Human Vertebral Column Anatomy
The human vertebral column, also known as the spine or backbone, is a crucial component of the human skeletal system. It is a curved structure composed of 33 distinct vertebrae, which are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs. The vertebral column extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx.
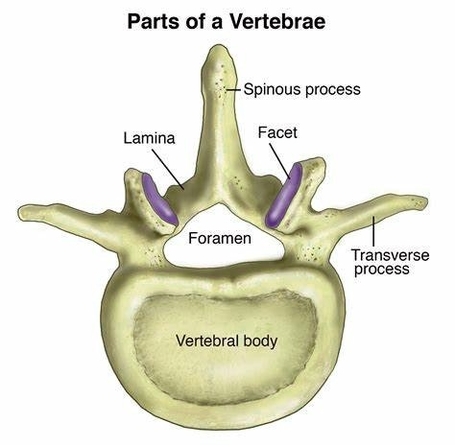
tructure of Vertebrae
Each vertebra consists of an anterior vertebral body and a posterior vertebral arch. The vertebral body forms the weight-bearing component, with vertebrae in the lower portion of the column having larger bodies than those in the upper portion to better support the increased weight. The vertebral arch forms the lateral and posterior aspect of each vertebra. In combination with the vertebral body, the vertebral arch forms an enclosed hole, the vertebral foramen.
Regions of the Vertebral Column
The vertebral column is divided into five regions:
1. Cervical Vertebrae (7): These are located in the neck region.
2. Thoracic Vertebrae (12): These form the upper back and each vertebra articulates with a pair of ribs.
3. Lumbar Vertebrae (5): These constitute the lower back.
4. Sacrum (5 fused): This is a triangular bone in the lower back situated between the two hip bones of the pelvis.
5. Coccyx (3-4 fused): Also known as the tailbone, it is the final segment of the vertebral column.
Functions of the Vertebral Column
The vertebral column serves four main functions:
1. Protection: It encloses and protects the spinal cord within the spinal canal.
2. Support: It carries the weight of the body above the pelvis.
3. Axis: It forms the central axis of the body.
4. Movement: It plays roles in both posture and movement, allowing you to twist, bend, and sway your trunk in almost any direction.
Joints and Ligaments
The vertebrae are interlaced by strong joints and ligaments. Intervertebral discs, uncovertebral, zygapophyseal (facet), craniovertebral (atlanto-occipital, atlanto-axial), costovertebral, and sacroiliac joints are present. Ligaments include longitudinal (anterior, posterior), ligamenta flava, interspinous, supraspinous, nuchal, alar, cruciate ligament of atlas, costotransverse, and ligaments of the head of the rib.
Clinical Relevance
Conditions such as intervertebral disc herniation, where the intervertebral disc, a fibrocartilaginous cylinder that lies between the vertebrae, protrudes out of its normal location, can cause severe pain and other complications.
In conclusion, the vertebral column is a complex structure that plays a vital role in human anatomy and function. Its intricate design allows for a wide range of movements while also providing essential protection for the spinal cord..