The human brain, an organ of immense complexity and the center of our consciousness, is divided into several distinct parts, each with its own specific functions.
1. Cerebrum
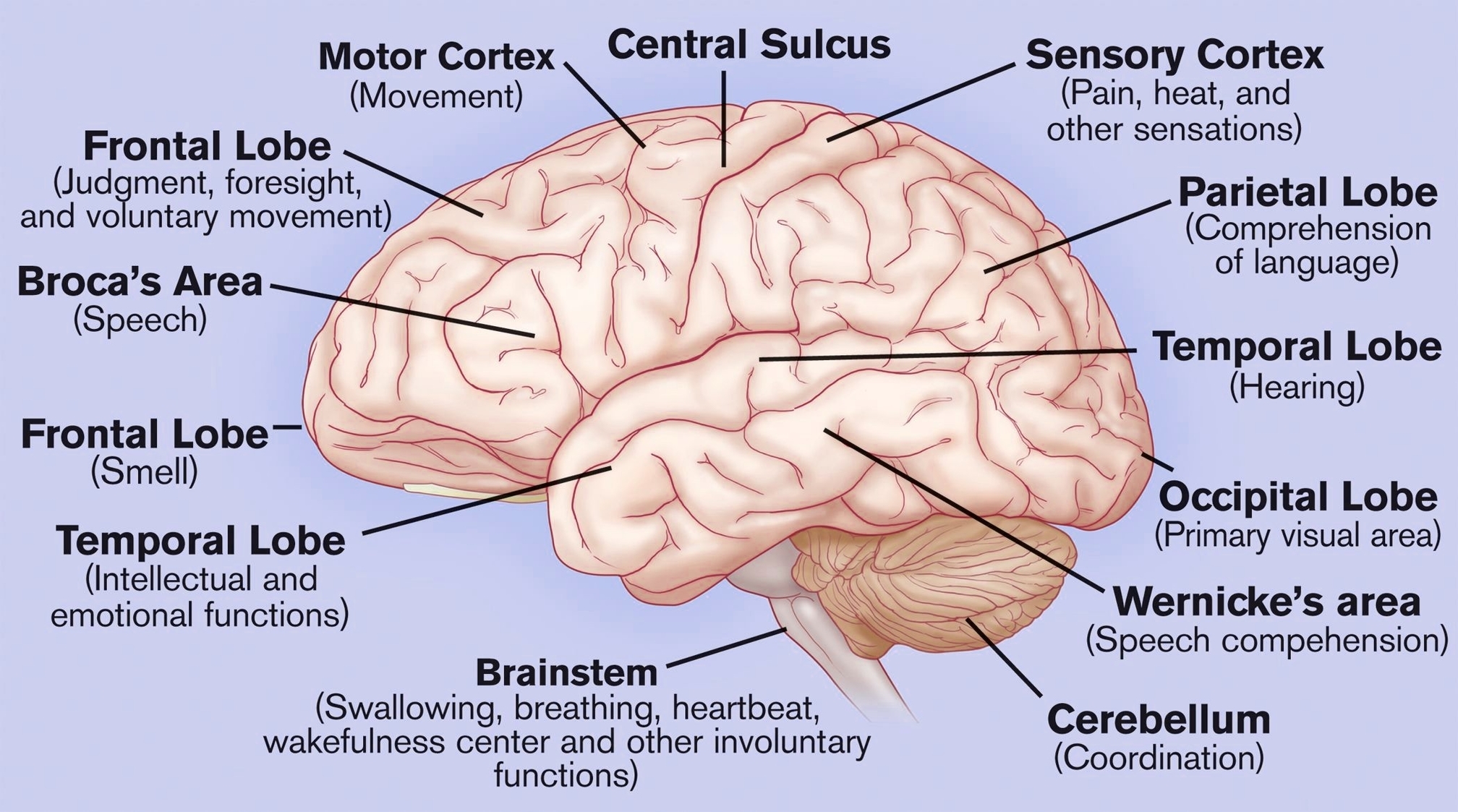
The cerebrum, the largest part of the brain, initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. It is responsible for higher functions like speech, judgment, thinking, reasoning, problem-solving, emotions, and learning. The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres, each with four sections or lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital.
– Frontal Lobe: This lobe is associated with reasoning, motor skills, higher level cognition, and expressive language.
– Parietal Lobe: The parietal lobe processes tactile sensory information such as pressure, touch, and pain.
– Temporal Lobe: This lobe interprets sounds and language we hear. It is also heavily associated with the formation of memories.
– Occipital Lobe: The occipital lobe is primarily responsible for vision.
2. Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, the outermost layer of the cerebrum, is responsible for consciousness, higher-order thinking, imagination, information processing, language, memory, perception, reasoning, sensation, and voluntary physical action.
3. Cerebellum
The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, is responsible for coordinating voluntary movements, maintaining posture, and balancing.
4. Brainstem
The brainstem controls automatic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
5. Limbic System
The limbic system, located deep within the brain, is responsible for emotions, survival instincts, and memory.
6. Gray and White Matter
The brain is composed of gray and white matter. Gray matter, found in the outer portion of the brain, is primarily composed of neuron somas (the round central cell bodies). White matter, located in the inner section, is mostly made of axons (the long stems that connect neurons together) wrapped in myelin (a protective coating). Gray matter is primarily responsible for processing and interpreting information, while white matter transmits that information to other parts of the nervous system.
In conclusion, the human brain is a marvel of biological engineering, with each part playing a crucial role in maintaining our daily functions and experiences. Despite the vast knowledge we have gained about the brain, there is still much to learn about this complex organ..