Human Body Anatomy
Human body anatomy is the scientific study of the body’s structures. It involves the examination of the entire structure of a human being, which is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues, subsequently forming organs and organ systems. These structures ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
The human body consists of five basic parts: the head, neck, torso (which includes the thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet. Some of these structures are very small and can only be observed and analyzed with the assistance of a microscope, while other larger structures can readily be seen, manipulated, measured, and weighed.
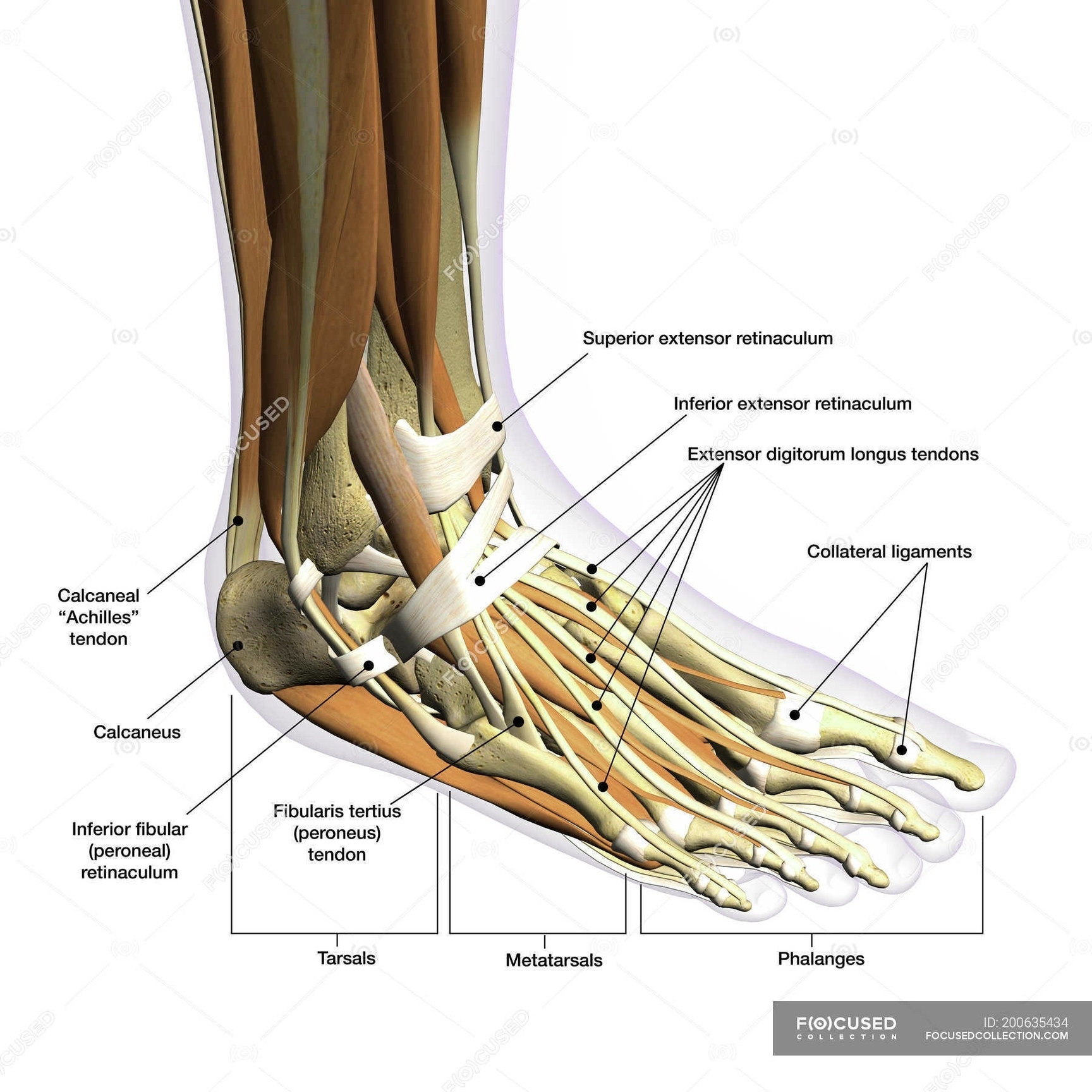
The body’s major structures include the abdominal cavity, adrenal gland, aorta, bone, brain, ear, eye, heart, kidney, large intestine, lung, nose, ovary, pancreas, pituitary gland, small intestine, spinal cord, spleen, stomach, testis, thymus, thyroid gland, tooth, uterus, and vertebral column.
The human body is composed of elements including hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, calcium, and phosphorus. These elements reside in trillions of cells and non-cellular components of the body. The adult male body is about 60% water for a total water content of some 42 litres.
The body contains trillions of cells, the fundamental unit of life. At maturity, there are roughly 3037 trillion cells in the body. The body is also host to about the same number of non-human cells as well as multicellular organisms which reside in the gastrointestinal tract and on the skin.
The human body is the physical substance of the human organism, composed of living cells and extracellular materials and organized into tissues, organs, and systems. Like all chordates, the human animal has a bilaterally symmetrical body that is characterized at some point during its development by a dorsal supporting rod (the notochord), gill slits in the region of the pharynx, and a hollow dorsal nerve cord.
The study of the human body includes anatomy, physiology, histology, and embryology. Anatomy focuses on the description of form, or how body structures at different levels look. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions.
In conclusion, human body anatomy is a vast and complex field of study that provides us with a detailed understanding of the structures that make up the human body. This knowledge is crucial for health professionals, physiologists, anatomists, and artists to assist them in their work.