Human Body Anatomy
The human body is a complex and intricate system, composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues, organs, and organ systems. These components ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
1. Basic Structure
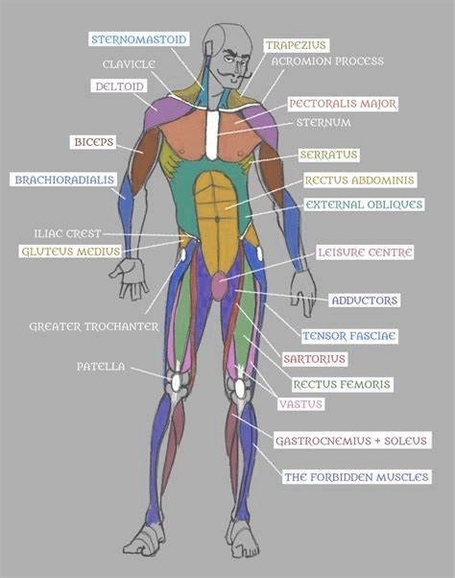
The human body consists of the head, neck, torso (which includes the thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet. The skeleton, composed of cartilage and bone, gives the body its shape.
2. Cells and Tissues
The body contains trillions of cells, the fundamental unit of life. These cells sit in an extracellular matrix that consists of proteins such as collagen, surrounded by extracellular fluids. Not all parts of the body are made from cells. Some parts are non-cellular material such as bone and connective tissue.
3. Organ Systems
The human body is organized into several major organ systems. Each system has a specific function and is made up of specific organs and tissues.
– Cardiovascular System: This system includes the heart and blood vessels. It circulates blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
– Digestive System: It breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and used by the body.
– Endocrine System: It consists of glands that produce hormones, which regulate many body functions like growth and metabolism.
– Renal System: It filters the blood and removes waste products through urine.
– Muscular System: It allows movement and provides support to the body.
– Nervous System: It controls and coordinates body activities and senses the environment.
– Reproductive System: It allows humans to reproduce.
– Respiratory System: It brings in oxygen and expels carbon dioxide.
– Skeletal System: It provides structure, protects organs, and enables movement.
4. Biochemical Constituents
The human body is composed of elements including hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, calcium, and phosphorus. These elements reside in trillions of cells and non-cellular components of the body. The main electrolytes in body water outside cells are sodium and chloride, whereas within cells it is potassium and other phosphates.
5. Development and Aging
The human body undergoes various stages of development, from conception through old age. This includes prenatal development, growth, and aging.
In conclusion, the human body is a marvel of biological engineering, with each part working in harmony to ensure the survival and well-being of the individual. Understanding its anatomy and physiology is crucial for medical and health-related fields.