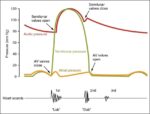
The heart’s internal anatomy features four chambers with septa dividing left and right, atria receiving blood via smooth posterior walls and pectinate anterior plus auricles, ventricles with trabeculae carneae and papillary muscles anchoring chordae tendineae to AV valvestricuspid right, mitral left. Semilunar pulmonary and aortic valves guard outflows, with crista supraventricularis in right directing flow. Endocardium lines all, myocardium spirals, and openings position strategically for efficient unidirectional flow.
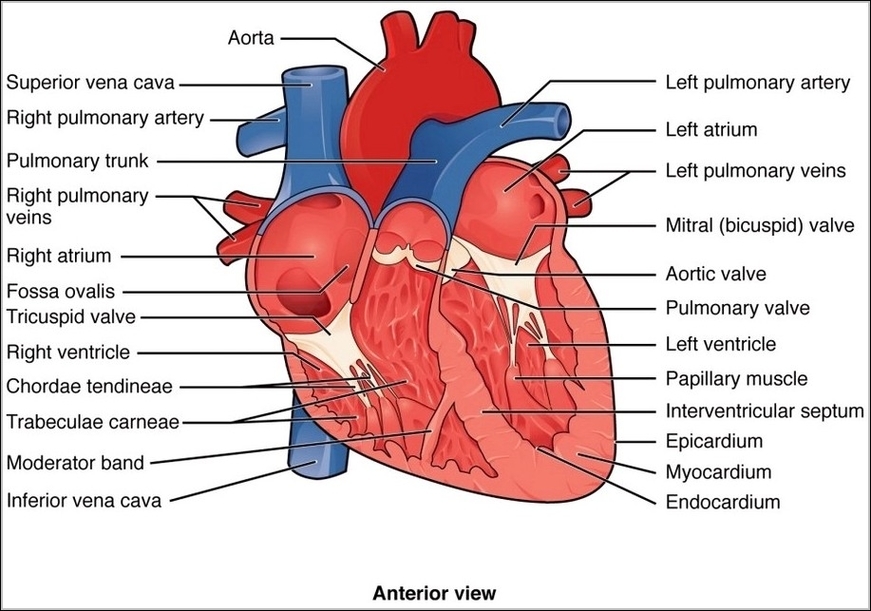
Internal Anatomy of the HeartN
Posted inOrgans