones, not including teeth and sesamoid bones (small bones found within cartilage). These bones are classified by their shapeas long, short, flat, and irregular.
Bone Structure
A bone is a somatic structure composed of calcified connective tissue. Ground substance and collagen fibers create a matrix that contains osteocytes, the most common cell found in mature bone responsible for maintaining bone growth and density.
Types of Bone Tissue
There are three types of bone tissue:
1. Compact Tissue: The harder, outer tissue of bones.
2. Cancellous Tissue: The sponge-like tissue inside bones.
3. Subchondral Tissue: The smooth tissue at the ends of bones, covered with cartilage.
Gross Anatomy of Bones
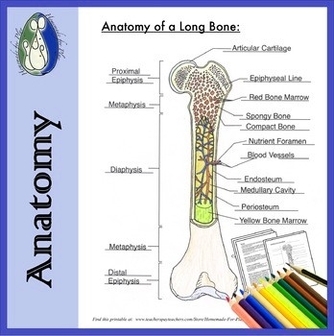
A typical long bone has two main regions: the diaphysis and the epiphysis.
– Diaphysis: The hollow, tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. Inside the diaphysis is the medullary cavity, filled with yellow bone marrow in an adult.
– Epiphysis: The wider section at each end of the bone, filled internally with spongy bone. Red bone marrow fills the spaces between the spongy bone in some long bones.
Other Structures
– Periosteum: The tough, thin outer membrane covering the bones. Beneath the hard outer shell of the periosteum are tunnels and canals through which blood and lymphatic vessels run to carry nourishment for the bone.
– Endosteum: A layer of bone cells lining the inside of the bone adjacent to the medullary cavity.
Bone Cells
There are several types of bone cells:
1. Osteoblast: Found within the bone, its function is to form new bone tissue.
2. Osteoclast: A very large cell formed in bone marrow, its function is to absorb and remove unwanted tissue.
3. Osteocyte: Found within the bone, its function is to help maintain bone as living tissue.
4. Hematopoietic: Found in bone marrow, its function is to produce red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Conclusion
Bones are living tissues that provide shape and support for the body, protect some organs, serve as a storage site for minerals, and provide the mediummarrowfor the development and storage of blood cells. The complexity of a bone’s function, from providing strength and support for the body to serving as a site for development and storage of blood cells, means there are many disorders and diseases that can affect bone..