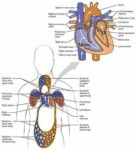
Heart Anatomy Glossary
1. Heart: A muscular organ that pumps blood around the body by circulating it through the circulatory/vascular system.
2. Endocardium: The thin inner lining of the heart chambers and also forms the surface of the valves.
3. Myocardium: The thick middle layer of muscle that allows your heart chambers to contract and relax to pump blood to your body.
4. Pericardium: The sac that surrounds your heart.
5. Aorta: The largest artery in the body and the main vessel to supply blood from the heart.
6. Aortic valve: The valve that regulates blood flow from the heart into the aorta.
7. Ventricles: The two lower chambers of the heart that receive blood from the atria and contract to force it into the arteries.
8. Atria: The two upper chambers of the heart that receive blood from the veins and contract to force it into the ventricles.
9. Pulmonary veins: Vessels that deliver oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
10. Superior and Inferior vena cavae: The largest veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart.
11. Tricuspid valve: The valve that controls blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
12. Mitral valve: The valve that lets oxygen-rich blood from your lungs pass from the left atrium into the left ventricle.
13. Pulmonary valve: The valve that controls the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs.
14. Aneurysm: A sac-like protrusion from a blood vessel or the heart, resulting from a weakening of the vessel wall or heart muscle.
15. Angina: Chest pain that occurs when diseased blood vessels restrict blood flow to the heart.
16. Angiography: An x-ray technique in which dye is injected into the chambers of your heart or the arteries that lead to your heart.
17. Arrhythmia: An abnormal heartbeat.
18. Arteriography: A test that visualizes an artery or the arterial system after injection of a contrast dye.
19. Antiarrhythmics: Medicines used to treat patients who have irregular heart rhythms.
20. Anticoagulant: Any medicine that keeps blood from clotting; a blood thinner.
21. Antihypertensive: Any medicine or other therapy that lowers blood pressure.
22. Antiplatelet therapy: Medicines that stop blood cells (called platelets) from sticking together and forming a blood clot.
23. Aphasia: The inability to speak, write, or understand spoken or written language because of brain injury or disease.
24. Acquired heart disease: Heart disease that arises after birth, usually from infection or through the build-up of fatty deposits in the arteries that feed the heart muscle.
25. Alveoli: Air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
This glossary provides a basic understanding of the heart’s anatomy and its associated terms. Each term is a crucial component of the intricate system that enables the heart to perform its vital function: to keep blood flowing throughout the body.