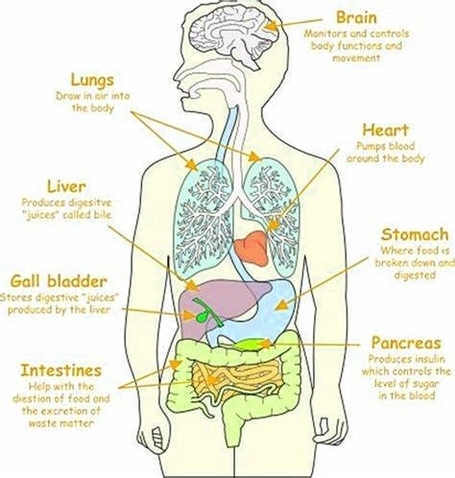
Human Body Organs
1. Brain: The brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system?. It consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem, and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body?.
2. Heart: The heart is a muscular organ around the size of a closed fist, and it sits in the chest, slightly to the left of center?. The heart beats around 100,000 times a day, pumping approximately 8 pints of blood throughout the body 24/7?.
3. Lungs: The human lungs are a pair of spongy organs within the thoracic cavity that facilitate gaseous exchange?. They are a part of the respiratory system, which also includes the nose, nasal sinuses, mouth, pharynx, larynx, and trachea?.
4. Liver: The liver is located in the upper right-hand portion of the abdominal cavity, beneath the diaphragm, and on top of the stomach, right kidney, and intestines. It regulates most chemical levels in the blood and excretes a product called bile.
5. Kidneys: The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They are located just below the rib cage, one on each side of your spine. Healthy kidneys filter about a half cup of blood every minute, removing wastes and extra water to make urine.
6. Gallbladder: Your gallbladder is located in the upper right region of your stomach. Its function is to store bile thats produced by your liver[^30^].
7. Pancreas: The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland?.
8. Stomach: The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper belly (abdomen). Its part of the digestive system. Its between the end of the food pipe (esophagus) and the start of the first part of the small bowel (duodenum).
9. Skin: The skin is the bodys largest and heaviest organ. It is made up of several different types of cells and its main purpose is to protect the inside of the body from the environment.
Each of these organs plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s overall health and functionality. They work together to ensure the body can perform its necessary functions, from breaking down food for energy to protecting the body from harmful substances. Understanding the role of each organ can help us appreciate the complexity and efficiency of our own bodies..