Human Body Muscles
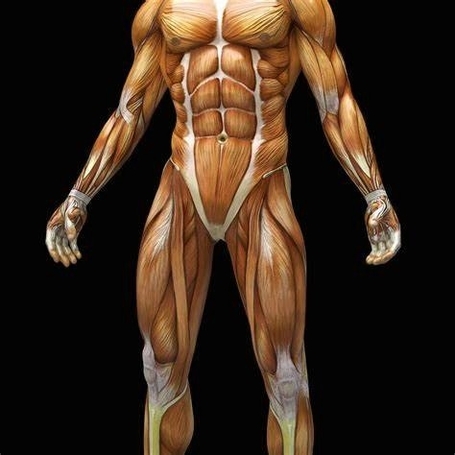
The human body is a complex system that relies on muscles for movement, posture, and balance. There are three major types of muscles in the human body: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle.
1. Skeletal Muscle: These muscles are attached to the bones by tendons and are under voluntary control. They are responsible for movement and maintaining posture. Skeletal muscles are often divided into various groups based on their location and function. For instance, the muscles of the head and face include the frontalis muscle, orbicularis oculi muscle, and corrugator supercilii muscle, among others.
2. Cardiac Muscle: This type of muscle makes up the mass of the heart and is responsible for the rhythmic contractions of this vital organ. Cardiac muscle is under involuntary control.
3. Smooth Muscle: Found in the walls of structures such as blood vessels, the urinary bladder, the intestines, and the stomach, smooth muscle is also under involuntary control.
Each muscle type has unique cellular components, physiology, specific functions, and pathology. For example, the arrangement of smooth muscle and cardiac muscle in humans is identical to the arrangement found in other vertebrate animals.
The human body has approximately 640 muscles. These muscles provide strength, balance, posture, movement, and heat for the body to keep warm. The muscles of the human body work the skeletal system and are concerned with movement, posture, and balance.
The understanding of gross human muscular anatomy provides a basic framework for the large muscle groups and their actions. For instance, the frontalis muscle in the head helps in retracting the scalp, the orbicularis oculi muscle helps in closing the eyelids, and the superior rectus muscle helps in adducting, elevating, and medially rotating the eye.
In conclusion, the human body muscles play a crucial role in various bodily functions. Their complexity and diversity are a testament to the intricate design of the human body. Understanding these muscles and their functions can provide valuable insights into human health and physiology.